Cosmetics - Biological aspects and design of cosmeceutical products
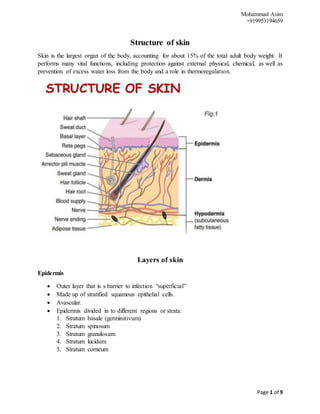
- 1. Mohammad Asim +919953194659 Page 1 of 9 Structure of skin Skin is the largest organ of the body, accounting for about 15% of the total adult body weight. It performs many vital functions, including protection against external physical, chemical, as well as prevention of excess water loss from the body and a role in thermoregulation. Layers of skin Epidermis Outer layer that is s barrier to infection “superficial” Made up of stratified squamous epithelial cells. Avascular. Epidermis divided in to different regions or strata: 1. Stratum basale (germinitivum) 2. Stratum spinosum 3. Stratum granulosum 4. Stratum lucidum 5. Stratum corneum
- 2. Mohammad Asim +919953194659 Page 2 of 9 Dermis Middle layer that contains nerves Hair roots Sweat and oil glands and blood vessels. Dermis lies between the epidermis and subcutaneous layer and contains many types of sensory receptor for touch, pressure, vibration, pain, temperature etc. The type of cells located in the dermis are: 1. Fibroblasts 2. Mast cells 3. Histocytes 4. Hair follicles, nerves 5. lymphatic vessels 6. sweat glands Hypodermis Fat, blood vessels and connective tissue that help to maintain body temperature. Deep to skin and also known as subcutaneous tissue. Consist of loose connective tissue with collagen and elastic fibers. Functions as: Energy source and Insulation Main type of cells in hypodermis are: 1. Fibroblast 2. Adipose tissue 3. Macrophages Skin relating problems Dry Skin Dry skin has a low level of sebum and can be prone to sensitivity. which refers to roughened, flaky, or scaly skin that is less flexible than normal and dry to feel. The dry skin is the common problem in all age groups, but more in elderly individuals. The content of the stratum corneum play important role for maintaining the normal appearance and texture of skin. It usually feels “tight”. Uncomfortable after washing. Chapping and cracking are signs of dehydrated skin. It looks dull, mainly on the cheeks and around the eyes. Causes Poor diet, nutritional deficiencies, and especially deficiencies of vitamin A and the vitamin B can also contribute to dry skin. Dry skin is not a sign of skin diseases, but is simply caused by harsh soaps, itchy clothing, exposure to sun, cold environment, chemicals and long hot showers. The oil glands do not produce enough lubrication to the skin which lead to dry skin.
- 3. Mohammad Asim +919953194659 Page 3 of 9 Medications you take and even medical conditions such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, malnutrition can also cause severe dry skin. Prevention Skip long hot shower. Hot water strips oils from the skin faster than warm water. Use a gentle cleanser or shower gel with moisturizer. Go for soap free or mild soap cleansers instead of harsh cleanser. Moisturize while skin is moist moisturizer increases the water content of the outer layers of skin and gives it a soft look. Acne Acne is an inflammatory skin condition that occurs when oil and dead skin cells blocks the pore opening causing sebum to build up inside the pores. Acne is affected by two major factors: heredity and hormones. Treatment Use cleansers for oily skin toners also help to remove excess sebum. Avoid using fatty skin care and cosmetic products; use non comedogenic products (designed and proven not to clog the follicles). Do not use harsh products or over clean acne-prone skin as this can lead to inflammation. Mild and moderate cases of acne can be treated by trained salon and spa etc. Use anti-androgen, anti-biotic like tetracycline, co- trimoxazole to stop growth of bacteria and reduce inflammation. Pigmentation Pigmentation means coloring. Skin pigmentation disorders affect the color of skin. Skin gets its color from pigment called melanin. It occurs due to the deposition of the melanin, which is produce by specialized cells called melanocytes with in melanosomes and transferred to keratinocytes. Treatment Topical prescription medication such as 4% hydroquinone are often use to treat hyperpigmentation. Aloe Vera contain aloin, a natural depigmenting compound. Gentle cryotherapy uses to treat variety of lesions. (in very low temp) Over the counter brightening product that contain licorice root, pine tree, vitamin E, vitamin C. Drugs used to treat pigmentation- 1. Corticosteroids 2. azelaic acid 3. Trichloro acetic acid
