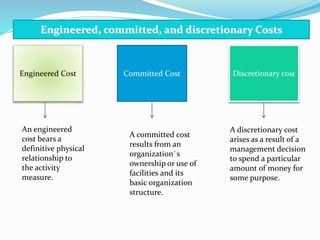
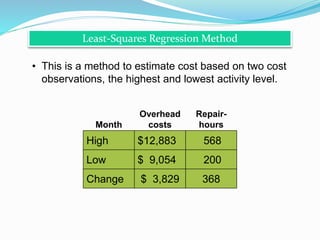
Cost estimation involves determining the relationship between costs and activity levels using historical data. There are several types of cost behaviors such as variable, fixed, and semi-variable costs. Managers must understand these cost behaviors to predict how costs will change with activity levels. Common cost estimation methods include account classification, regression analysis, visual fitting, high-low analysis, and engineering estimates. These methods analyze past cost and activity data to develop cost behavior models. Accurate cost estimation requires high quality source data without issues like missing information, outliers, or inconsistent time periods.