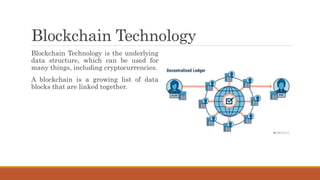
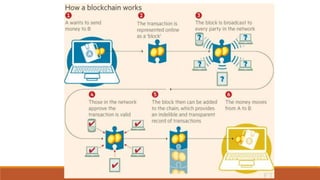
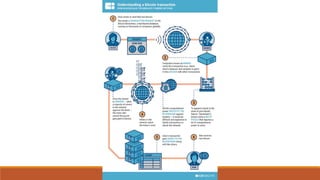
The document discusses India's introduction of a central bank digital currency called the digital rupee (e₹). It will be issued by the Reserve Bank of India as a tokenized digital version of the Indian rupee. The digital rupee pilot was launched in 2022 for wholesale transactions, and later for retail users. Unlike cryptocurrencies, the digital rupee is centralized and regulated by the RBI. It aims to promote a cashless economy, financial inclusion, and reduce costs associated with physical cash. The document compares features of the digital rupee to cryptocurrencies and explains forms of central bank digital currencies.