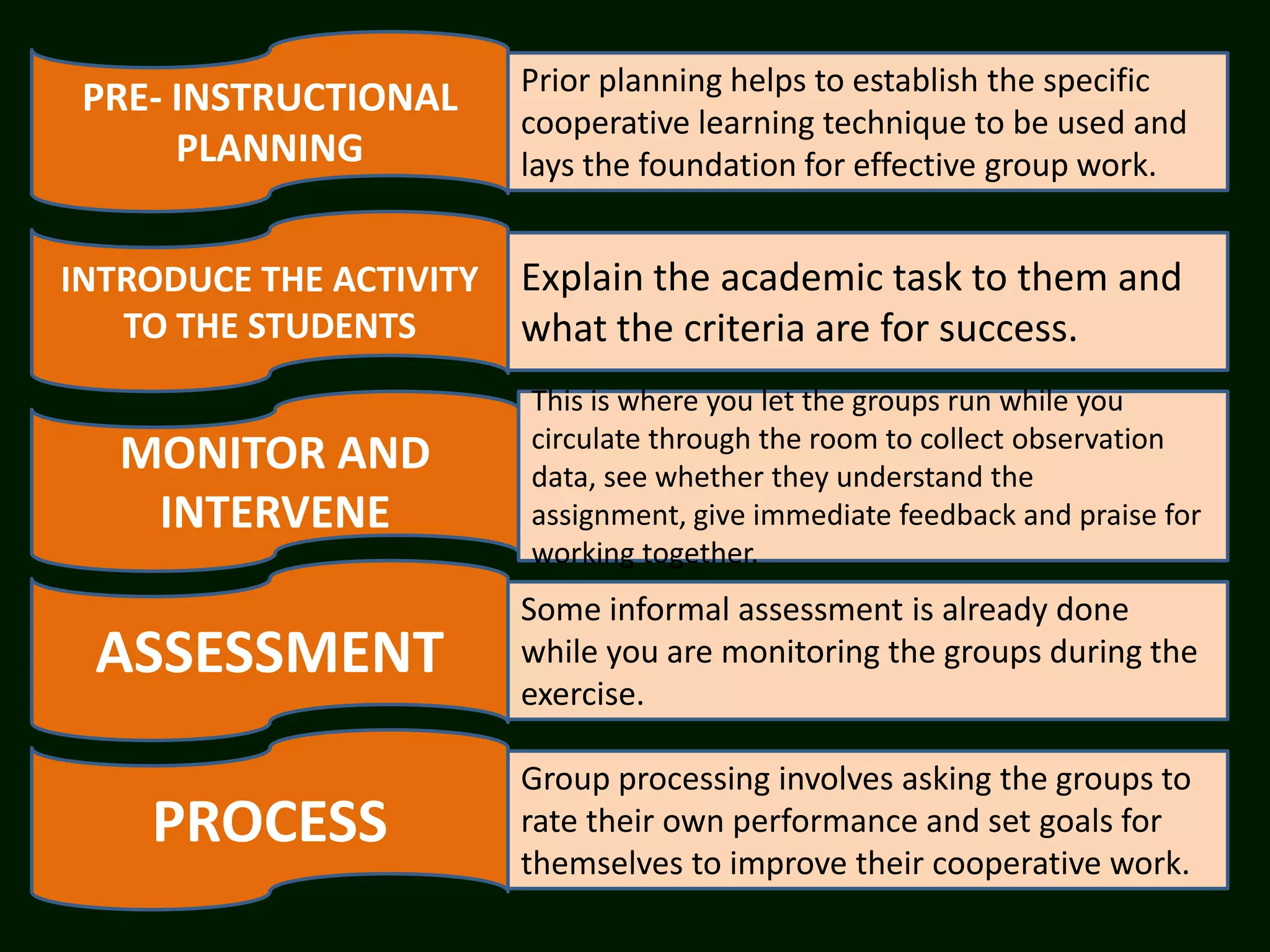
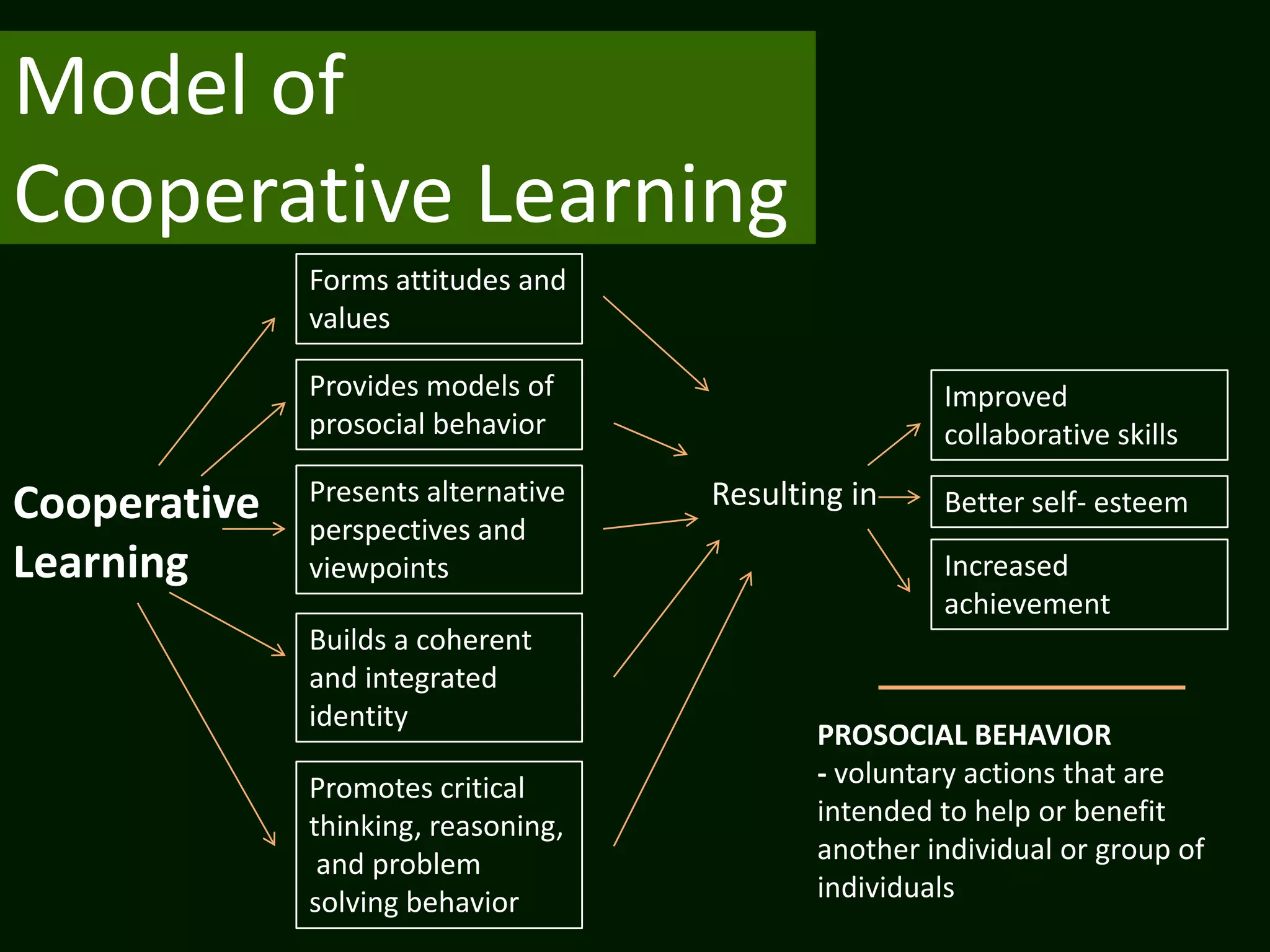
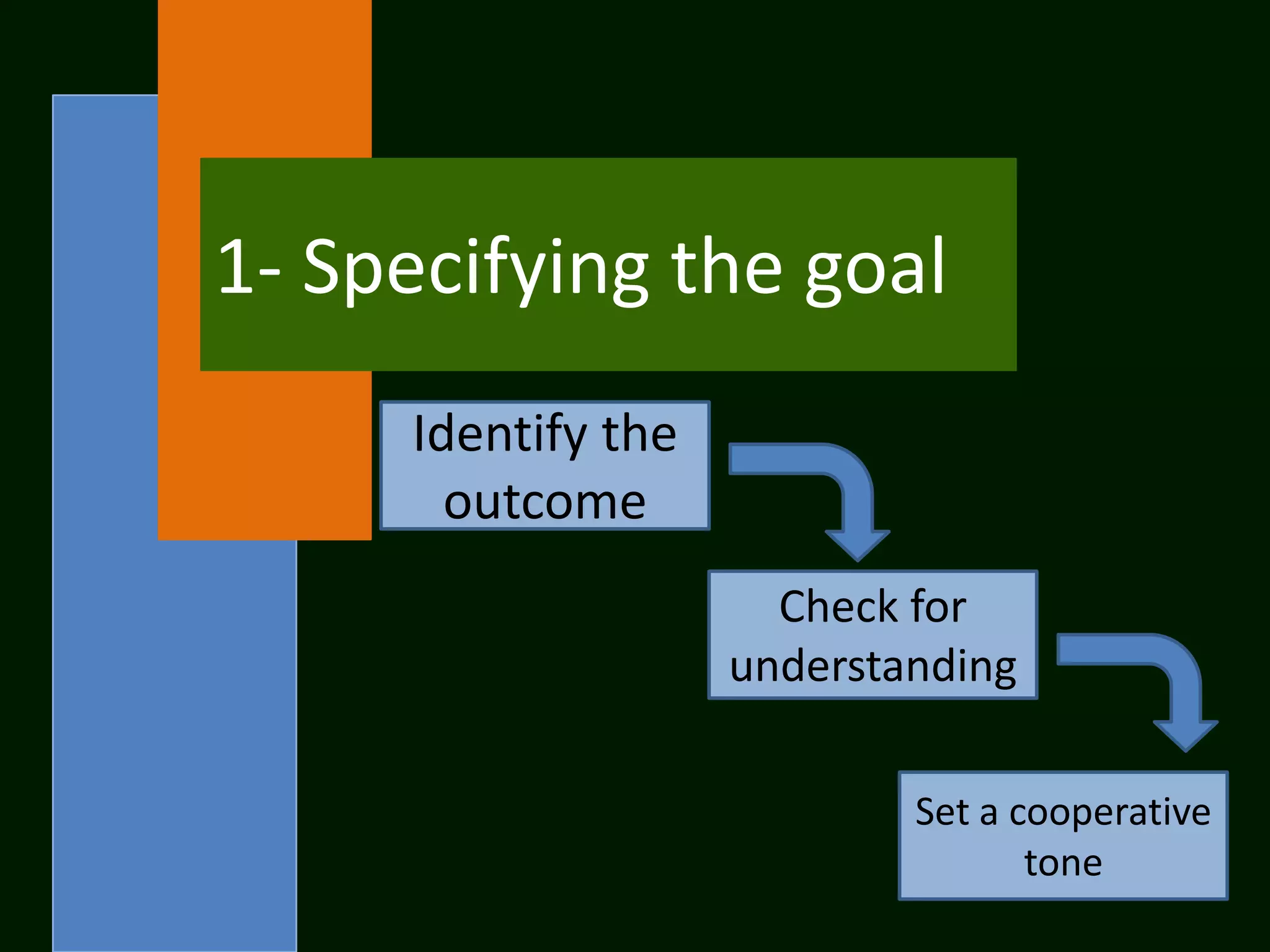
