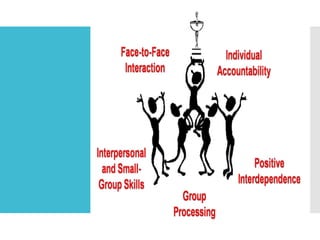
The document outlines the principles and benefits of cooperative learning, emphasizing that it involves students working in small, mixed-ability groups to enhance both individual and collective learning. Key components include positive interdependence, face-to-face interaction, and individual accountability, with a focus on fostering social skills and improving student achievement. Teachers are encouraged to use this instructional strategy effectively by monitoring group dynamics and ensuring the tasks align with cooperative learning principles.