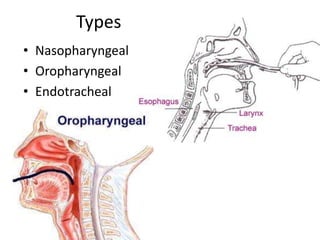
The document outlines suctioning procedures by Dr. Sachin Chaudhary, focusing on indications, types, and equipment involved. It details the steps for endotracheal and nasopharyngeal suctioning, emphasizing the importance of precautions and potential hazards associated with the procedure. The learning objectives include understanding indications for suctioning, types of suctioning apparatus, and associated risks.