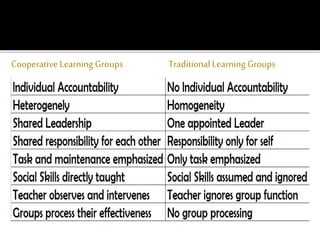
Cooperative learning involves organizing students into small groups so they can work together to maximize their own learning and each other's learning. It aims to provide academic and social learning experiences. Key aspects of cooperative learning include positive interdependence, individual accountability, promotive interaction, developing social skills, and group processing. Structuring learning activities in this way has benefits like increased understanding, memory, and positive self-image for students.