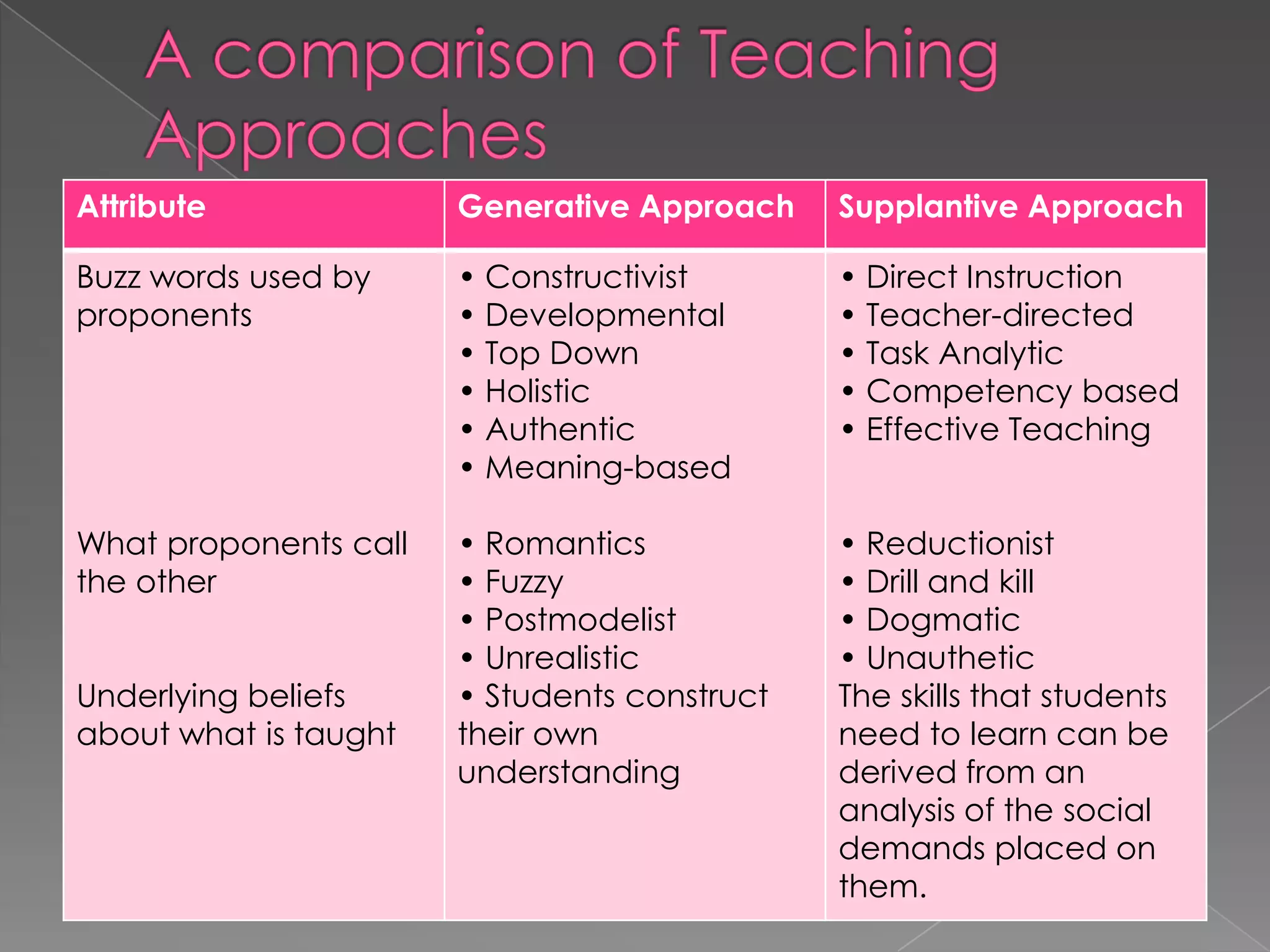
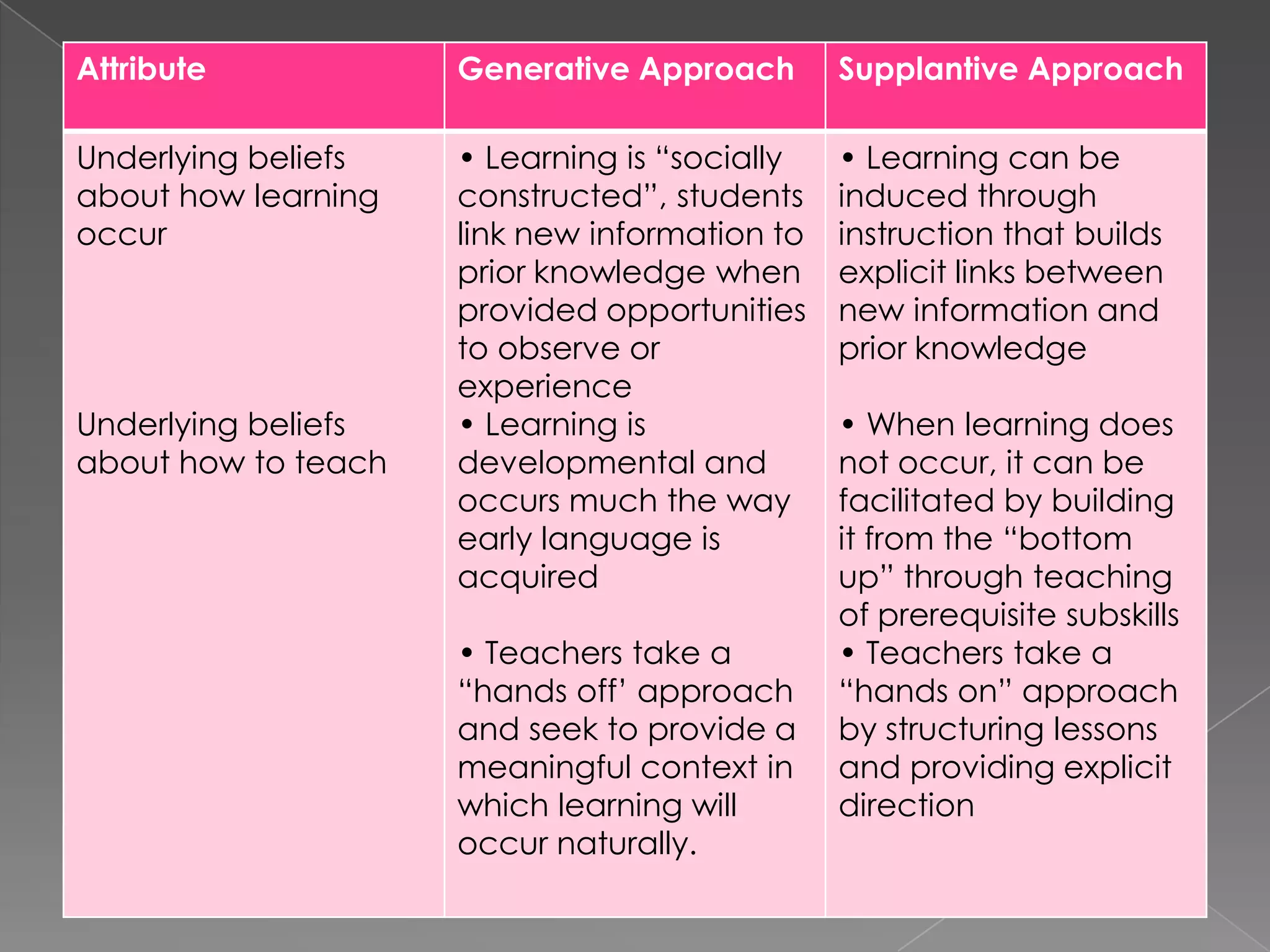
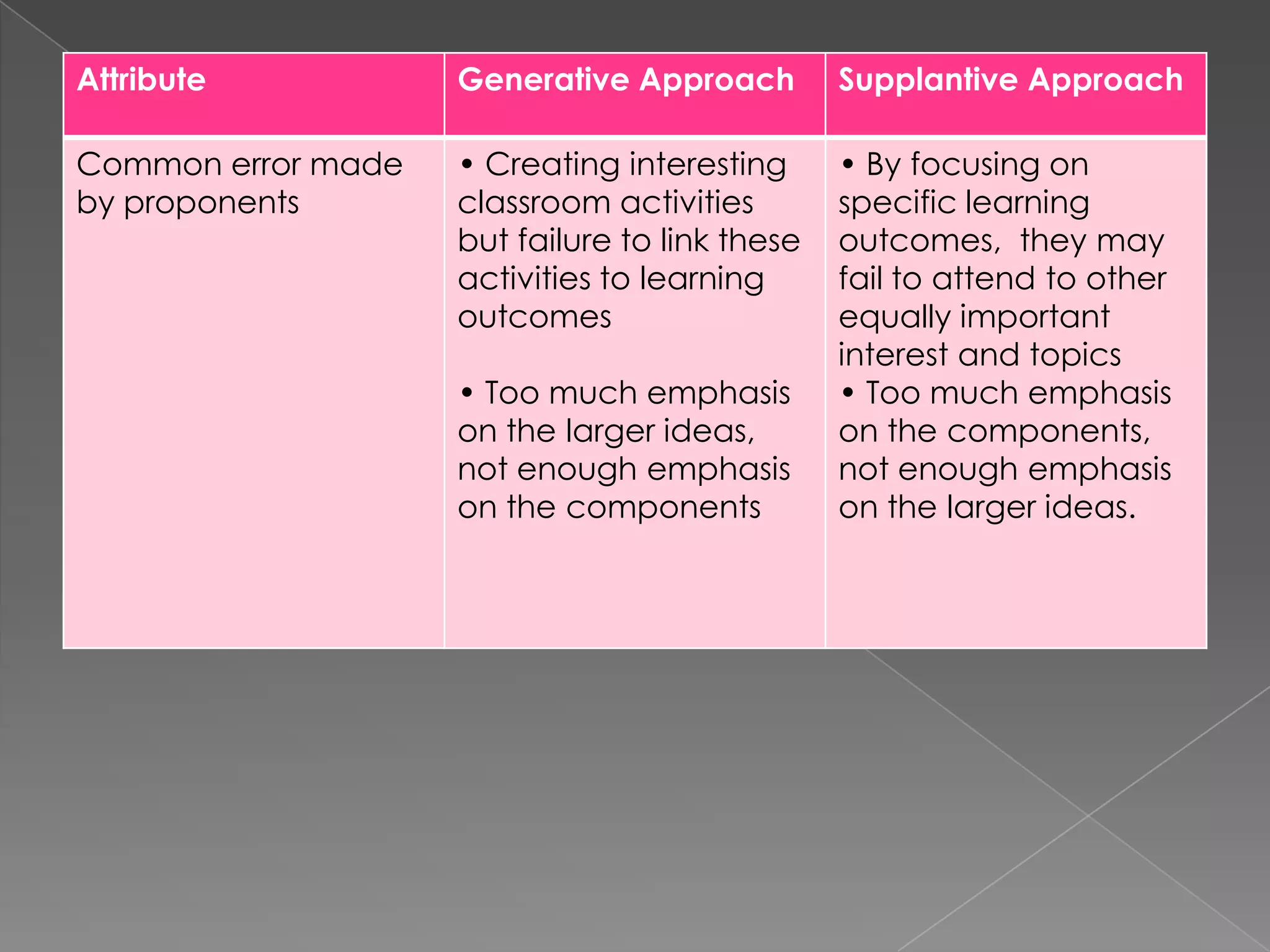
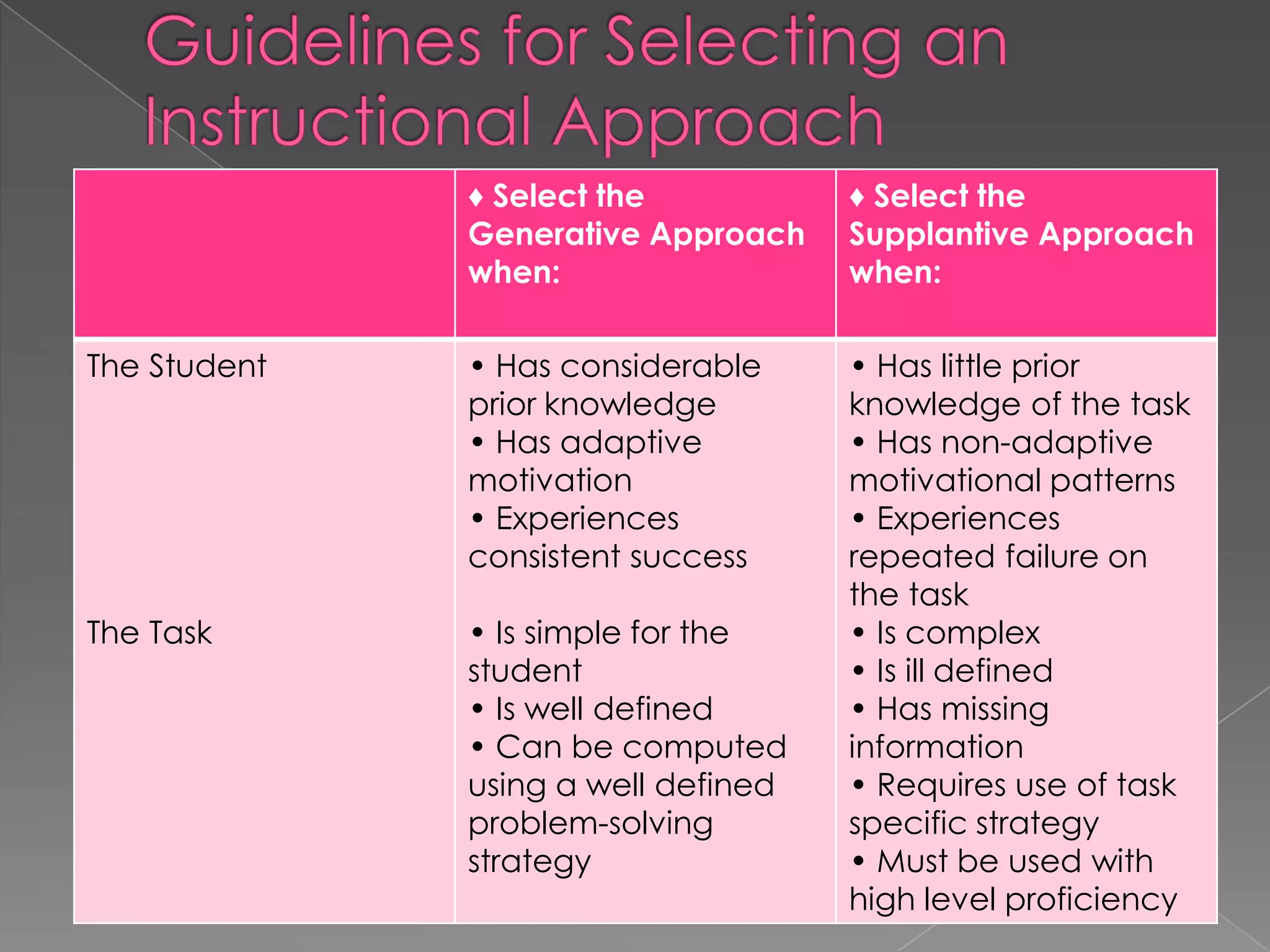
