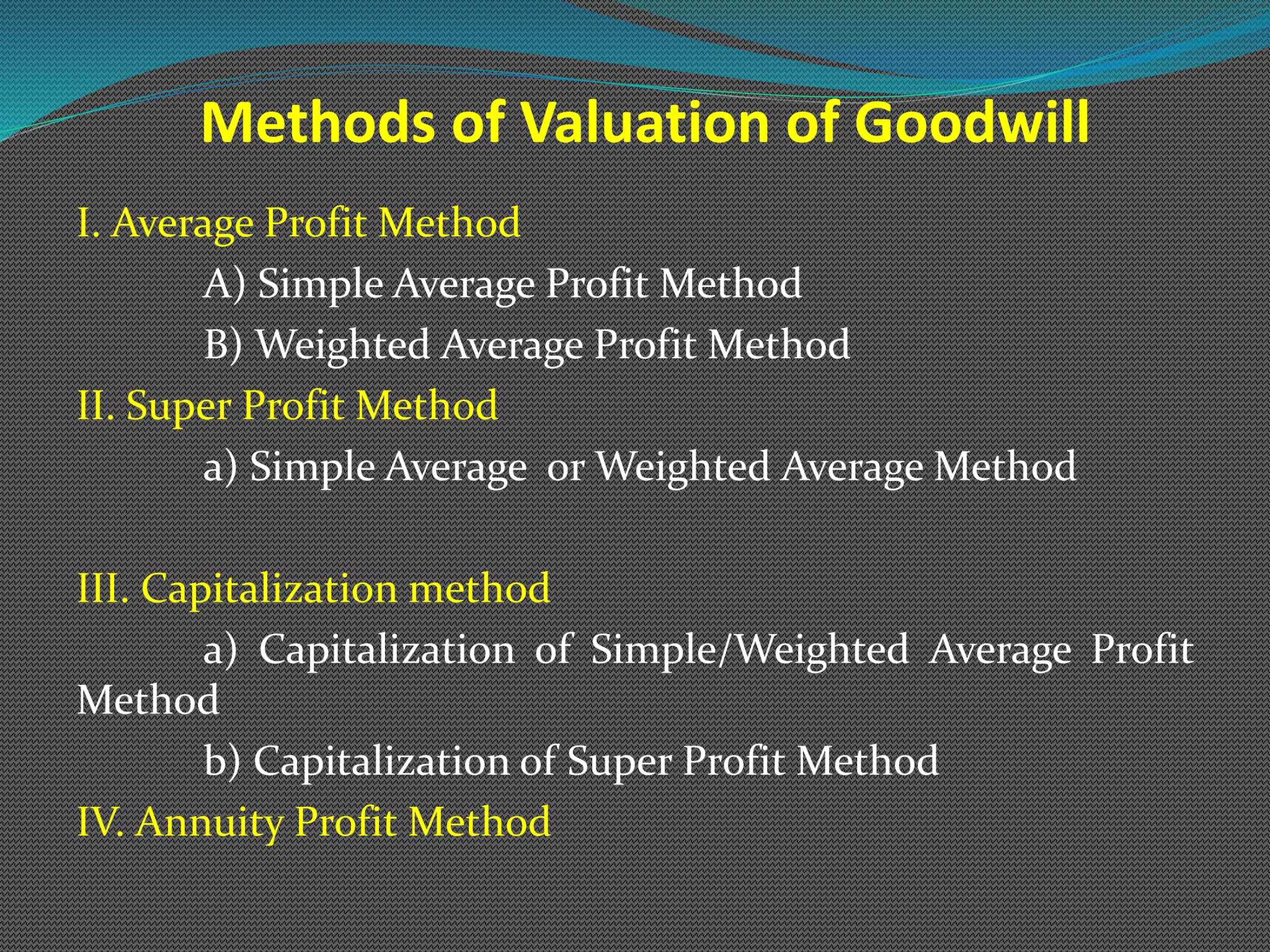
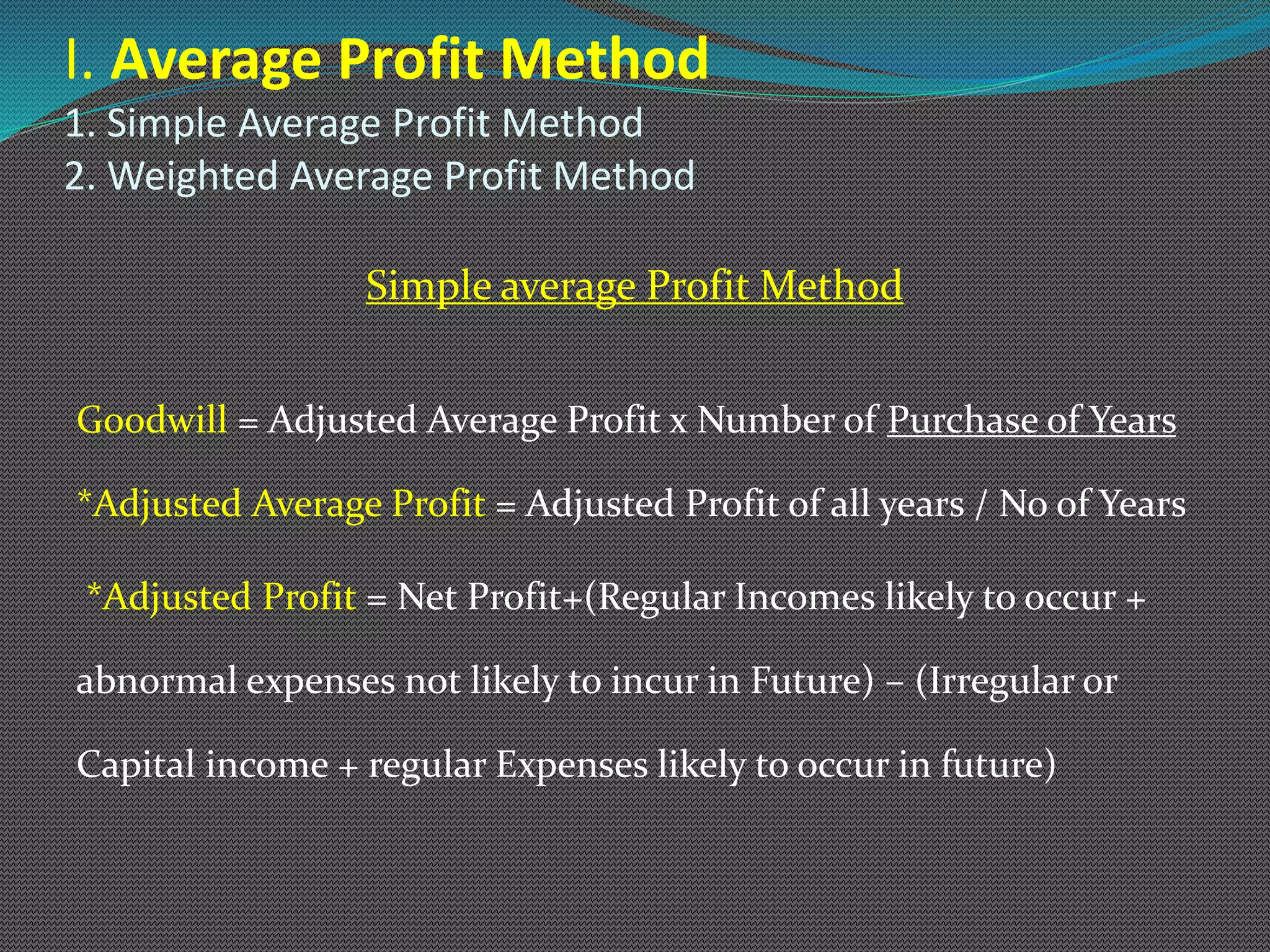
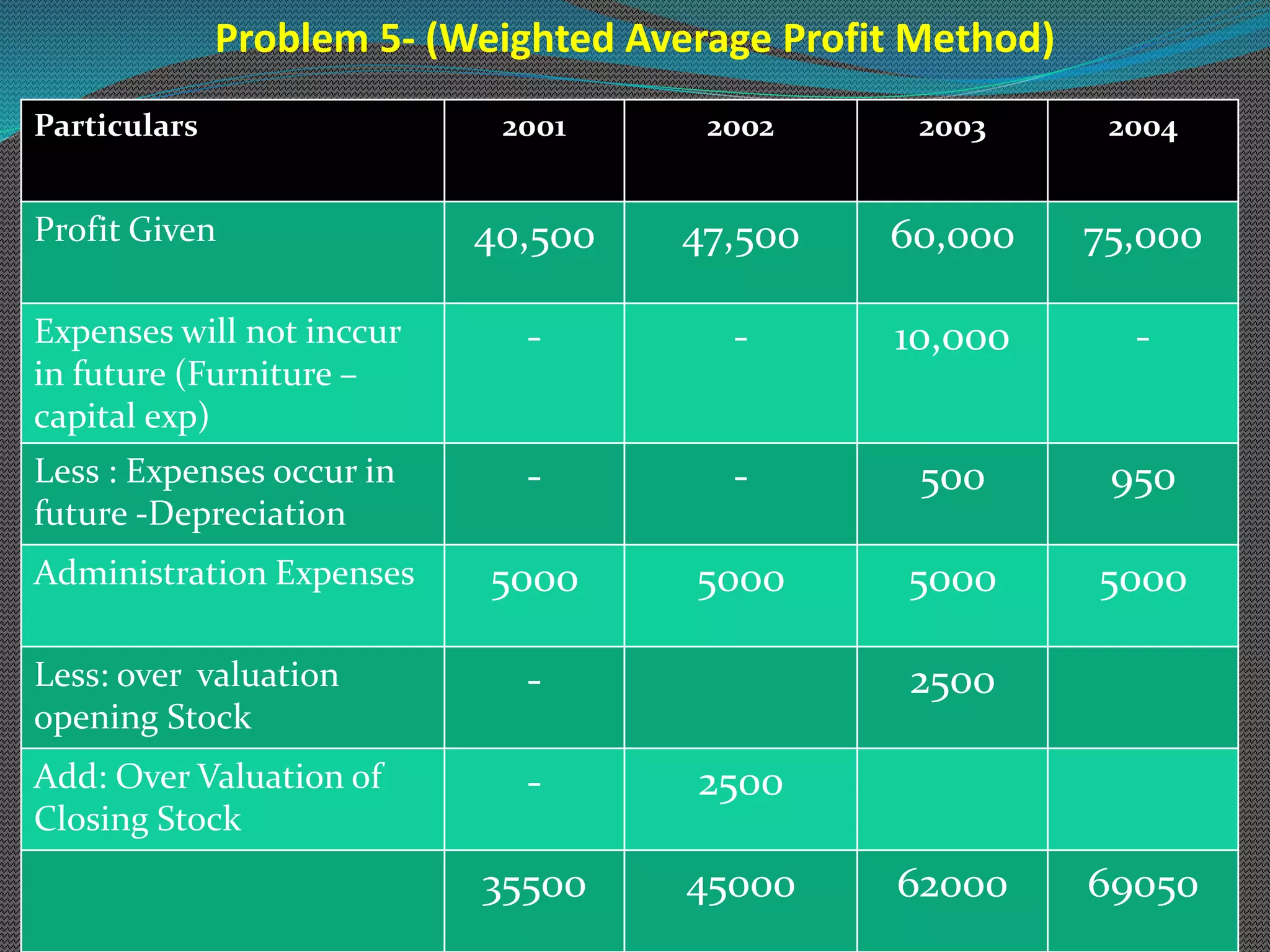
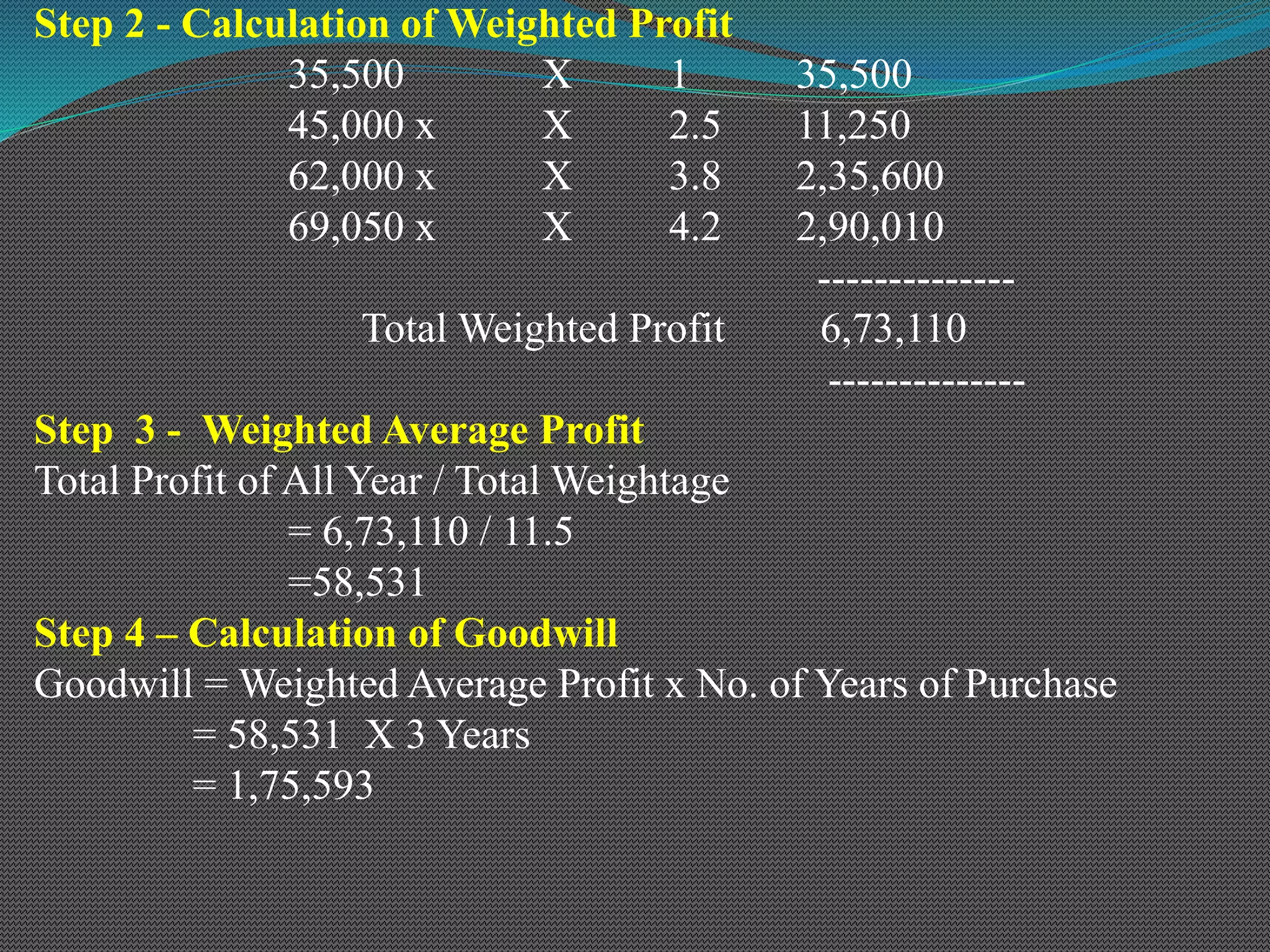
The document discusses various methods of valuing goodwill, including the average profit method, super profit method, and capitalization method. Under the average profit method, goodwill is calculated as the adjusted average profit multiplied by the number of years of purchase. The super profit method calculates goodwill as the super profit (adjusted average profit less normal profit) multiplied by the number of years of purchase. Worked examples are provided to illustrate calculating goodwill under both the simple average method and weighted average method for the average profit and super profit approaches.