This document provides information about binary counting circuits, including:
- Binary numbers use only 0 and 1 to represent values, making it the simplest counting system for electronic circuits.
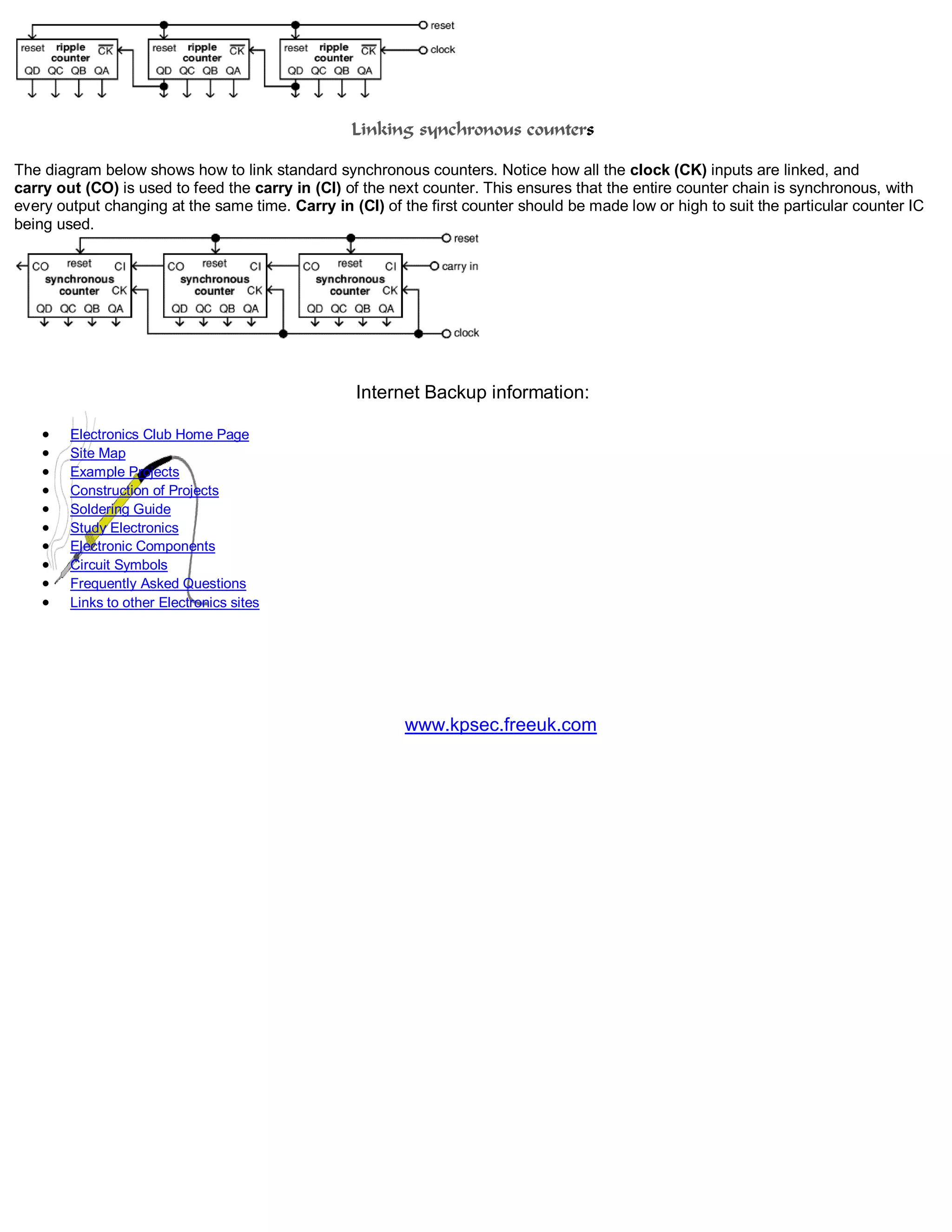
- Counters work by advancing the count on either the rising or falling edge of a clock signal. Ripple counters count on the falling edge while synchronous counters typically count on the rising edge.
- Individual binary digits are called bits, with a group of 8 bits called a byte. Common number systems like hexadecimal and binary coded decimal are discussed.
- Circuits like decoders and 7-segment displays are used to display binary counts in decimal form. Counters can also be linked to count higher values.