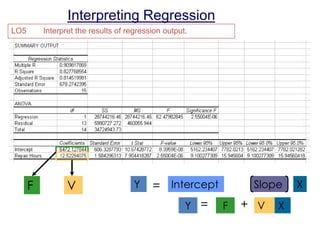
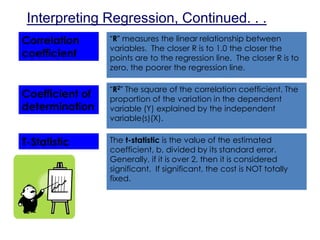
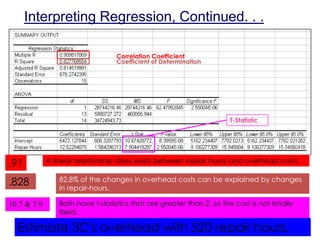
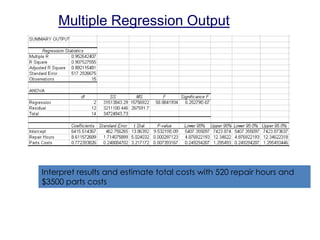
This document discusses statistical cost estimation techniques, including variable costs, fixed costs, and mixed costs. It explains how to use the scattergraph method and regression analysis to derive a total cost equation and estimate mixed costs. Specifically, it discusses using regression to interpret results like the correlation coefficient, coefficient of determination, and t-statistic. It provides an example of using multiple regression with two predictor variables and interpreting those results. Finally, it discusses potential problems that can occur with regression data like curvilinear costs, outliers, spurious relations, and violating assumptions.