- 4. Mohammad Asim +919953194659 Page 4 of 9 4. Retinoic acid 5. Kojic acid 6. Niacinamide 7. Ellagic acid 8. Ascorbic acid Prickly Heat Heat rash is the generic group name for a number of skin problems that arise or worsen because of heat exposure. Common names for heat rash include prickly heat, sweat retention syndrome, and "sun” allergy. This disorder occurs all year round in the tropics, and elsewhere in the summer months when the weather is hot and humid. In the tropics it is most commonly seen from March to September especially in visitors from cooler climates. Causes Heat rash is caused by a blockage of the sweat glands, especially after repeated episodes of sweating, leading to inflammation when sweat escapes into adjacent tissue. This causes itching and prickling sensations that most people seek treatment for, as well as the red rash, which may be extensive. Treatment Remain in a cool environment e.g. air conditioning, or close to a fan, and allow for adequate ventilation of the skin. Take cool showers or baths, several times a day, and always after exercise or heat exposure. Always pat dry the skin with a towel, do not rub vigorously. Use cool packs on affected areas (but not for longer than 20 minutes per hour). Wrinkles Wrinkles are lines and furrow that form in your skin. These are especially noticeable around your mouth, neck, hands, and eyes. Causes Smoking: Smoking can accelerate the normal aging process of your skin, contributing to wrinkles. This may be due to changes in the blood supply to your skin. Repeated facial expressions: Facial movements and expressions, such as squinting or smiling, lead to fine lines and wrinkles. Each time you use a facial muscle, a groove forms beneath the surface of the skin. And as skin ages, it loses its flexibility and is no longer able to spring back in place. These grooves then become permanent features on your face. Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light: Ultraviolet radiation, which speeds the natural aging process, is the primary cause of early wrinkling. Exposure to UV light breaks down your skin's connective tissue — collagen and elastin fibers, which lie in the deeper layer of skin (dermis).
- 5. Mohammad Asim +919953194659 Page 5 of 9 Age. As you get older, your skin naturally becomes less elastic and more fragile. Decreased production of natural oils dries your skin and makes it appear more wrinkled. Treatment Topical retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, retinoids — such as tretinoin (Renova, Retin- A) and tazarotene (Avage, Tazorac) — that you apply to your skin may reduce fine wrinkles, splotches and skin roughness. Because retinoids can make your skin burn more easily, you'll need to use a broad-spectrum sunscreen and wear protective clothing daily. Retinoids may cause redness, dryness, itching, and a burning sensation. Nonprescription wrinkle creams: The effectiveness of anti- wrinkle creams depends in part on the active ingredients. Retinol, antioxidants and some peptides may result in slight to modest improvements in wrinkles. Rhytidectomy: is a type of cosmetic surgery procedure used to give a more youthful facial appearance. Sunscreens Sunscreen, also known as sunblock, sun cream or suntan lotion, is a lotion, spray, gel or other topical product that absorbs or reflects some of the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation and thus helps protect against sunburn. Diligent use of sunscreen can also slow or temporarily prevent the development of wrinkles, moles and sagging skin. Depending on the mode of action, sunscreens can be classified into physical sunscreens (i.e., those that reflect the sunlight) or chemical sunscreens (i.e., those that absorb the UV light). Active ingredients In addition to moisturizers and other inactive ingredients, sunscreens contain one or more of the following active ingredients, which are either chemical or mineral in nature: Organic chemical compounds that absorb ultraviolet light. Inorganic particulates that reflect, scatter, and absorb UV light (such as titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, or a combination of both). Organic particulates that mostly absorb UV light like organic chemical compounds, but contain multiple chromophores that reflect and scatter a fraction of light like inorganic particulates. An example is Tinosorb M. The mode of action is about 90% by absorption and 10% by scattering. The principal active ingredients in sunscreens are usually aromatic molecules conjugated with carbonyl groups. This general structure allows the molecule to absorb high-energy ultraviolet rays and release the energy as lower-energy rays, thereby preventing the skin-damaging ultraviolet rays from reaching the skin. So, upon exposure to UV light, most of the ingredients (with the notable exception of avobenzone) do not undergo significant chemical change, allowing these ingredients to retain the UV-absorbing potency without significant photodegradation. A chemical stabilizer is
