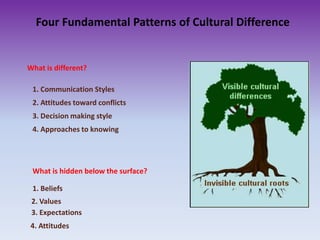
Culture is the lens through which people view and make sense of the world. It influences communication styles, approaches to conflicts, decision making, and ways of knowing. Communication involves both verbal and non-verbal codes like words, gestures, eye contact and appearance that can be interpreted differently across cultures. Effective cross-cultural communication is important for business, jobs, diversity, and understanding global markets. To improve cross-cultural communication, one should slow down, separate questions, avoid negatives, take turns, clarify meanings, and be mindful of etiquette and humor.