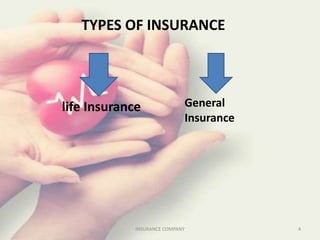
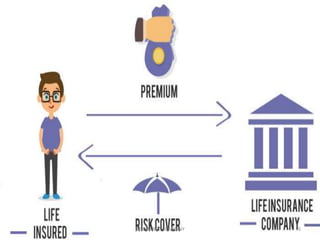
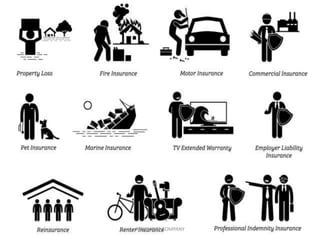
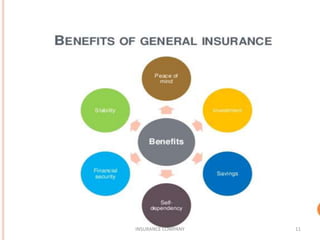
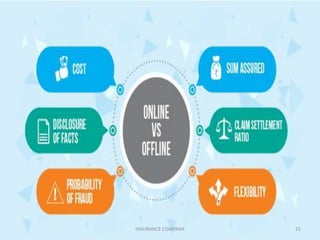
The document discusses the insurance sector in India. It explains that insurance transfers risk from the insured to the insurer in exchange for premiums. The main types of insurance are life insurance and general insurance. The regulatory body IRDAI was established in 1999 to regulate and develop the insurance industry in India and opened the sector to private companies. Major players in life insurance include LIC, ICICI Prudential, and SBI Life. In general insurance, major players are New India Assurance, National Insurance, and HDFC Ergo. The insurance sector has grown significantly since liberalization and is projected to reach $280 billion by 2020.