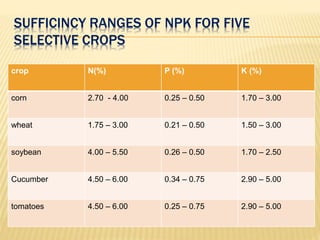
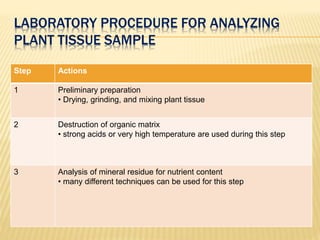
1) Plant tissue testing helps monitor crop nutrient status for optimal production, ensure balanced nutrient levels for quality produce, and predict nutrient problems to avoid losses. Samples should be taken when symptoms first appear from similar abnormal plants.
2) Information provided with samples includes crop type, variety, soil type, fertilization history, irrigation, and visual appearance. Young, old, diseased or damaged plants should be avoided.
3) Proper sampling techniques vary by crop, such as collecting the upper 1/3 of cotton plants before bloom or recently mature soybean leaves from the top of plants. Timely sampling and handling is important to get the best results.