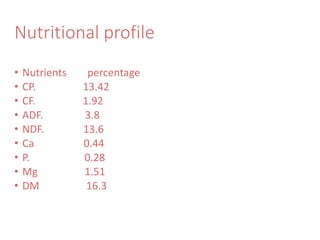
Corn is a popular grain used in animal feed worldwide. It provides good energy from its starch content but is low in protein. Corn can be included in ruminant diets at high levels when paired with protein supplements. For poultry and fish, corn is commonly included at around 75% of the diet due to its digestible energy. While corn provides good nutrition, it also contains some antinutritional factors like mycotoxins that can cause health issues if contaminated corn is consumed. The price of corn is approximately Rs 50 per kg.