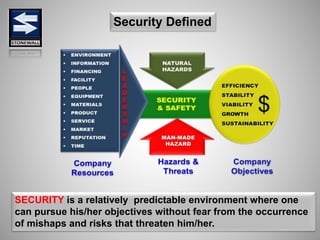
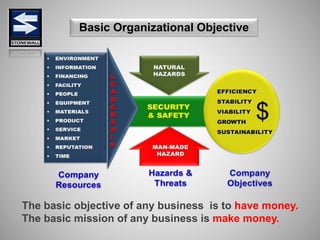
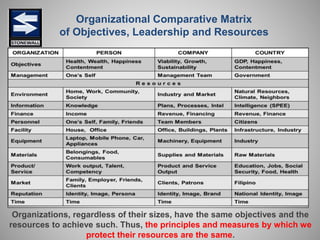
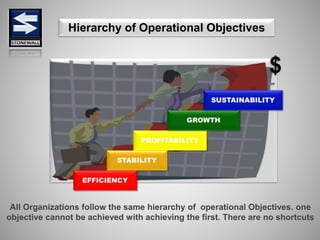
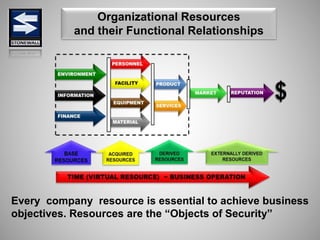
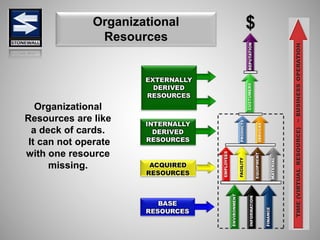
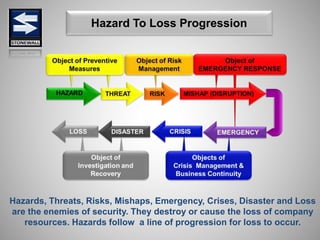
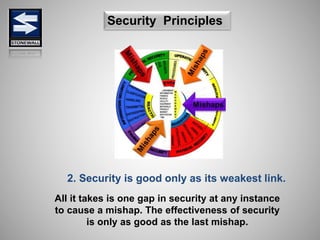
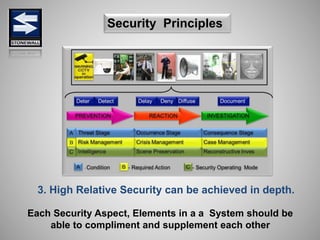
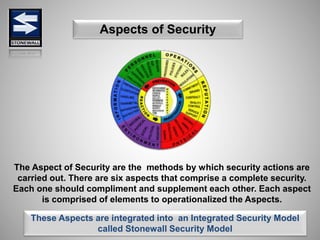
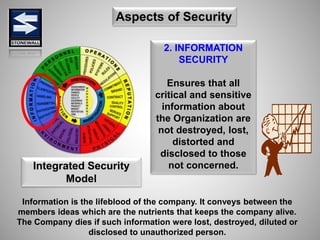
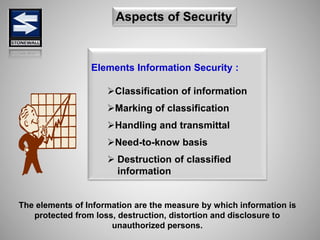
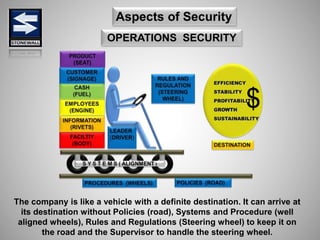
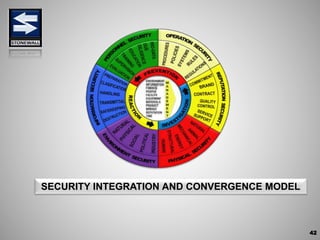
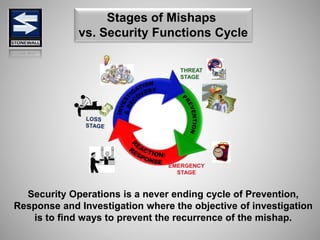
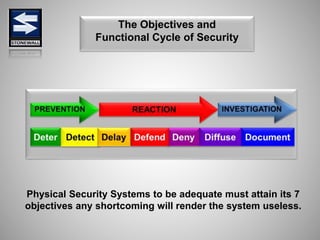
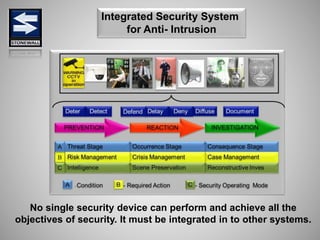
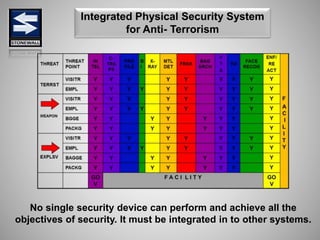
The document is a comprehensive presentation on basic security concepts developed by Joel Jesus M. Supan, focusing on organizational security culture and principles. It covers the definition of security, client objectives, hazards threatening companies, and the integration of security systems to protect resources. Key security principles emphasize that no system is foolproof and that security must involve all employees while addressing various internal and external threats.