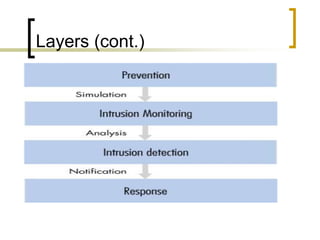
This document discusses physical security, which involves protecting personnel, hardware, programs, networks, and data from physical threats. It defines physical security and explains why it is important. The document outlines the key components of physical security, including accidental/environmental protection, monitoring systems, and recovery mechanisms. It also describes the layered approach to physical security, including environment design, access control, monitoring systems, and intrusion detection. Additional topics covered include physical security briefs, zoning of restricted areas, and implementation of a physical security plan.