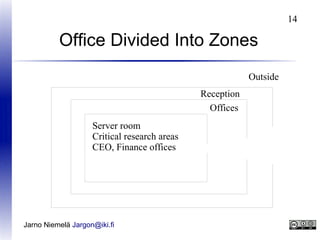
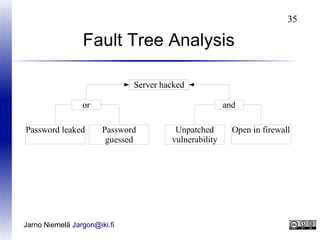
This document discusses corporate security and information security best practices for employees and buildings. It covers topics like employee screening and training, building access controls, alarms, fire safety, and document security. The goal is to protect corporate assets like people, equipment, and information by identifying security risks and managing them through prevention, detection, and response measures. Regular risk assessments are recommended to understand threats and how to cost-effectively limit damage from realized risks. Overall it promotes a comprehensive security program involving people, processes, and technology.