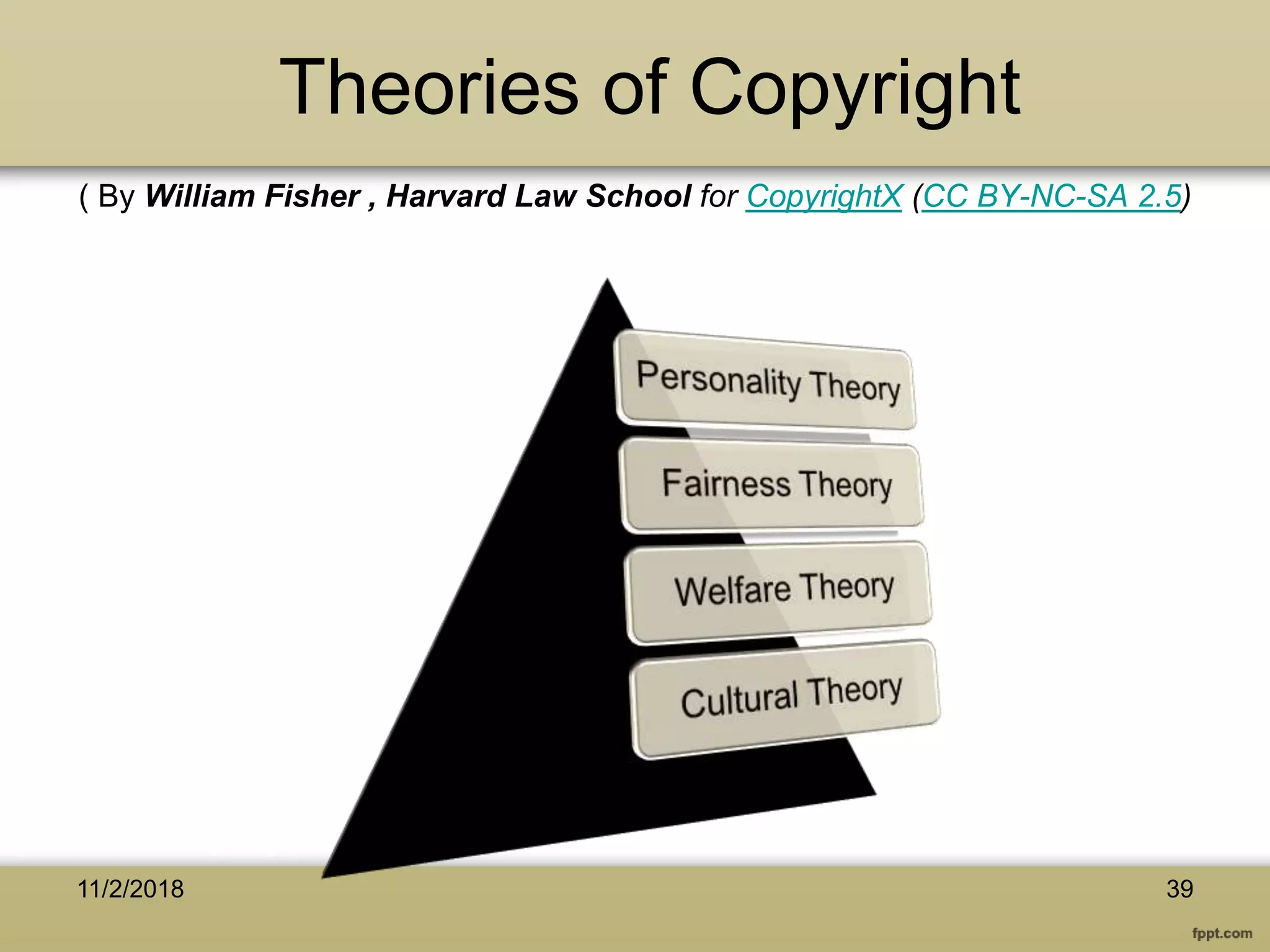
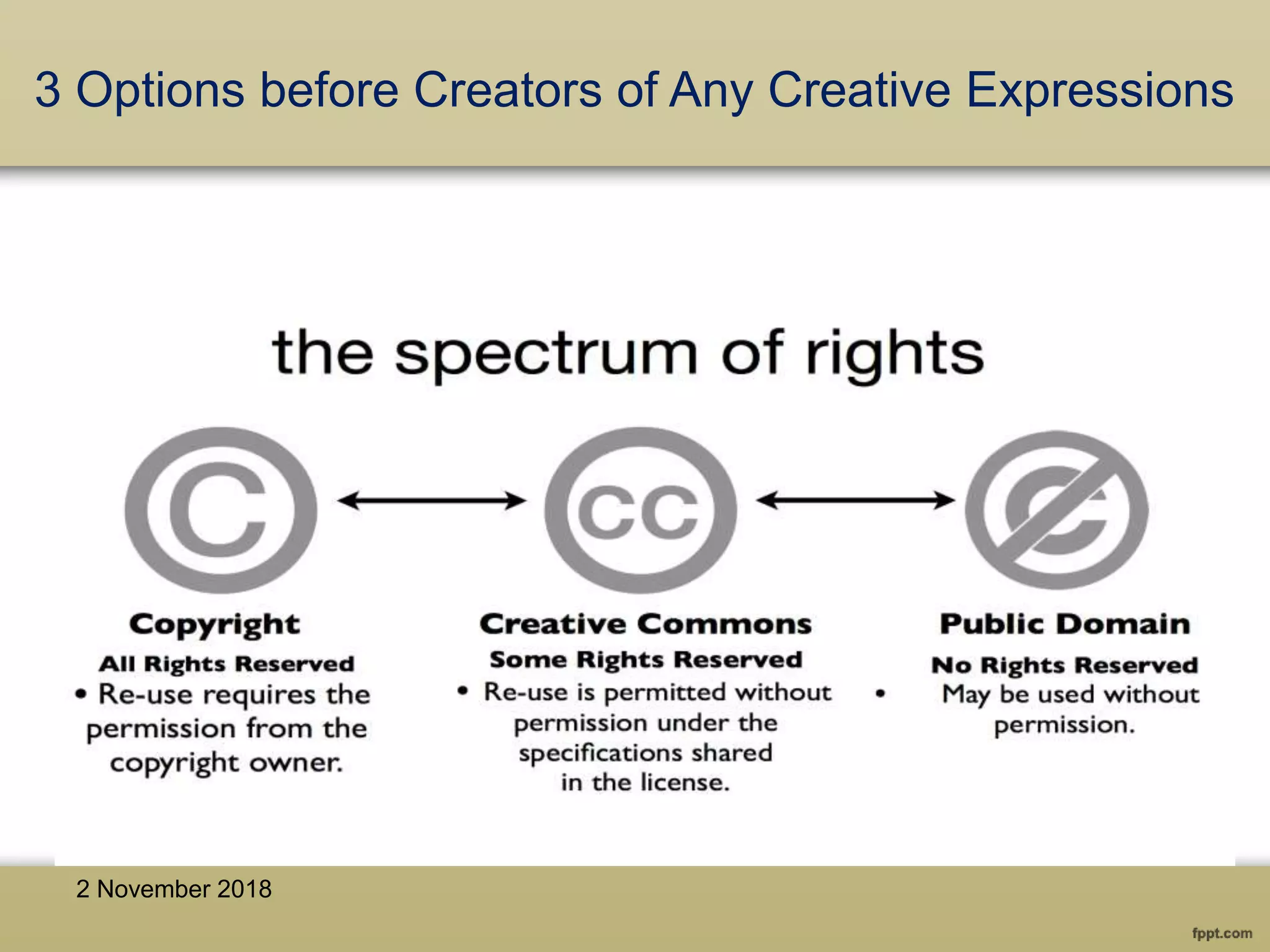
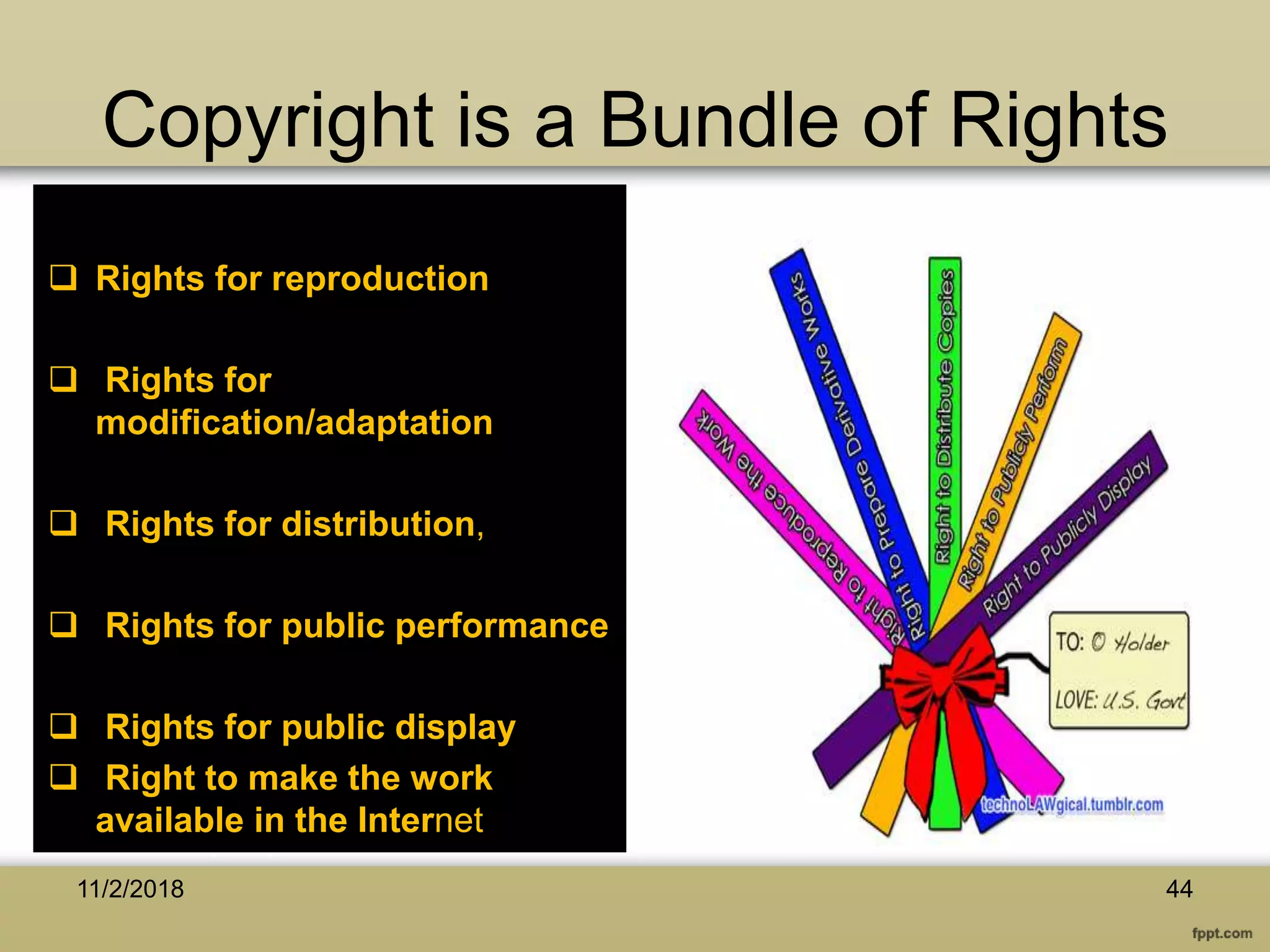
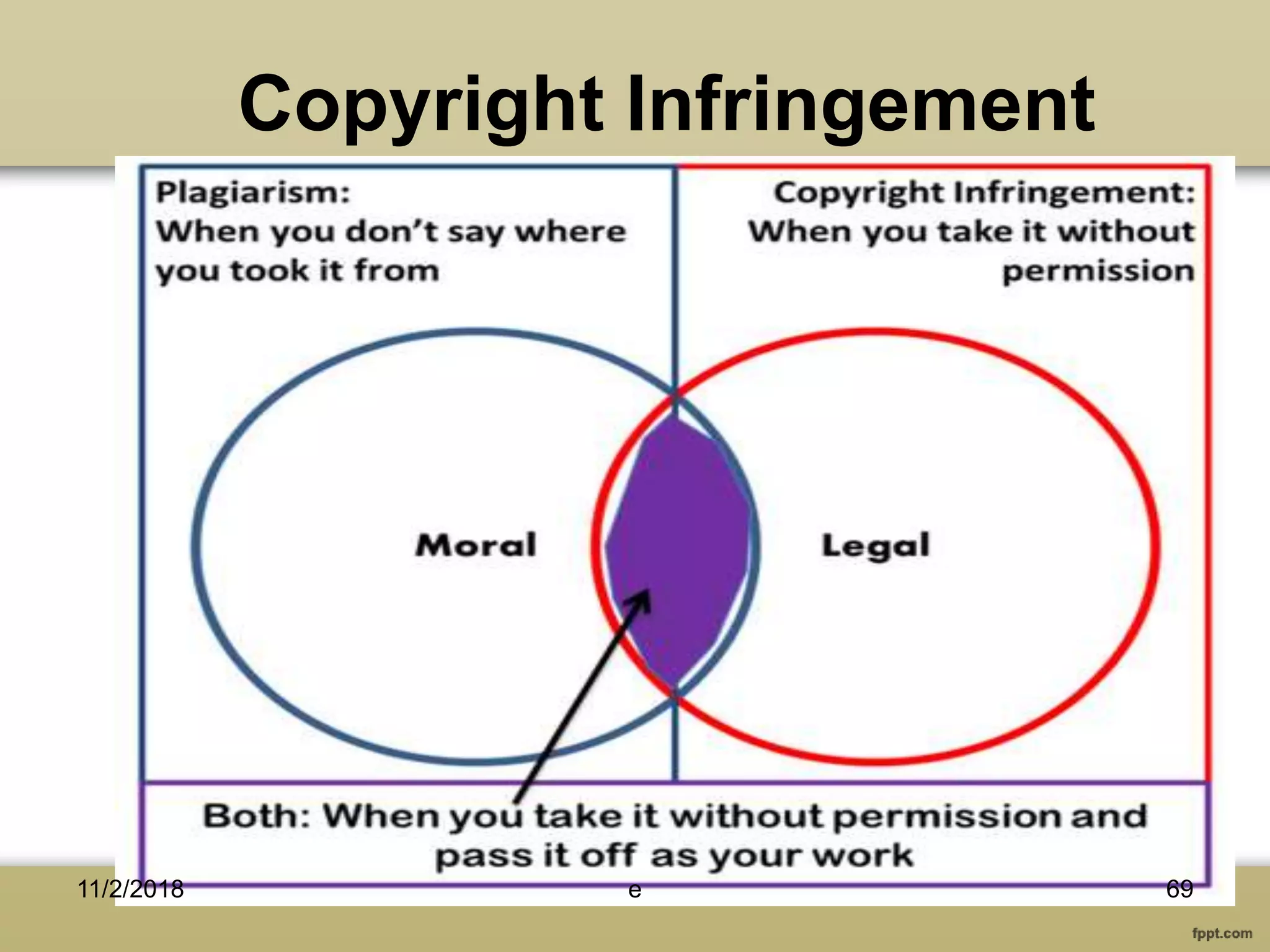