- 6. Mohammad Asim +919953194659 Page 6 of 9 included in some sunscreens containing avobenzone to slow its breakdown; examples include formulations containing Helioplex and AvoTriplex. The stability of avobenzone can also be improved by bemotrizinol, octocrylene and various other photostabilisers. Most organic compounds in sunscreens slowly degrade and become less effective over the course of several years if stored properly, resulting in the expiration dates calculated for the product. Sunscreening agents are used in some hair care products such as shampoos, conditioners and styling agents to protect against protein degradation and color loss. Currently, benzophenone-4 and ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate are the two sunscreens most commonly used in hair products. The common sunscreens used on skin are rarely used for hair products due to their texture and weight effects. Mechanism of action UV radiation may be blocked either by absorption or reflection/scattering of UV light. Based on their mechanism of protective action, sun-blocking agents are broadly divided into physical and chemical. Physical blockers are usually finely powdered and dispersed minerals, the most common being zinc oxide and titanium dioxide. They block UV radiation mainly by reflecting/scattering the rays. They are insoluble under typical conditions and only minimally absorbed into the skin. As a result, they are easy to rub off and may need to be reapplied especially frequently. Also, when applied to the skin, both zinc oxide and titanium dioxide create white-tinted matte look. To reduce this unsightly effect, some manufacturers employ microfine zinc oxide and/or titanium dioxide with particles smaller than 200 nm (a.k.a. nanoparticles). Such formulations are more transparent but raise concerns about possible penetration of nanoparticles into the skin and accumulation in vital body tissues. Chemical sunblocks work mainly by absorbing UV light. Most are synthetic chemicals that are soluble in oil and/or water. Many are absorbed into the skin and, possibly, into systemic circulation (and, therefore, need a thorough safety testing). Some degrade when exposed to UV radiation and/or interact with other sun-blocking agents or other cosmetic ingredients. There are a few agents that act as both physical and chemical sunblocks. One such hybrid sunblock is bisoctrizole (Tinosorb M). Even though titanium dioxide is typically considered a physical sunblock, some experts consider it a hybrid because considerable part of its activity is through UV absorption. Overall, physical sunblocks tend to have broader spectrum of UV protection and appear somewhat safer due to the lack of systemic absorption. On the other hand, they are unsightly (especially the safer, not-microfine versions) and require more frequent application. Organic sunscreens are aromatic compounds that absorb light energy in the UV region, and therefore reduce the amount of UVR reaching the stratum corneum. A benzene ring has the ability to transform high energy UVR into harmless long wave radiation above the 380-nm range, which
- 7. Mohammad Asim +919953194659 Page 7 of 9 is emitted from the skin as heat (294). The conversion of UVR to longer wavelength occurs through resonance delocalization. Most chemical sunscreens absorb up to 95% of the UVB spectrum, but do not absorb in the UVA range. Ultra-Violet radiations and human skin Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is defined as that portion of the electromagnetic radiation lies between X-rays and visible light which is from 200 to 400 nm. This ultraviolet radiation comprises 3 categories depending on wavelength as follows: UV-A Radiation: This radiation ranges between 320 to 400 nm. UV-A is most responsible radiation for immediate tanning or darkening of the skin due to excess production of melanin in the epidermis, premature photo ageing, suppression of