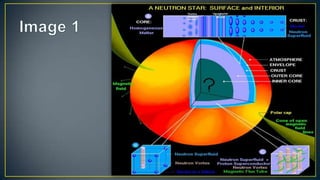
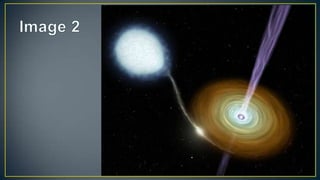
Pulsars are powered by the loss of rotational energy or by accretion of infalling matter. Magnetars are pulsars with extremely strong magnetic fields that provide their power. Neutron stars are formed during the gravitational collapse of massive stars over 8 times the mass of our Sun in a supernova explosion. They are only about 20 km in diameter but have around 1.4 times the mass of our Sun, making them incredibly dense - a teaspoon of neutron star material would weigh over a billion tons on Earth.