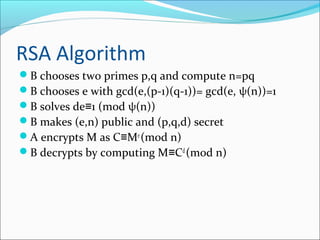
This document describes the RSA algorithm for public key cryptography. RSA is based on the idea that factoring large integers into their prime factors is difficult. It involves choosing two prime numbers p and q, computing n=pq, and selecting a public key e such that gcd(e,(p-1)(q-1))=1. The private key d is computed such that ed=1 (mod φ(n)). To encrypt a message M, the sender computes C=Me (mod n) using the recipient's public key. The recipient decrypts by computing M=Cd (mod n) using their private key. The security of RSA relies on the difficulty of factoring the modulus n.