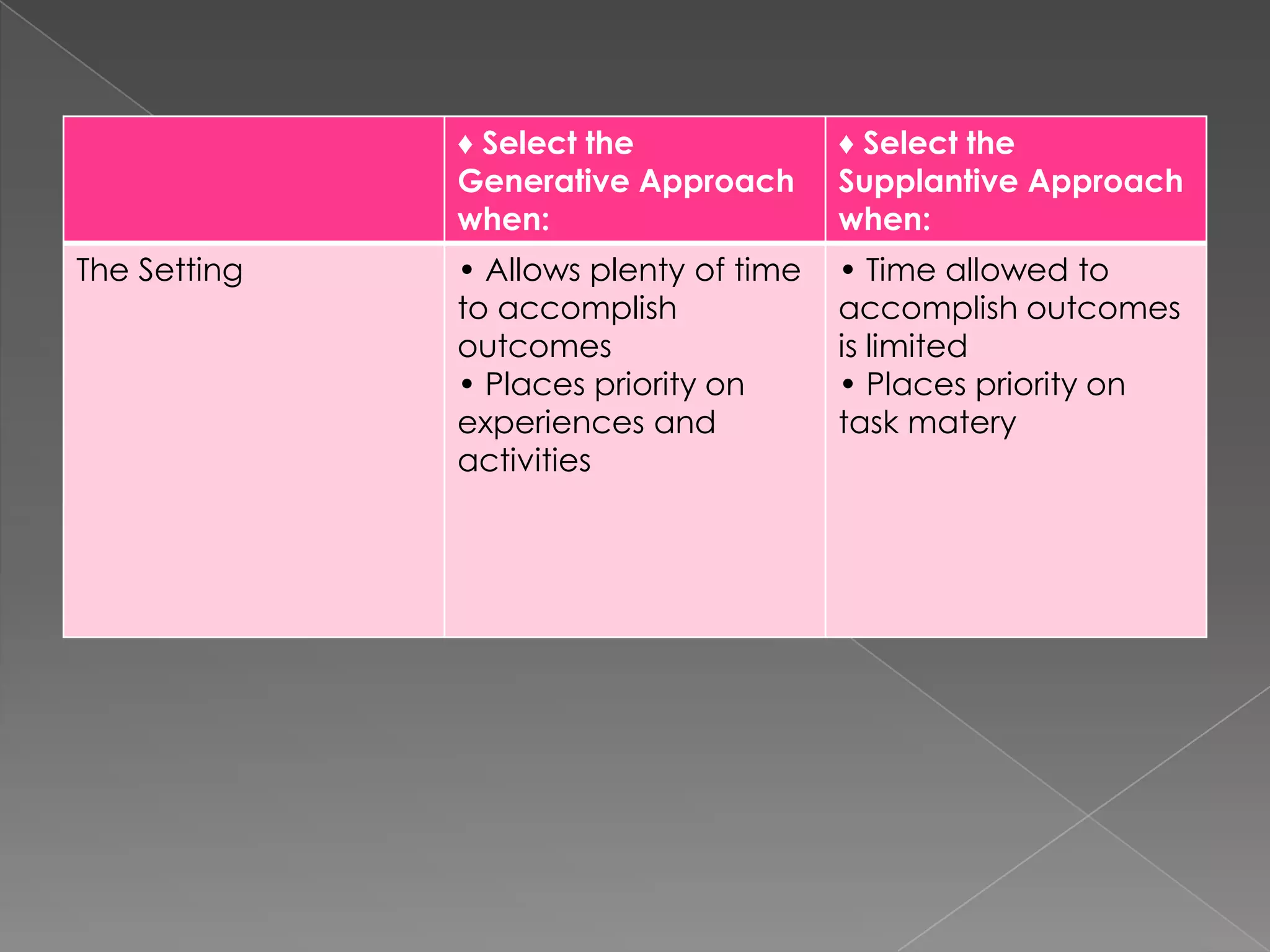
This document discusses two approaches to instruction: the generative approach and the supplantive approach. The generative approach views learning as student-directed and sees the teacher as a facilitator. It focuses on allowing students to make their own connections and develop strategies. The supplantive approach sees the teacher as providing explicit direction and explanations. It breaks down skills into subskills that are directly taught to students. The document provides details on the underlying beliefs, common practices, and situations each approach works best for.