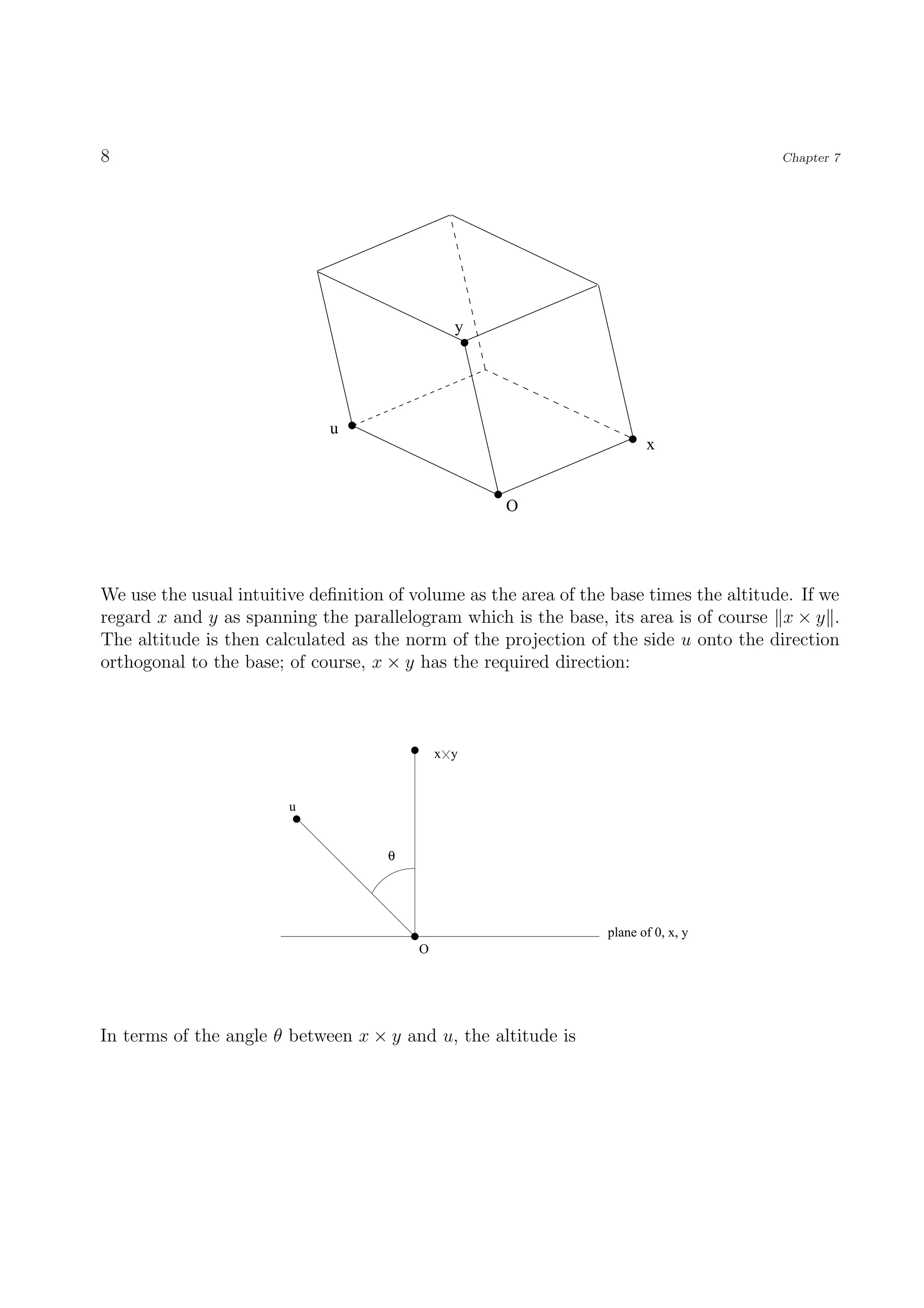
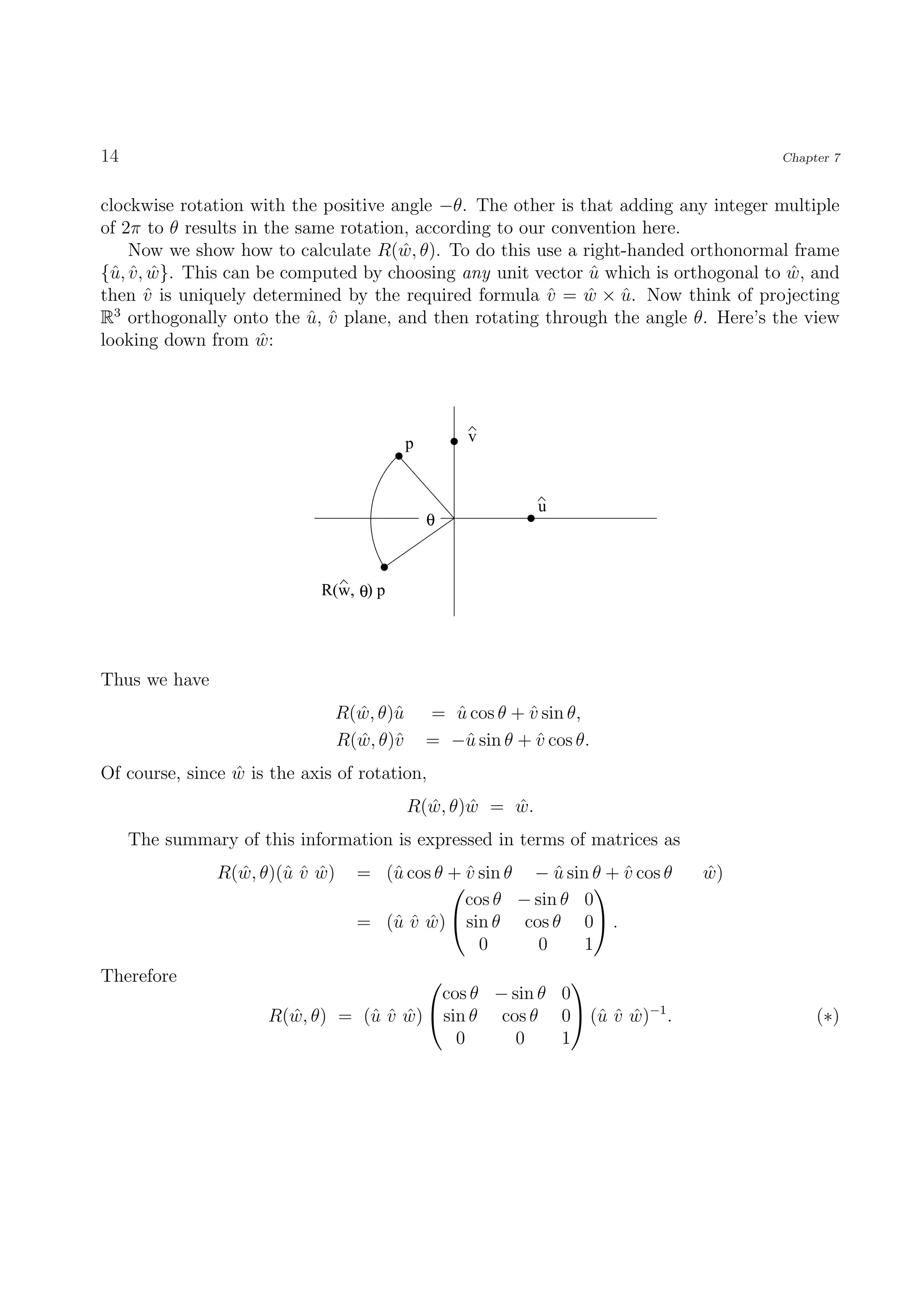
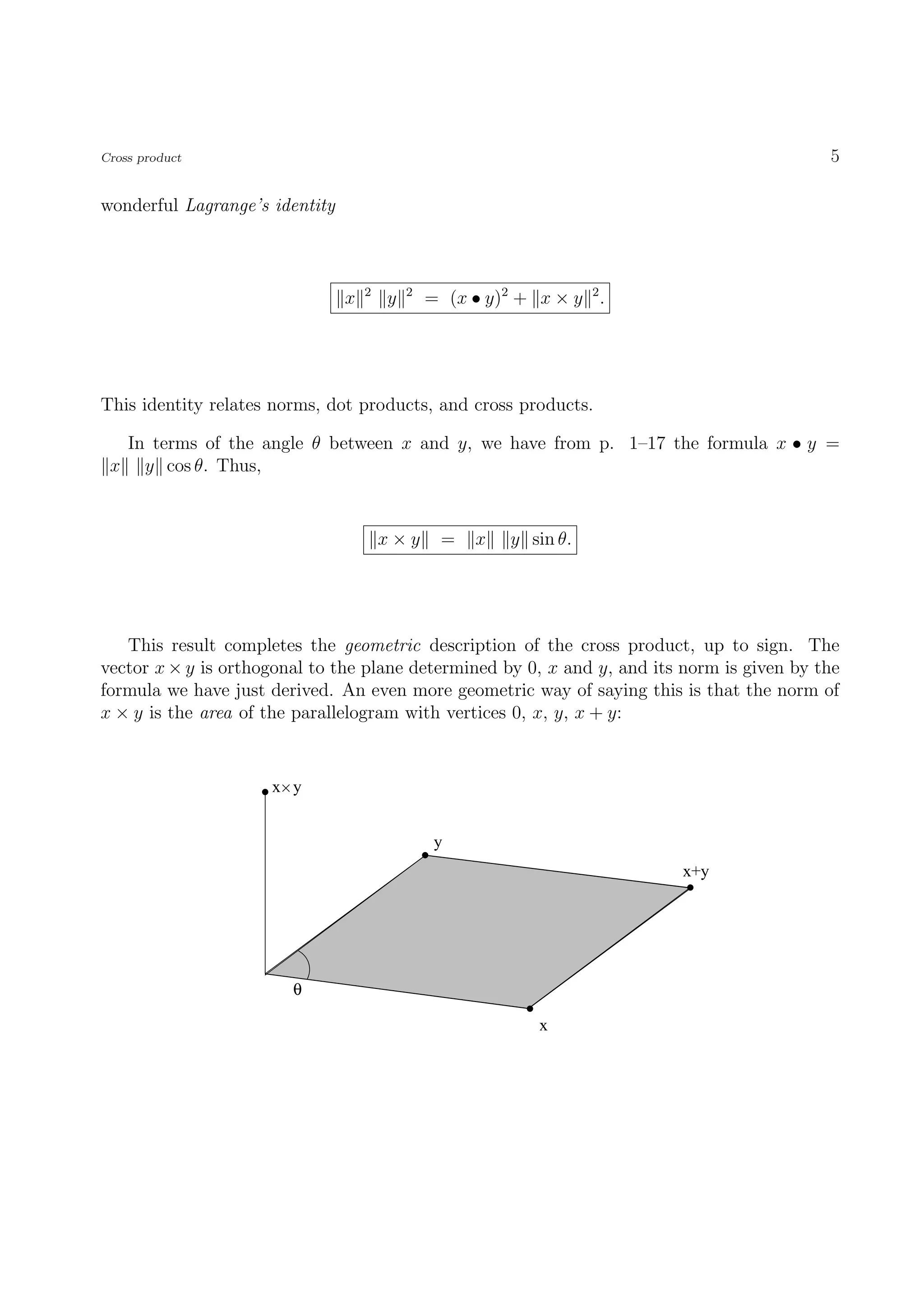
The document discusses the cross product of vectors in R3. It begins by defining the cross product as a vector z that is orthogonal to two given vectors x and y. It then shows that z can be uniquely defined as z = (x2y3 - x3y2, x3y1 - x1y3, x1y2 - x2y1). Several properties of the cross product are then discussed, including that it is anticommutative and relates to the area of the parallelogram formed by x and y. The cross product allows computing volumes of parallelepipeds in R3 and relates to both the dot product and scalar triple product of vectors.





