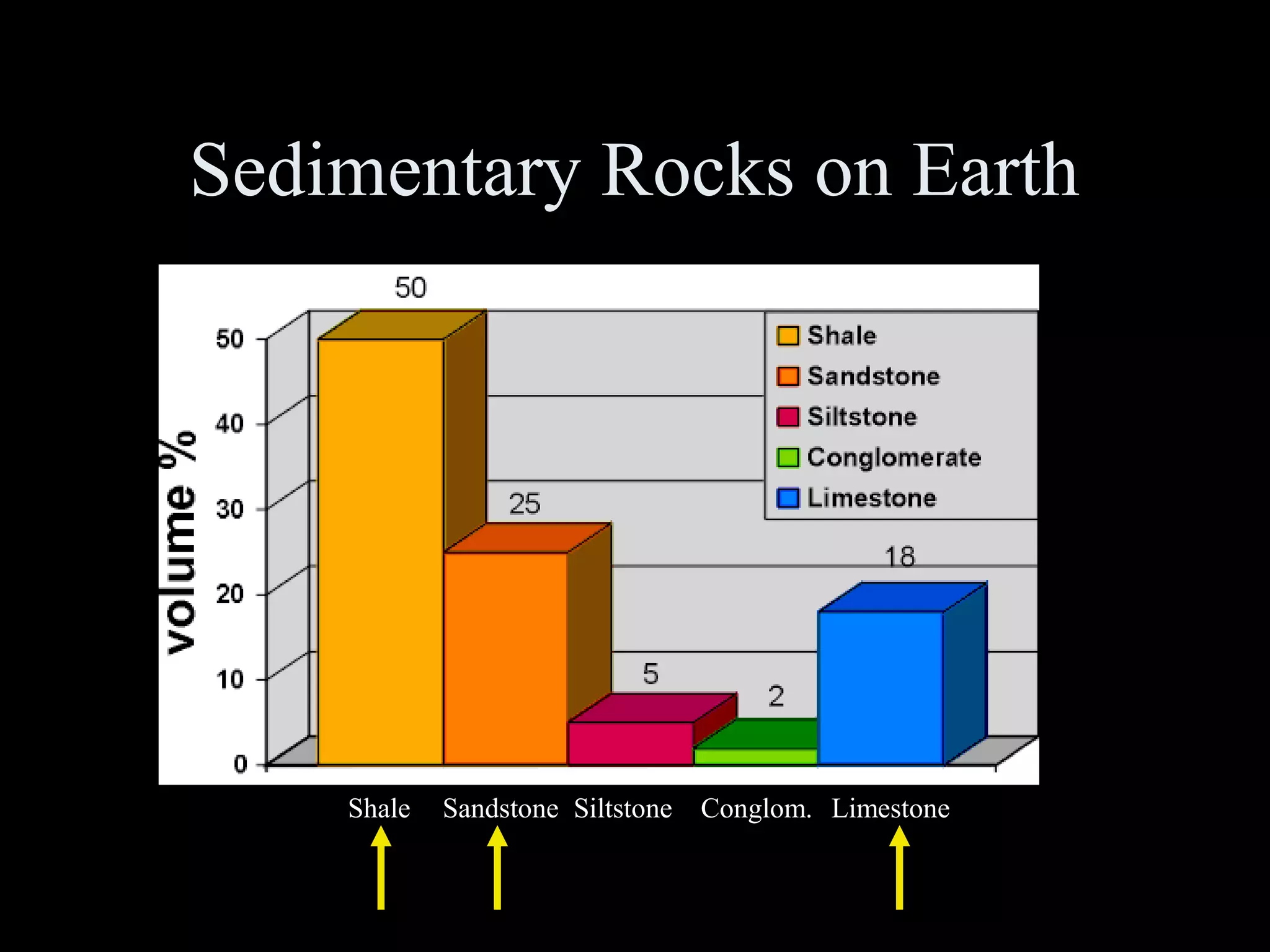
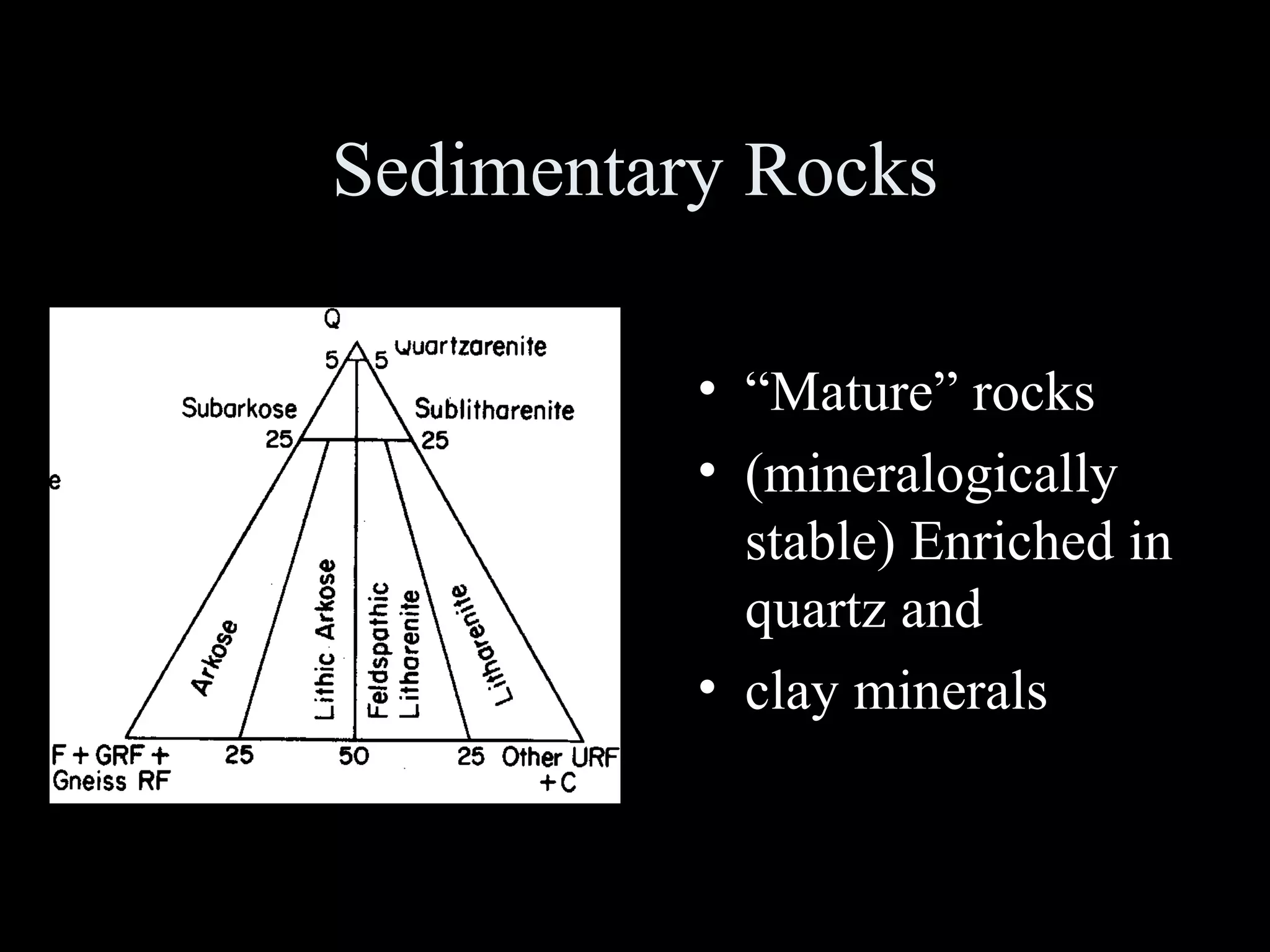
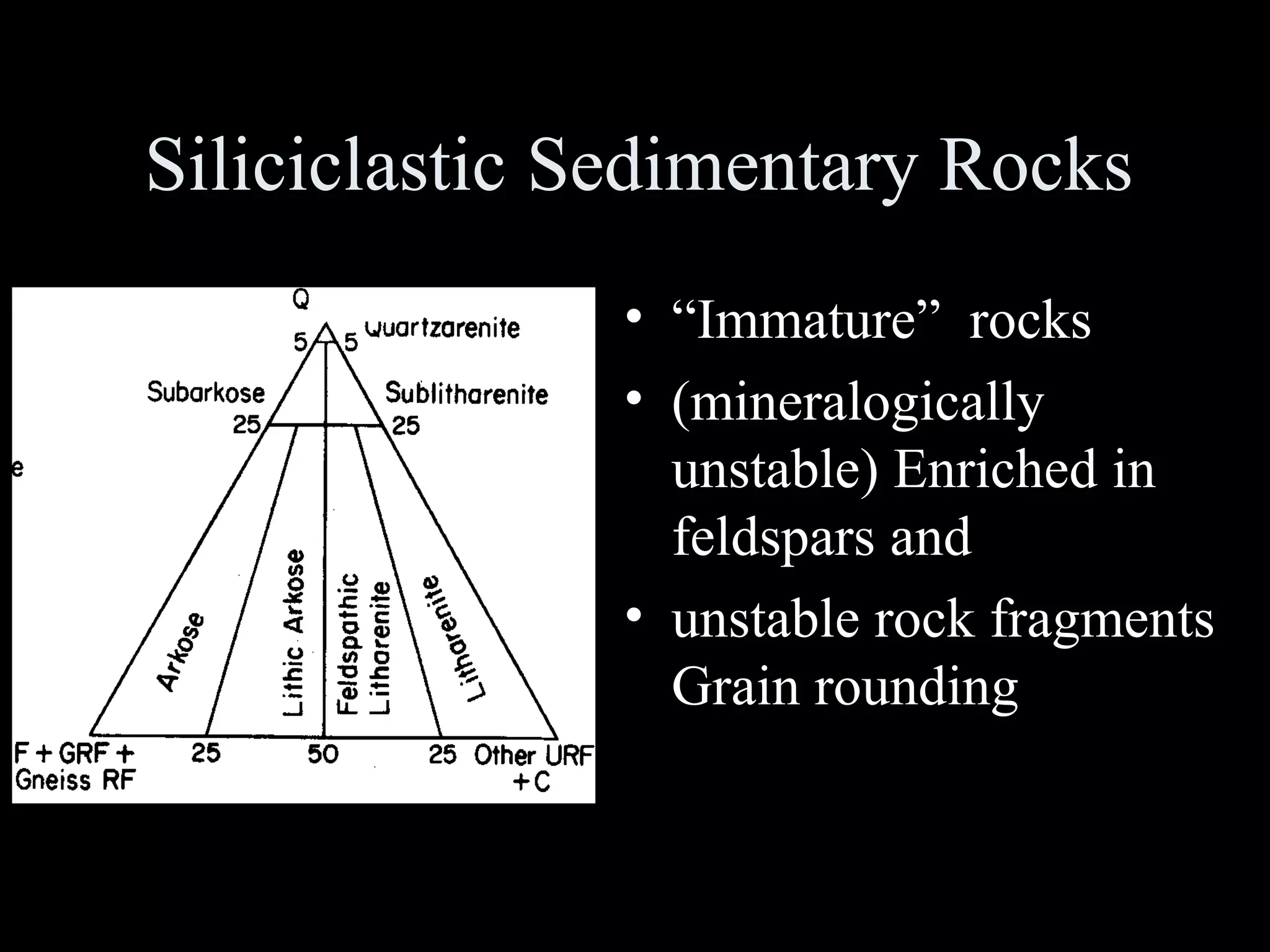
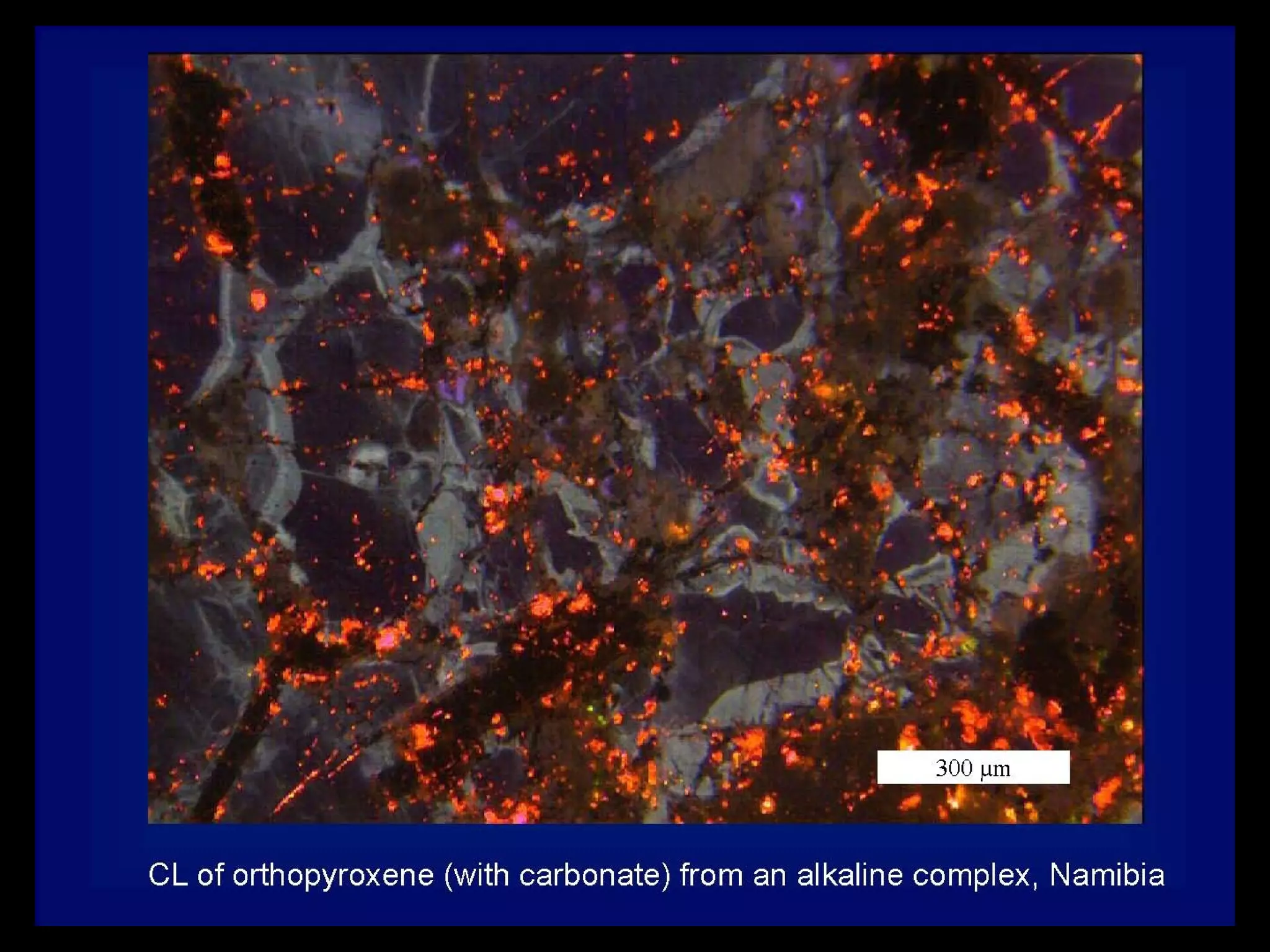
