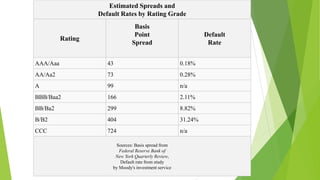
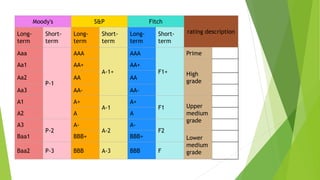
A credit rating agency assesses an issuer's ability to pay back debt. It assigns ratings using symbols like AAA or BB that represent varying levels of default risk. The ratings are based on factors like the issuer's finances, industry, economy and are assigned to specific debt instruments. Credit ratings help issuers and investors but do not guarantee performance and ratings can change over time as circumstances change. SEBI regulates agencies in India to promote transparency and accountability.