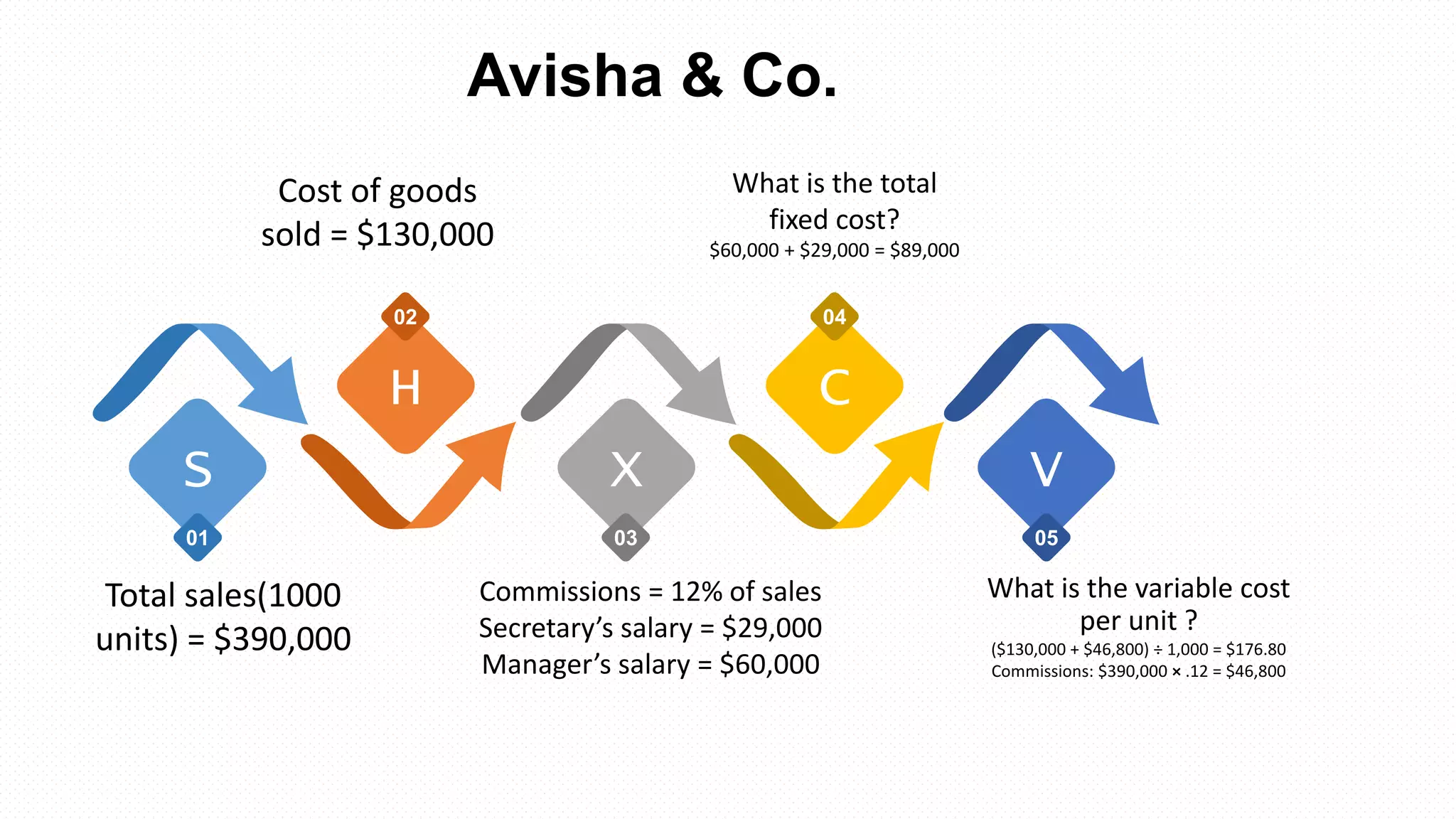
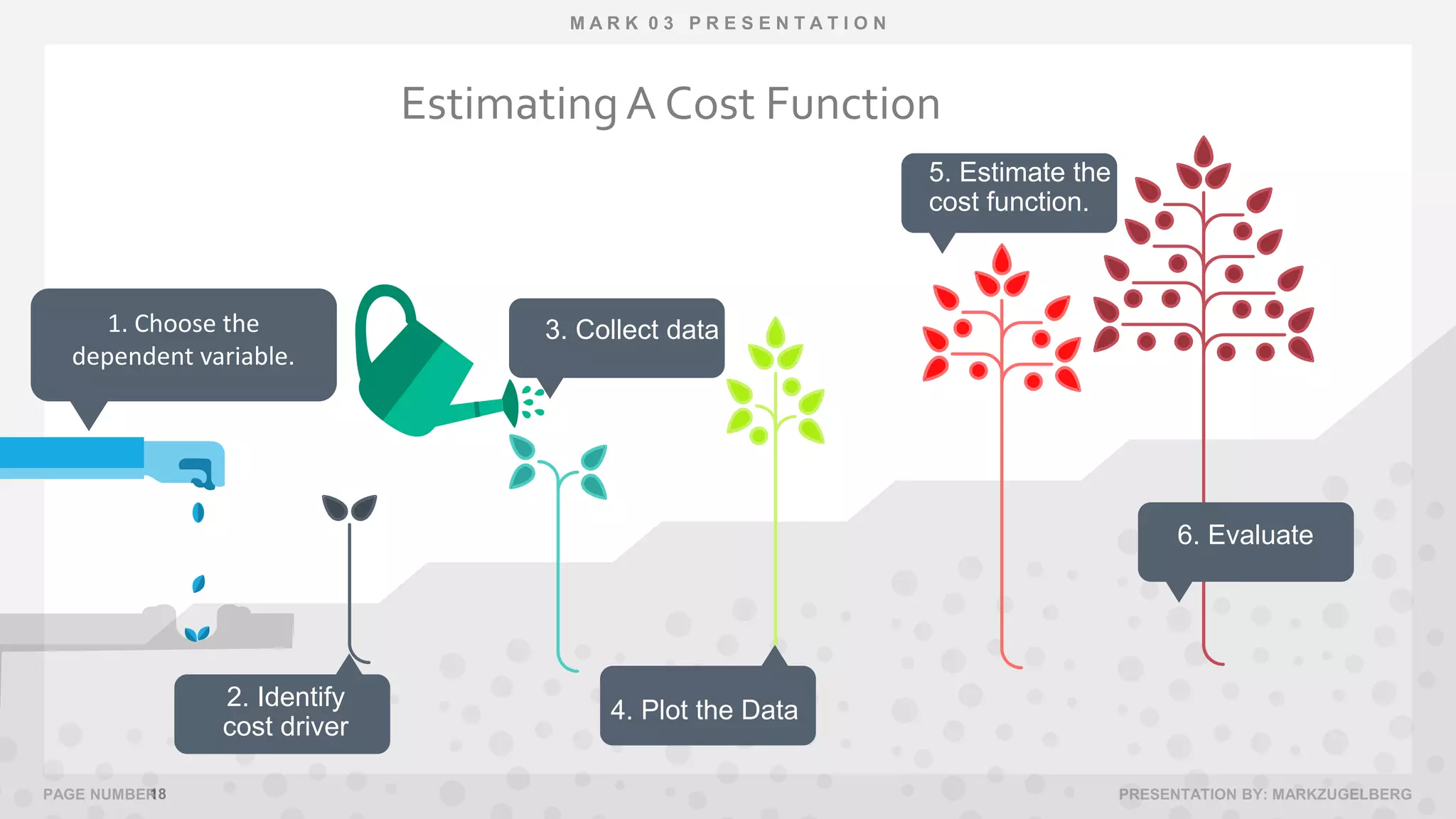
This document discusses various methods for determining and estimating cost behavior. It defines different types of costs such as fixed, variable, and mixed costs. It also explains cost functions and how managers can use cost functions to understand how costs change with activity levels. The document outlines some common assumptions made in estimating cost behavior and lists several quantitative and qualitative approaches to cost estimation including the industrial engineering method, conference method, account analysis method, and high-low method.