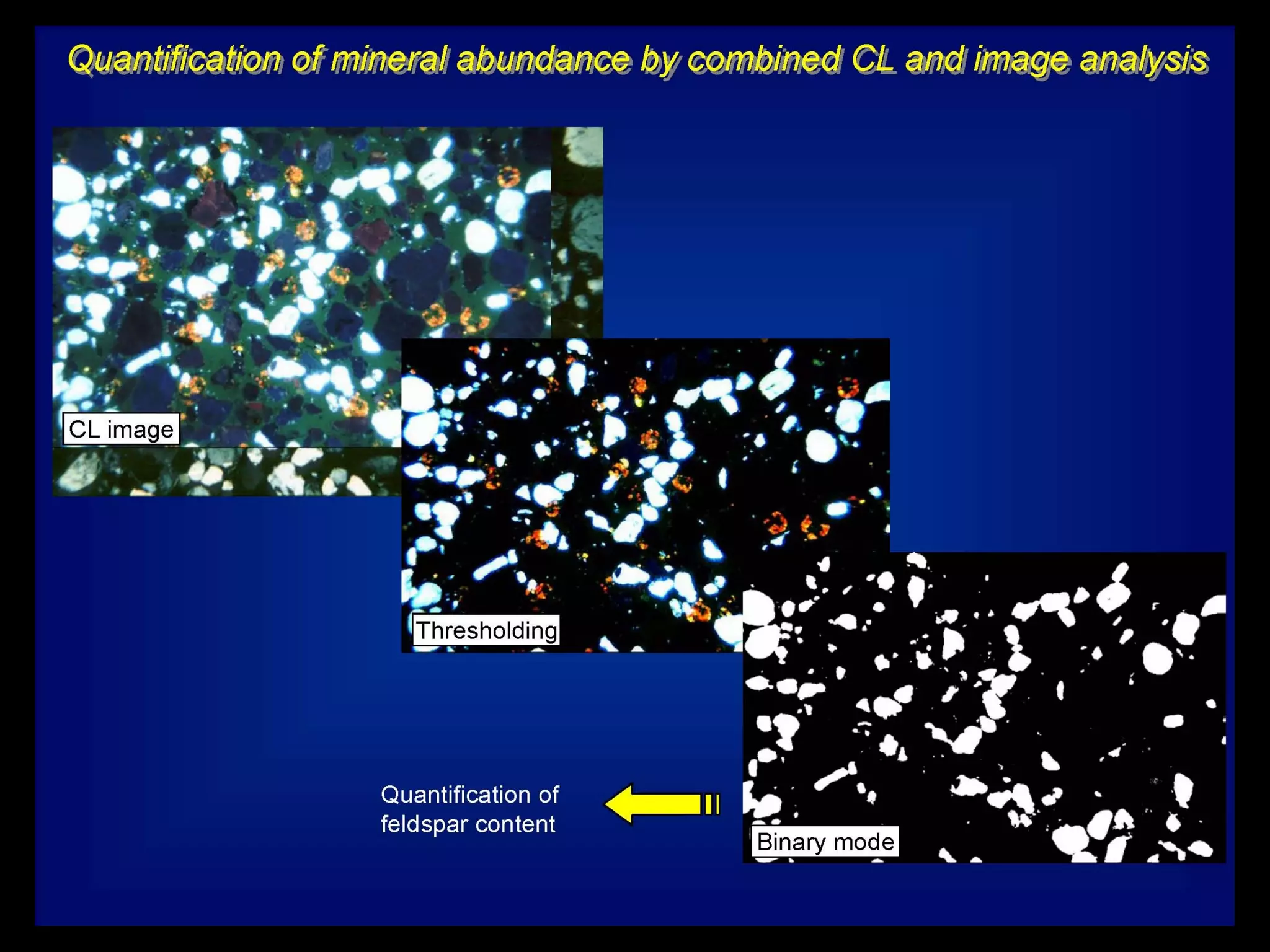
This document discusses key concepts in sedimentary petrology including the study of sedimentary rock characteristics, origins, and the processes involved in their formation. It describes how sedimentary rocks record information about sediment source, transport mechanisms, depositional environment, and post-depositional changes. Identification is based on composition and texture. Major rock types include siliclastic, volcaniclastic, and various carbonate rocks. Weathering of rocks produces sediment which is transported and deposited, becoming lithified over time into sedimentary rocks.