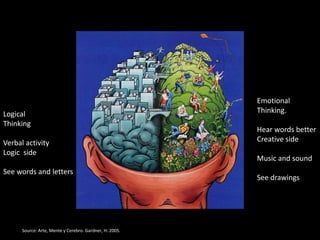
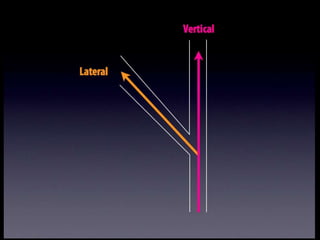
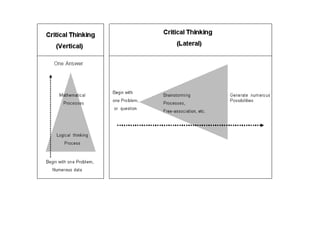
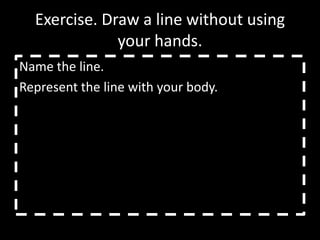
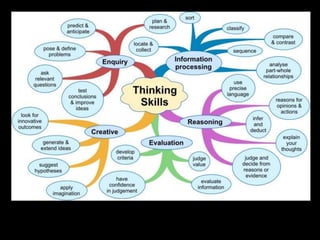
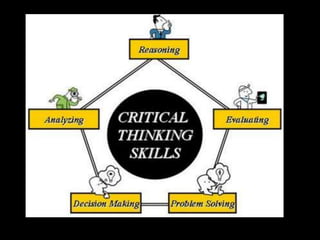
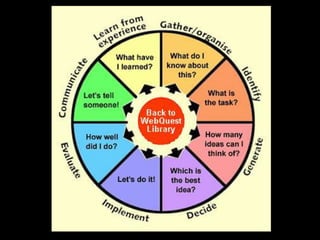
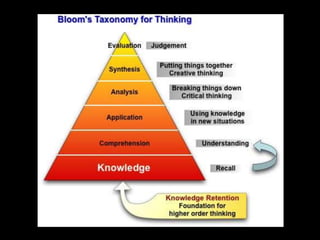
The document discusses various aspects of the creative process in art including vertical versus lateral thinking, thinking skills, and models of creative thinking proposed by Edward de Bono and Louis Raths. It provides examples of exercises to develop lateral thinking and outlines the typical stages involved in an art project from conceiving an idea to the final exhibition. Thinking skills like reflection and logical analysis can help focus creative thinking.