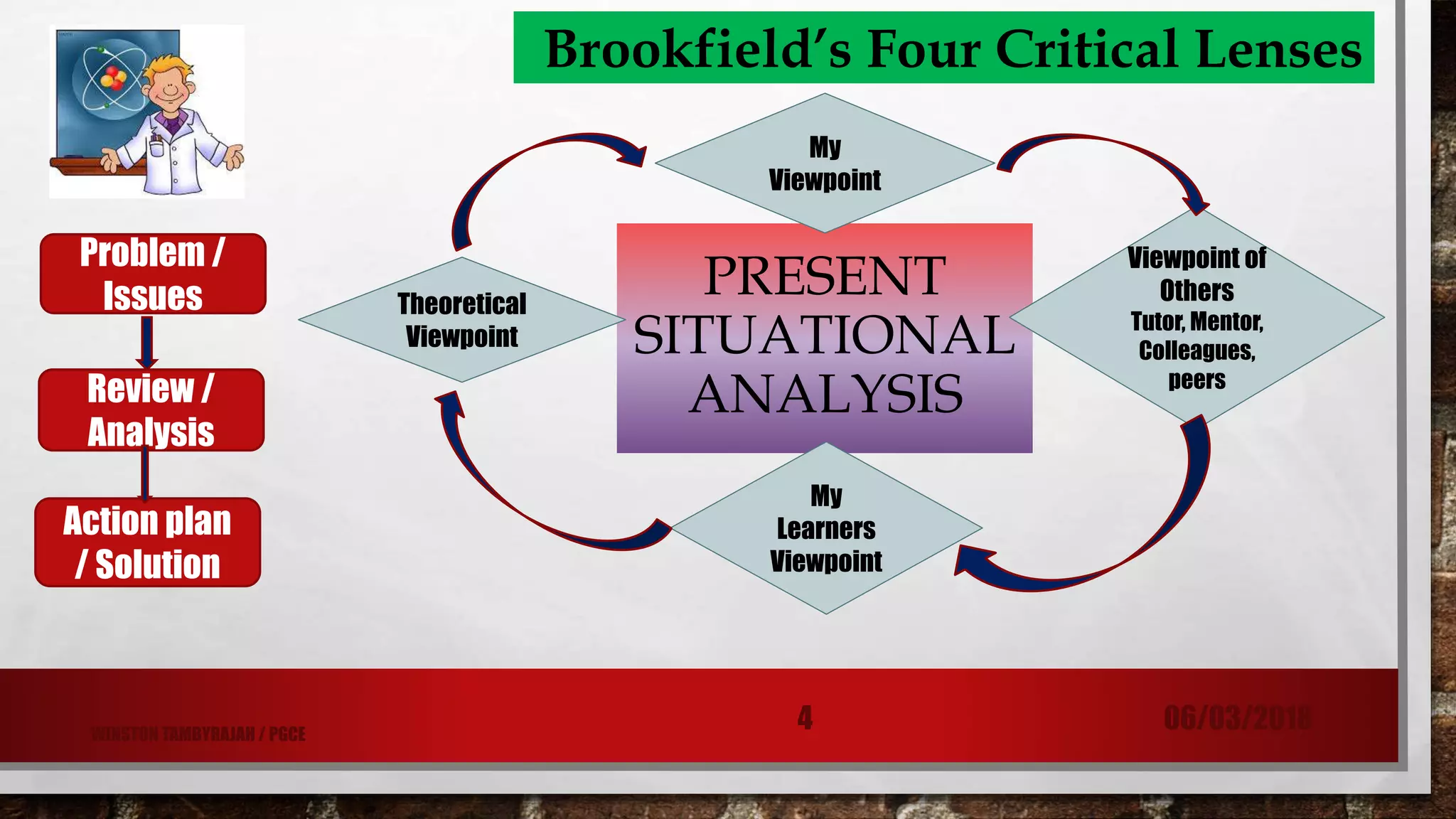
This document discusses Winston Tambyrajah's reflections on and improvements to his teaching methodology. It describes his past university teaching experience, which was lecturer-centered with limited student interaction. His current students have mixed abilities, backgrounds, and motivation levels. The document outlines how he used Brookfield's four critical lenses - his viewpoint, others' viewpoints, learners' viewpoints, and theoretical viewpoints - to identify issues, analyze problems, and develop solutions. Winston incorporated more active learning techniques like peer teaching, differentiated instruction, and improved worksheets. He also provided additional challenges and support for students of varying abilities.