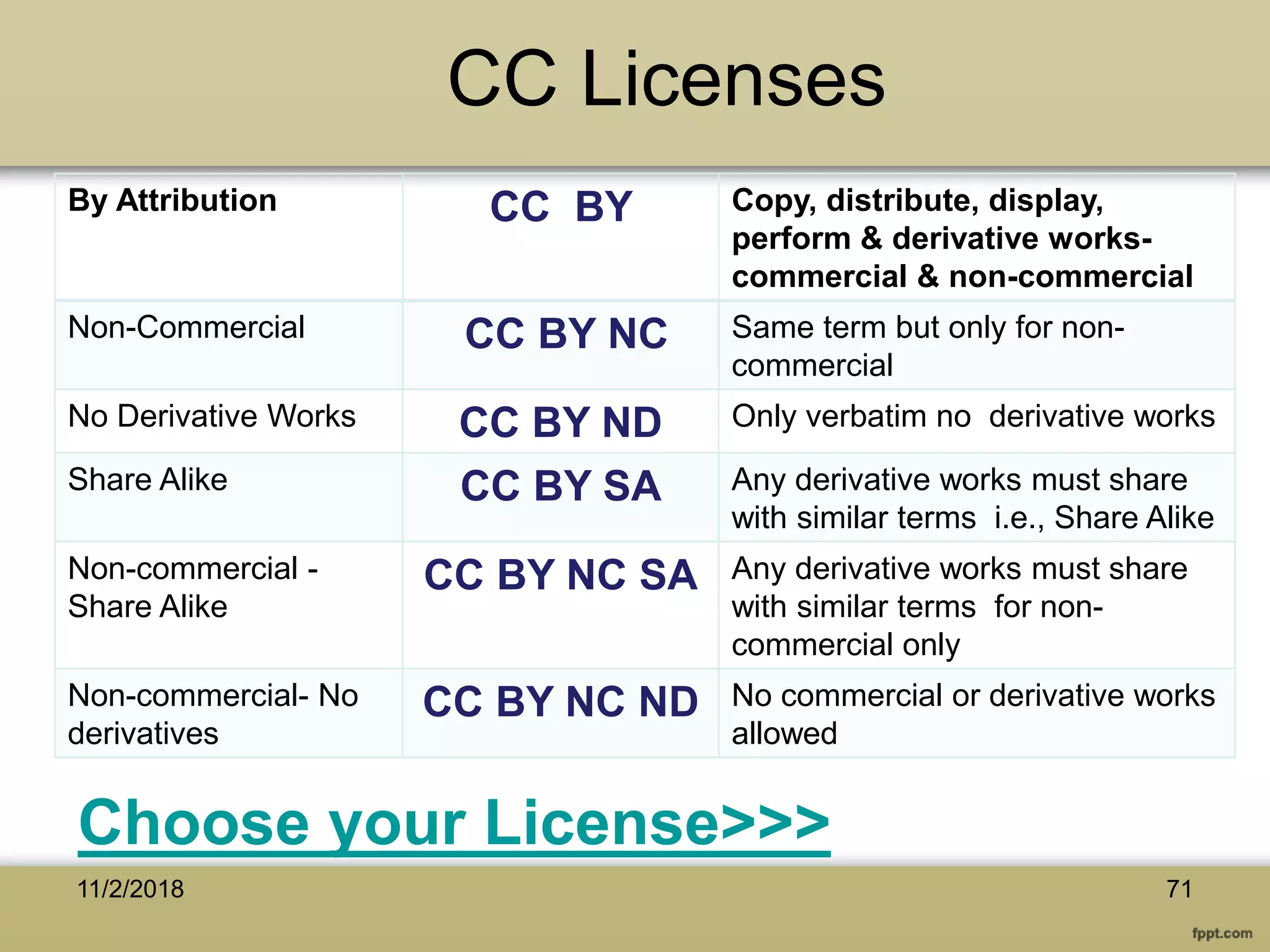
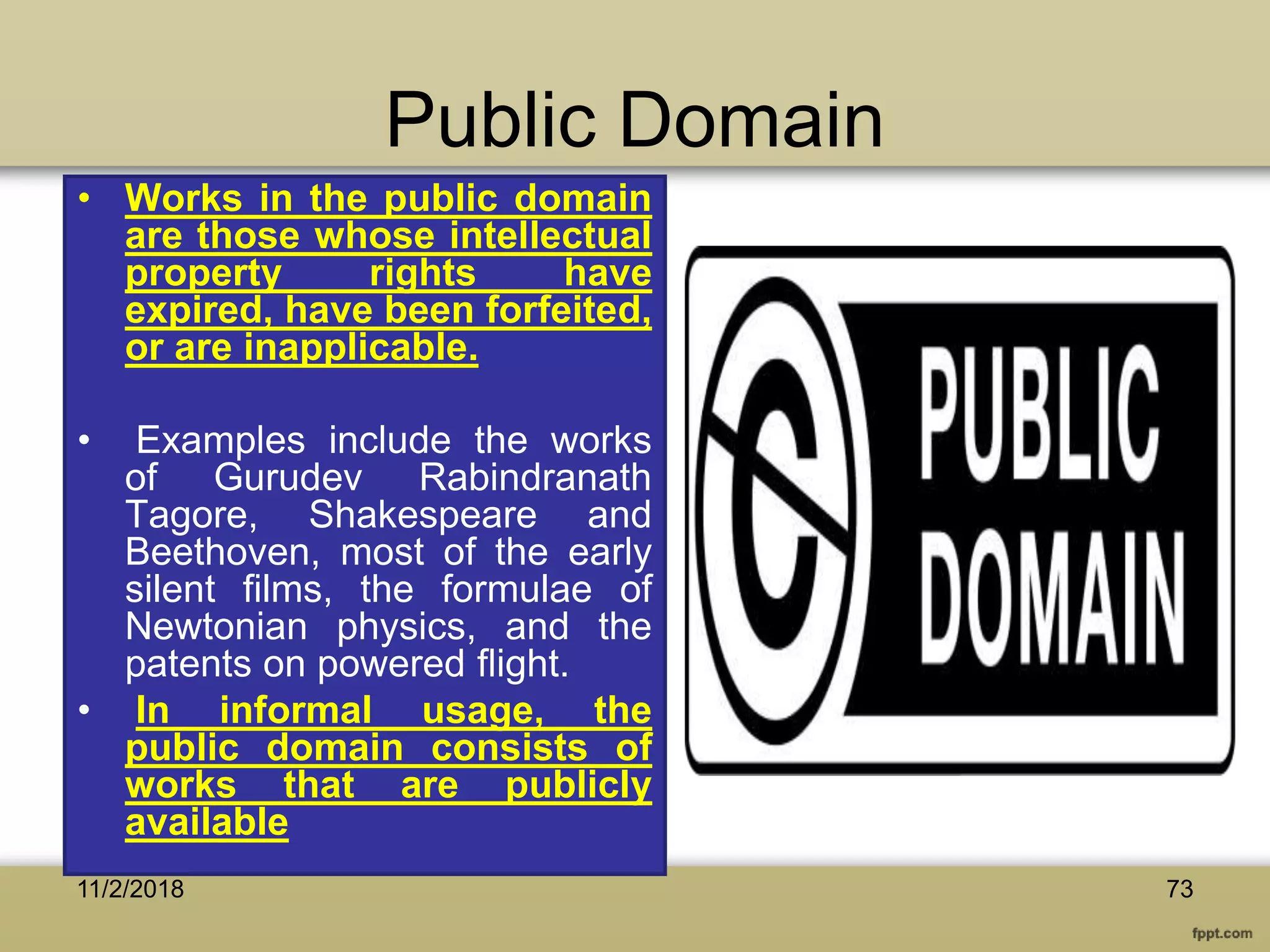
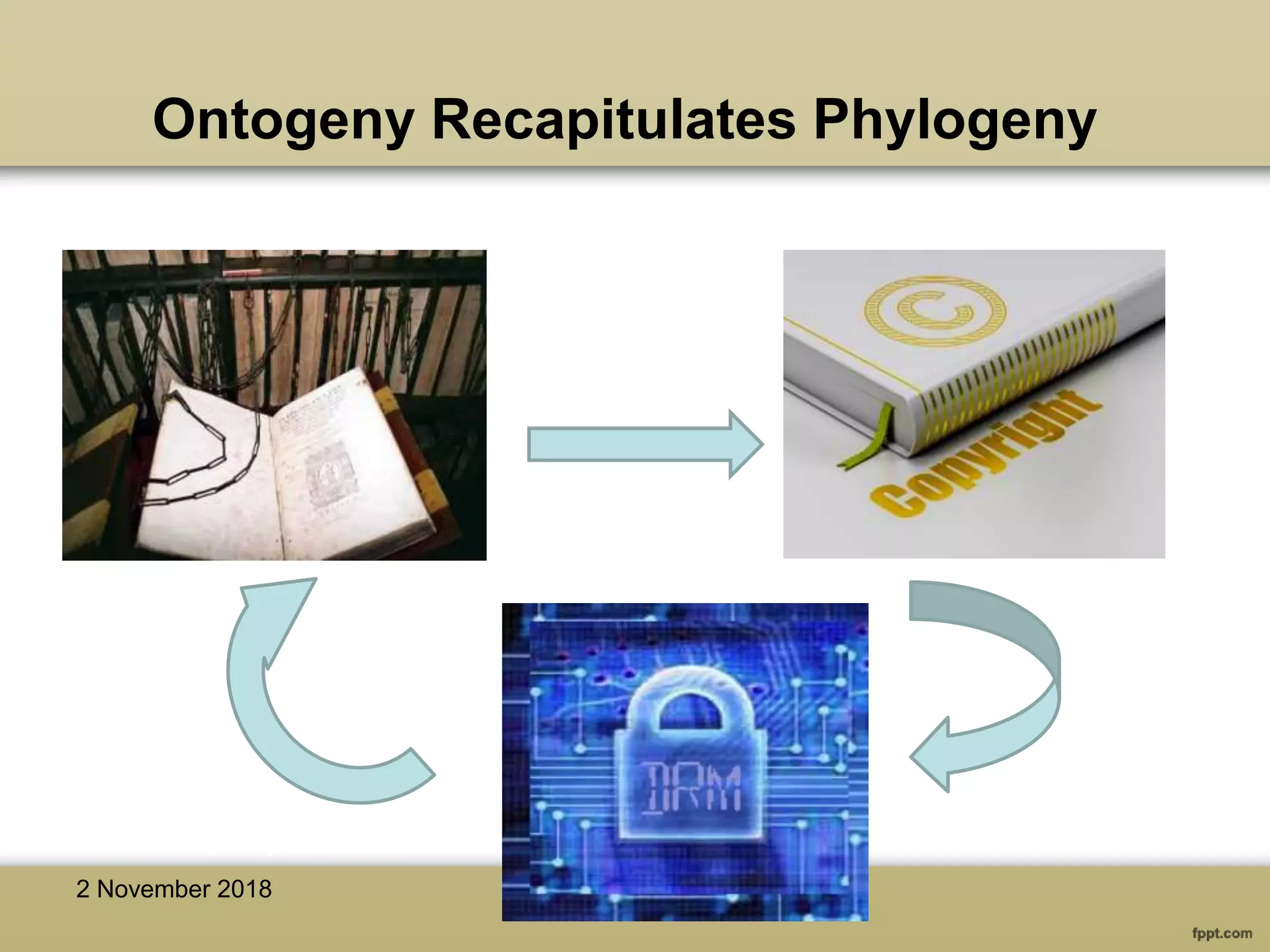
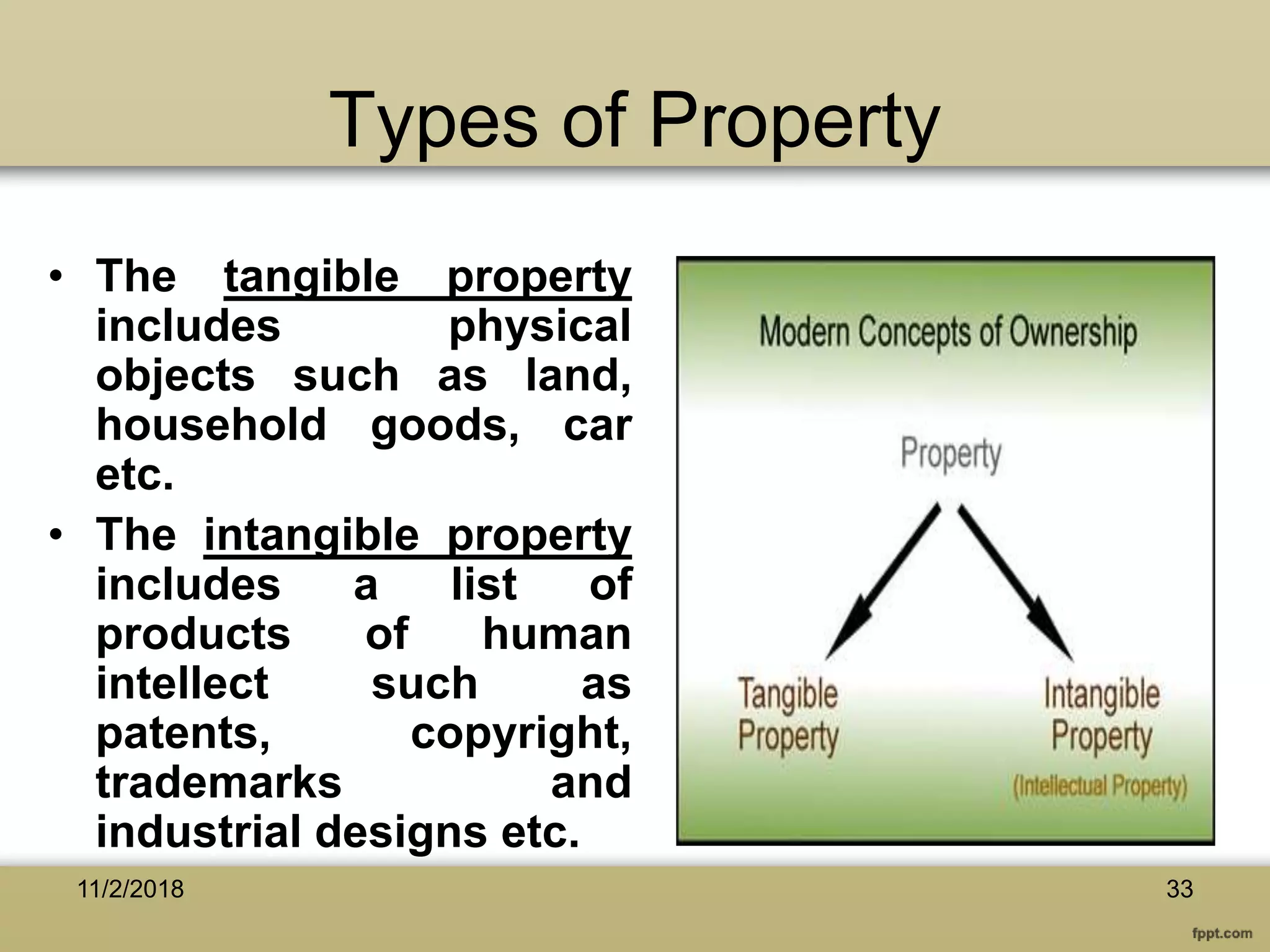
The document discusses various aspects of copyright law, particularly in the context of teaching and learning in the 21st century, emphasizing the challenges of fair use and copyright infringement in educational settings. It outlines the history of copyright, the rights conferred by copyright, and introduces key terminology related to intellectual property rights. Additionally, it touches on the issues surrounding plagiarism, the role of Creative Commons, and the distinction between copyright and public domain works.

























![First Copyright Law
• England's Statute of
Anne (1710) is widely
regarded as the first
modern copyright law
that for the first time
protected the rights of
authors rather than
publishers of books.
• Term of copyright
was 28 years [14 years
+ 14 years if the author
was still alive]
3711/2/2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lectureinaliahuniversity1-11-18-181102205042/75/Copyright-for-Teaching-Learning-in-the-21st-Century-37-2048.jpg)