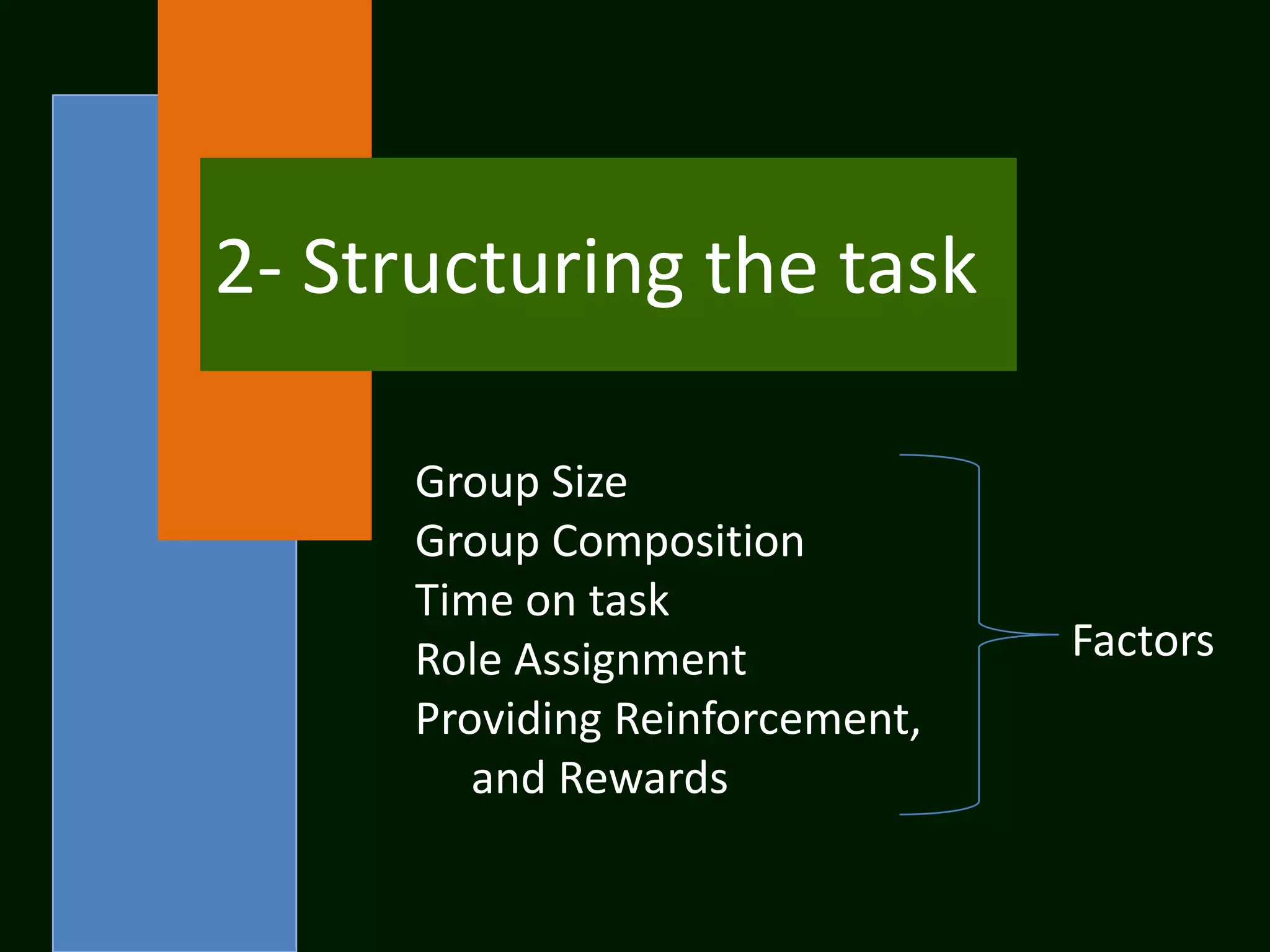
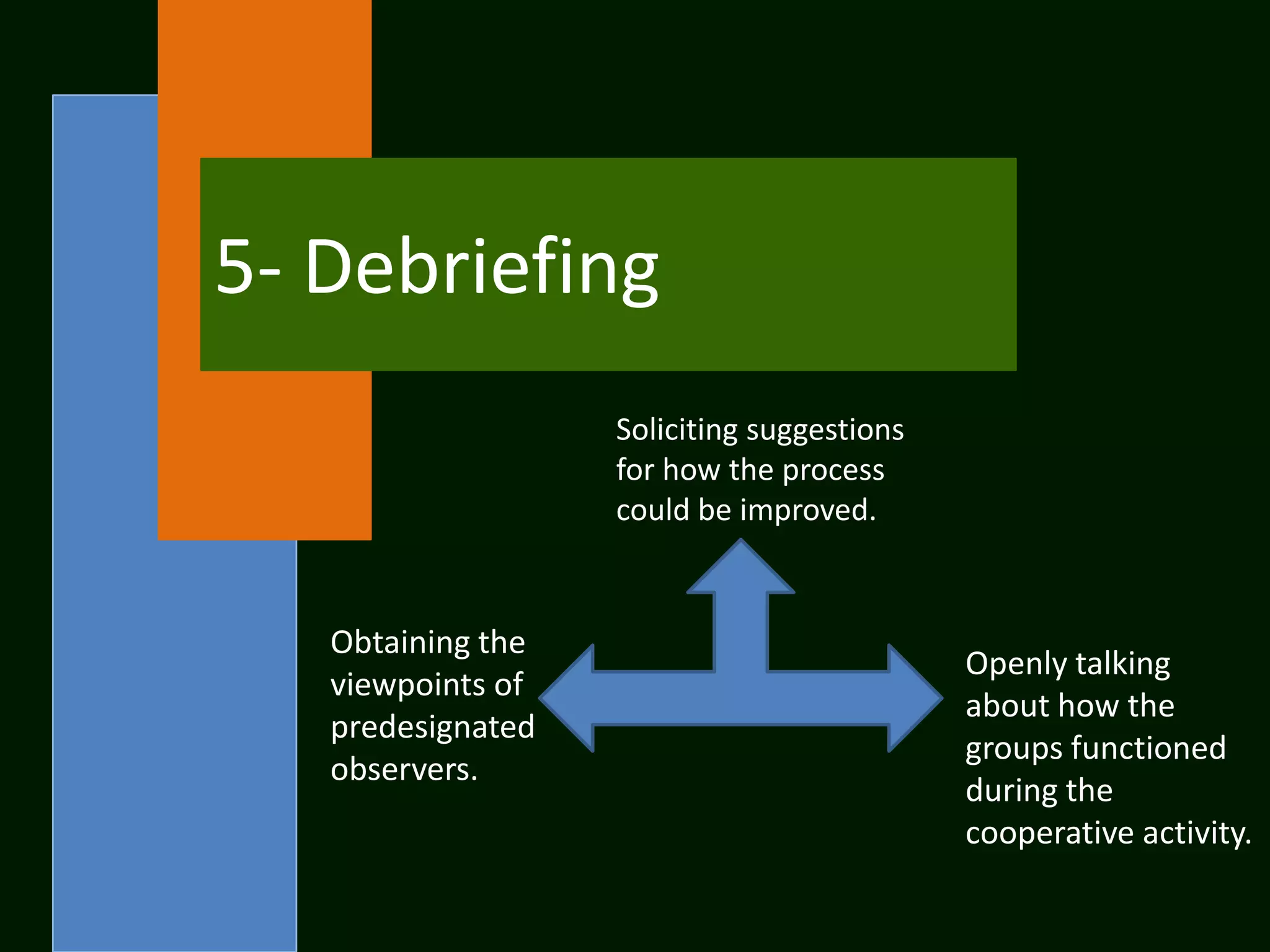
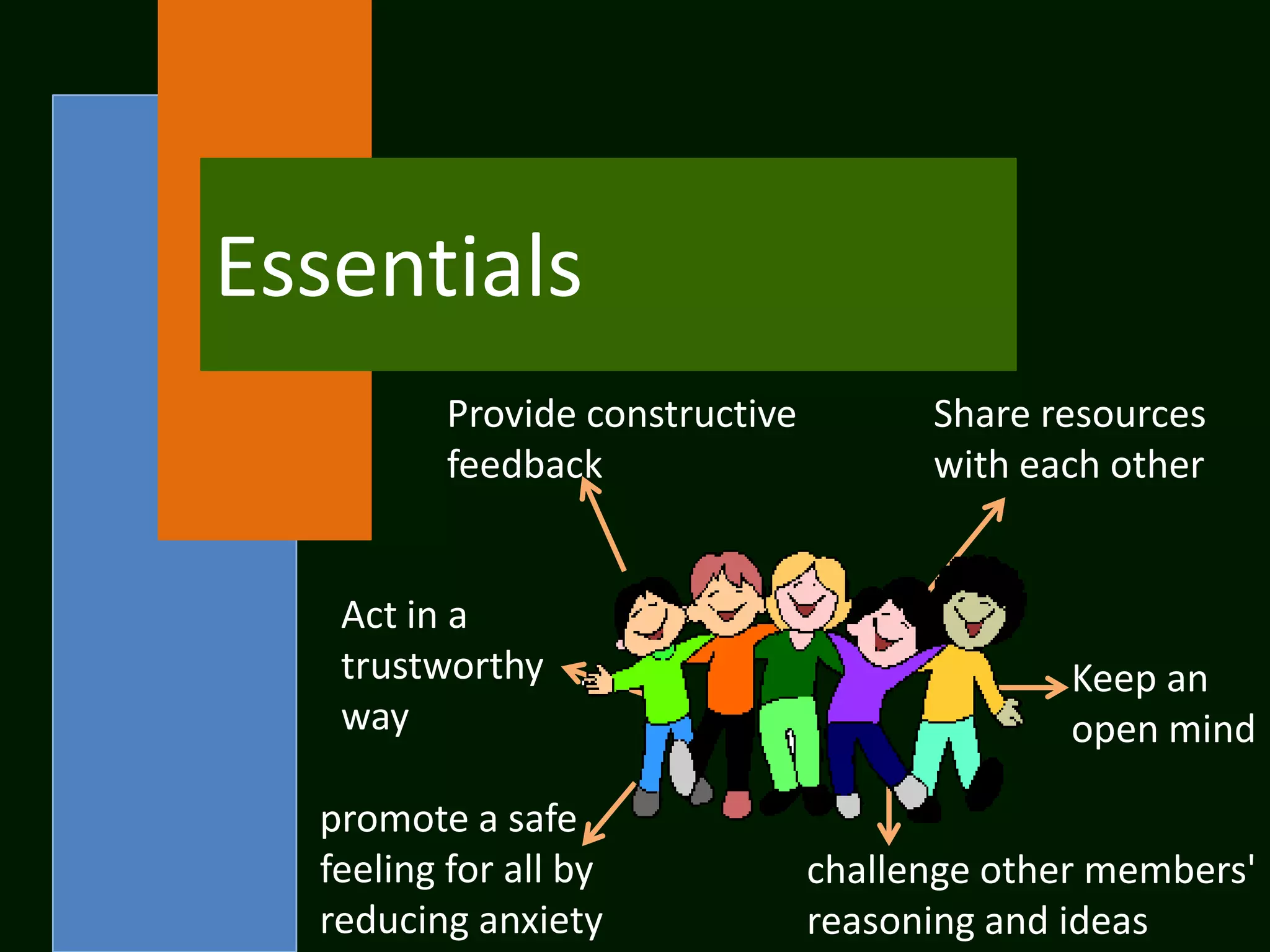
The document summarizes the cooperative learning approach, which is a teaching method where students work in teams on structured activities to achieve a common goal. Key aspects include positive interdependence, interaction between students, individual accountability, and teaching social skills. Effective implementation involves specifying goals, structuring tasks, monitoring groups, and debriefing. Research shows cooperative learning can improve attitudes, social behaviors, critical thinking skills, and achievement.