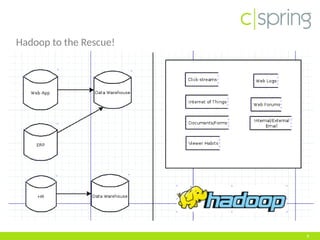
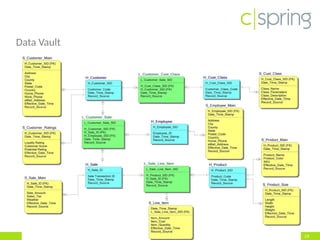
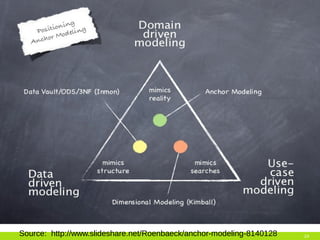
The document discusses the challenges and solutions associated with big data, particularly focusing on the importance of structuring unstructured data to avoid creating a 'data swamp.' It highlights the necessity of proper data management practices using frameworks like data vault and anchor models to build a data reservoir that is filtered and fit for purpose. Additionally, it addresses the significance of data quality and the tools needed to integrate and maintain effective data systems.