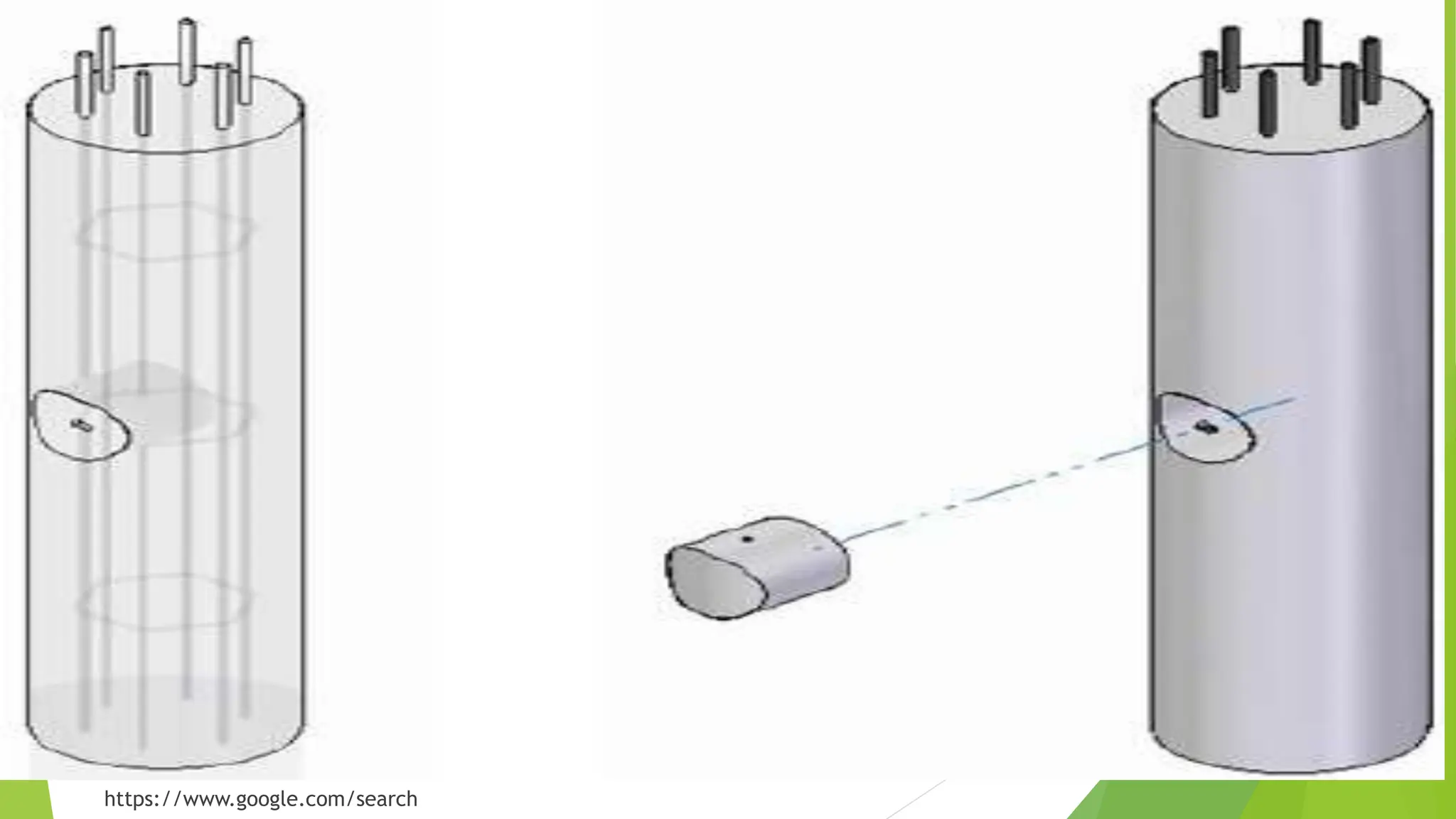
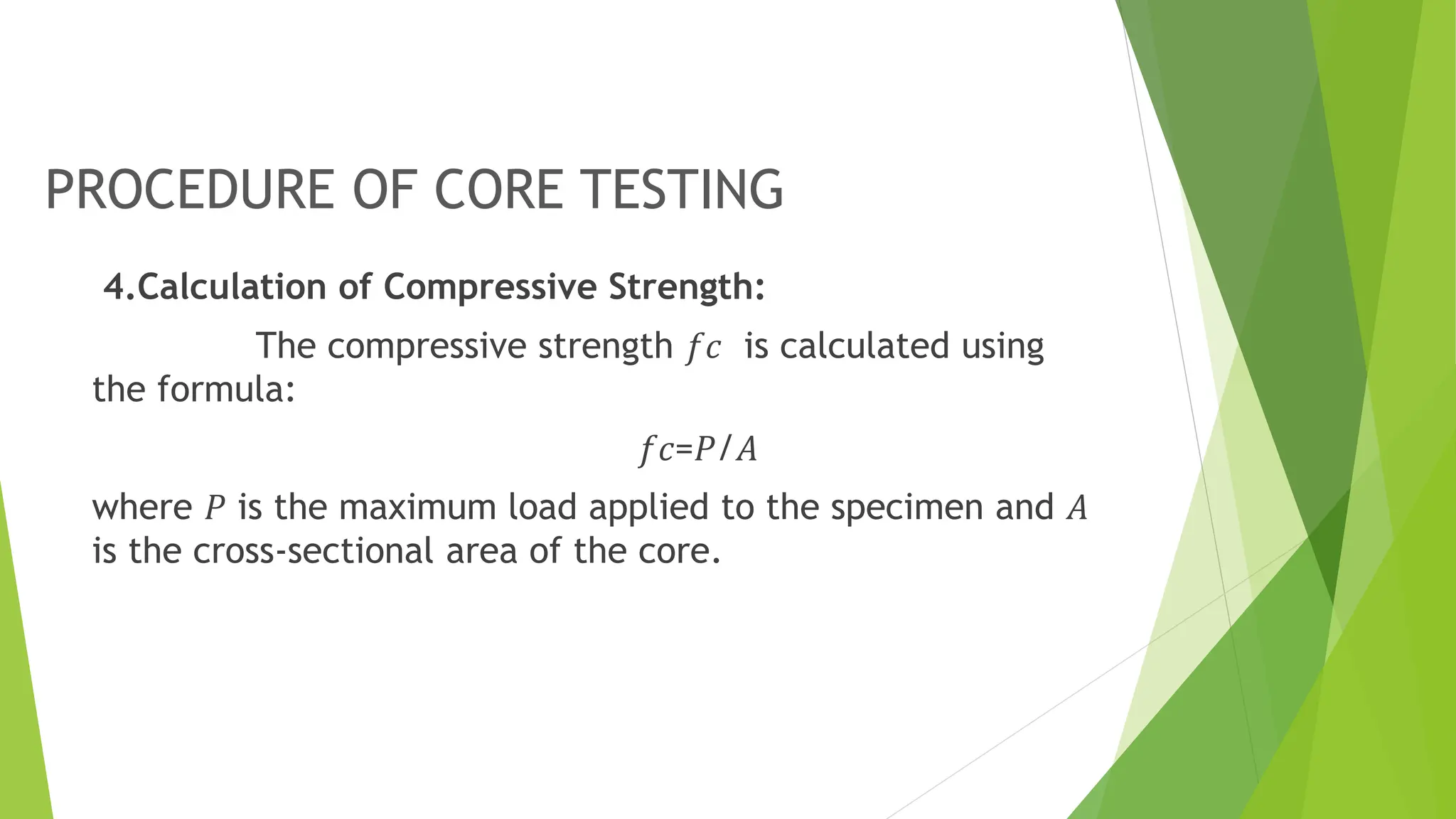
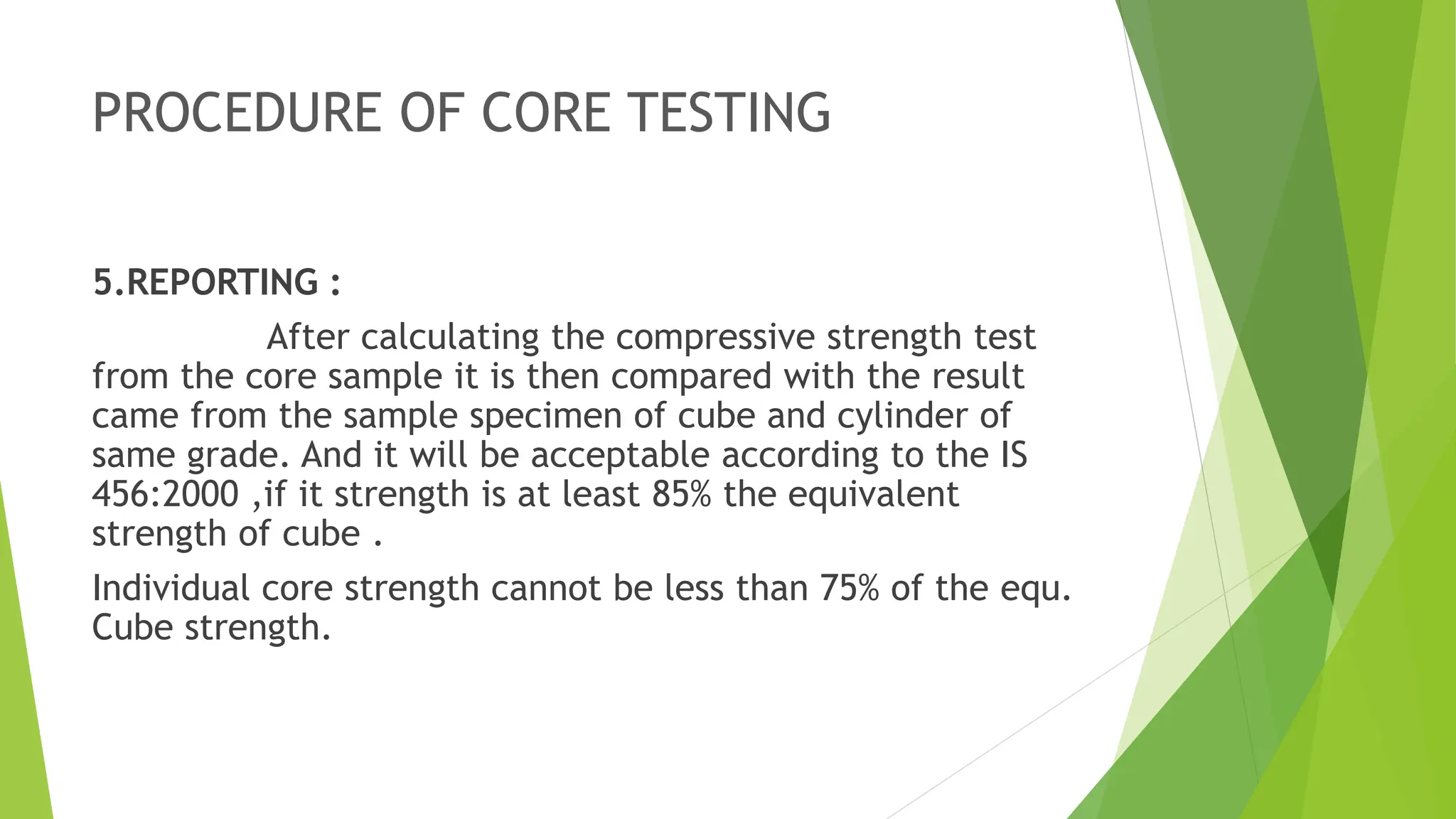
The core test of concrete is a procedure for evaluating the compressive strength and quality of hardened concrete by drilling cylindrical cores from the structure. This testing helps assess structural safety, quality, and thickness verification, along with investigating any distress in the concrete. Guidelines for core testing, including procedures and criteria for acceptable strength, are also outlined according to Indian standards IS 516:1959 and IS 456:2000.