![Cross product 7
(x × y) • u = (u × x) • y = (y × u) • x
= −(y × x) • u = −(x × u) • y = −(u × y) • x.
Thus we have the interesting phenomenon that writing x, y, u in order gives
(x × y) • u = x • (y × u).
So the triple product doesn’t care which you call × and which you call •. For this reason, it’s
frequently written
[x, y, u] = (x × y) • u.
PROBLEM 7–4. The vector triple product is (x × y) × u. It can be related to dot
products by the identity
(x × y) × u = (x • u)y − (y • u)x.
Prove this by using Problem 7–3 to calculate the dot product of each side of the proposed
formula with an arbitrary v ∈ R3 .
PROBLEM 7–5. Prove quickly that the other vector triple product satisfies
x × (y × u) = (x • u)y − (x • y)u.
The identities in Problems 7–4 and 7–5 can be remembered by expressing the right side of
each as
vector triple product = (outer•far) near − (outer•near) far.
The scalar triple product is exactly the device that enables us to compute volumes of
parallelepipeds in R3 . Consider three vectors x, y, u in R3 . They generate a region D called
a parallelepiped as follows:
D = {ax + by + cu | 0 ≤ a ≤ 1, 0 ≤ b ≤ 1, 0 ≤ c ≤ 1}.
PROBLEM 7–6. Prove that
[x × y, y × u, u × x] = [x, y, u]2 .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crossproduct-121215113230-phpapp01/75/Cross-product-7-2048.jpg)