immunologic functions, and even necrosis of endothelial cells and damage of dermal blood vessels. UV-B Radiation: This radiation ranges between 280 to 320 nm. UV-B radiations are known as burning rays as they are 1000 times more capable of causing sunburn than UV-A. UV- B rays act mainly on the epidermal basal cell layer of the skin but more genotoxic than UV-A radiations. Ultraviolet B (UVB) rays vary with time and season are major cause of sunburn. Sunburned skin is a leading risk factor for melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer. UV-C Radiation: This radiation ranges between 200 to 280 nm. UV-C radiations are filtered by stratospheric ozone layers so less effective and hazardous. The human skin is the largest organ of the body of surface area of approximately 1.5–2.0 m2. Skin acts as effective barrier against the harmful effects of environmental and xenobiotic agents. Among all factor chronic exposure of UV radiations is key factor in instigation of skin problems like cracks, burns, immune suppression, wrinkles, dermatitis, urticaria, ageing, hypopigmentation, hyperpigmentation and most complicated skin cancers. Role of infrared radiations in skin damage is unclear. SPF value The SPF has been defined as ratio between the UV exposure required to produce a minimally perceptible erythema on protected skin & the exposure that will produce the erythema on unprotected skin. The larger the SPF, the greater the sun protection. The formal definition of SPF by the OTC Panel of the US FDA was SPF value: MED (PS) / MED (US) PS: minimum erythemal dose for protected skin after the application of 2mg/cm² of the final formulation of the sunscreen product. US: minimum erythemal dose for unprotected skin i.e. Skin to which no sunscreen product has been applied. Skin type & choice of sunscreen
- 8. Mohammad Asim +919953194659 Page 8 of 9 US FDA classification system for sunscreen product comprises of five product category designation (PCD) to meet requirement of consumers with different type of skin. Depending upon skin type & tanning history they are classified into six groups: a. Always burns easily & never tan (i.e. Sensitive) b. always burns & tan minimally c. burns moderately & tan gradually to a shade of light brown (i.e. Normal) d. burn minimally & always tans well (i.e. Normal) e. barely burn & tans profusely skin become dark brown (i.e. Insensitive) f. never burn & skin become deeply pigmented For skin type mentioned above, sunscreening product with the following SPF are recommended: Skin type SPF I 8 or more II 6-7 III 4-5 IV 2-3 V 2 VI Not indicated Sunscreen Regulations US-FDA method: The FDA proposal measures in-vitro UV transmittance through a sunscreen film using the critical wavelength method. Sunscreen products offering primarily UVB protection would have a critical wavelength less than 320 nm, whereas those providing both UVB and UVA protection would have critical wavelengths between 320 and 400 nm. FDA requires that sunscreen products have a critical wavelength of at least 370 nm (the mean value must be equal to or greater than 370 nm) to be labeled as providing “broad spectrum” UVA and UVB protection. UK method of boot star rating: The UK method, called as Boots star rating system, also measures the UV transmittance through a sunscreen film. The substrate for measurement is abraded PMMA plates. The ratio between the mean UVA and UVB absorbance measured before and after irradiation of the sunscreen products is calculated. Australia: Australian standard (AS) method uses spectrophotometer for measurements of the solar radiation transmitted by a sunscreen product to yield a percentage of UVA radiation absorbed by the product. According to this test, a product is designated as a long wave protector only if it transmits less than 10% of the incoming UV radiation between 320 and 360 nm. India: Indian being Asian population comes under Type–IV skin pattern which burns minimally and tans easily. Freckles are rare but still use of sunscreen is necessary to avoid tan. Indian regulations date from the Indian Drug and Cosmetic Act (1940) as amended from time to time
- 9. Mohammad Asim +919953194659 Page 9 of 9 considers sunscreens as cosmetics. Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), a participating member of the ISO, sets the relevant cosmetic product standards. Key points are stability data is (similar to Australia) must and there is no maximum SPF rating for sunscreens.