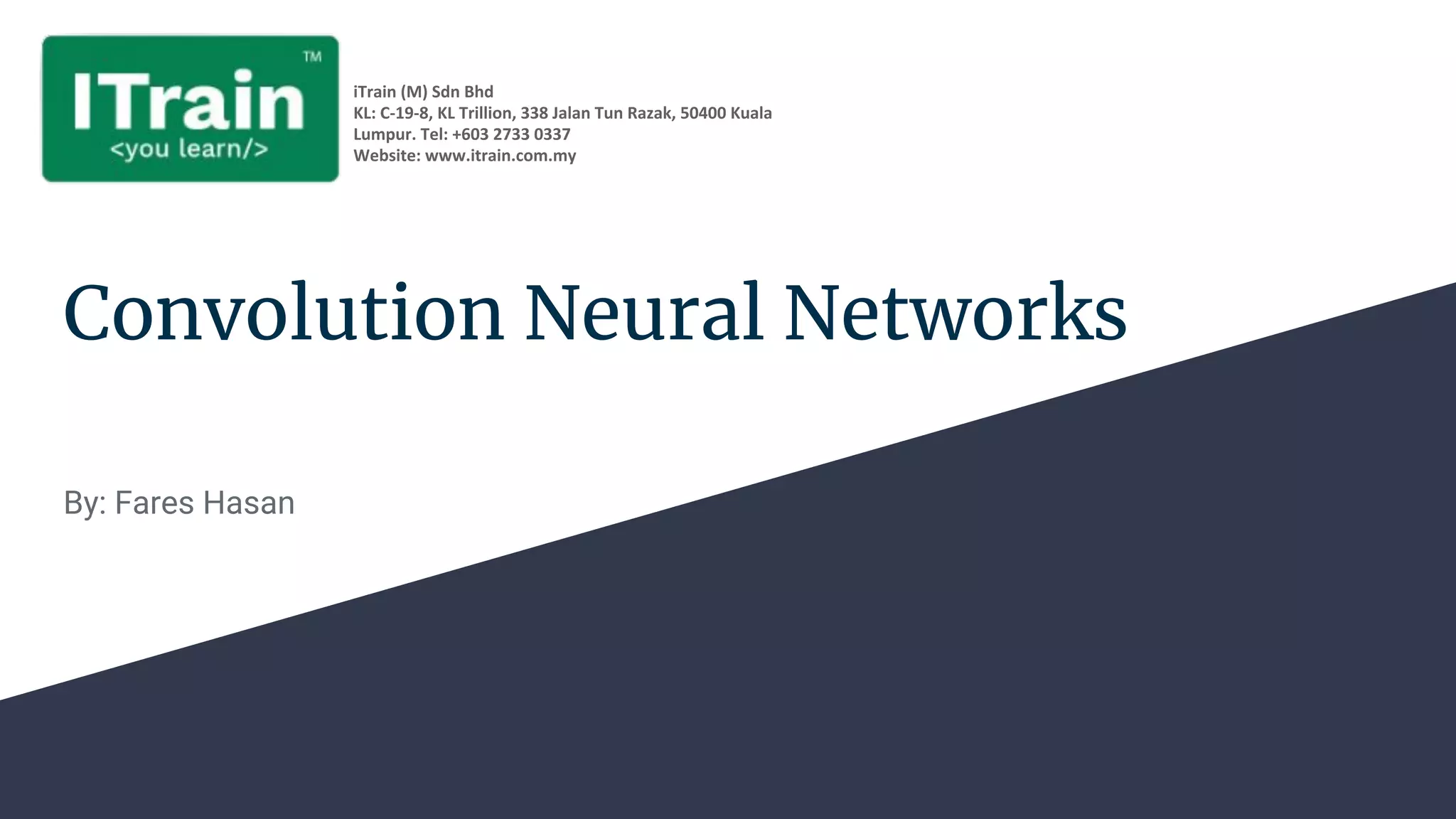
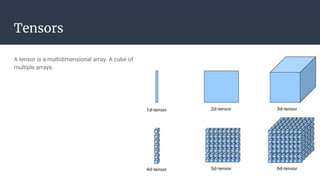
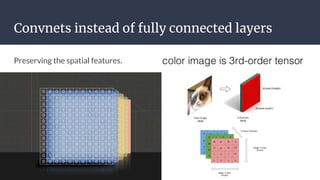
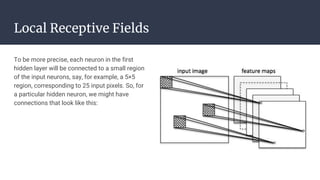
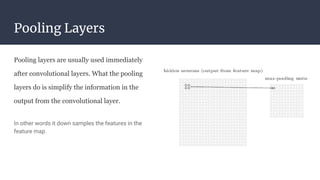
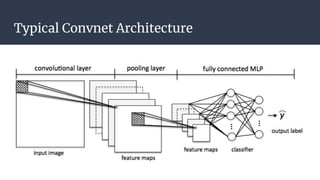
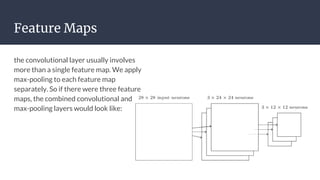
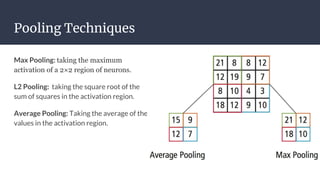
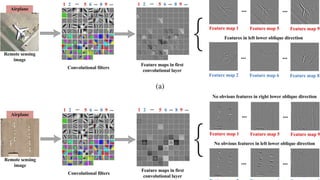
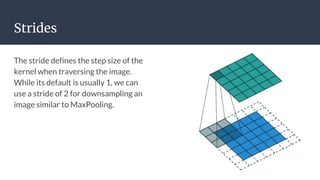
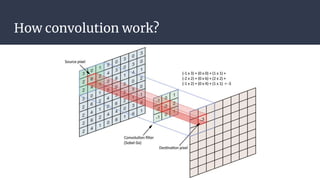
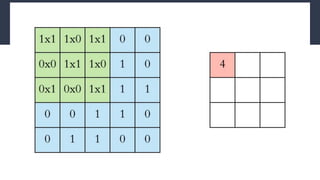
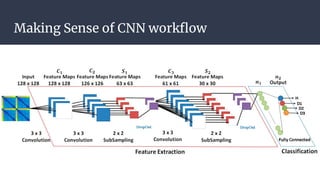
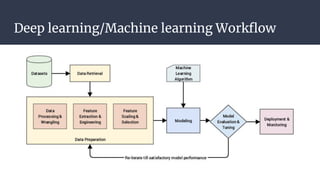
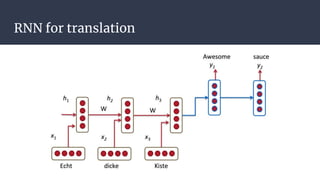
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are a type of neural network that use local receptive fields, shared weights, and pooling to process input images. CNNs preserve the spatial structure of images using local receptive fields that are connected to small regions of the input image. Shared weights and biases are used across these local receptive fields to detect the same features in different locations. Pooling layers simplify the output of convolutional layers by downsampling feature maps. RNNs are useful for tasks involving sequential data like text by incorporating information about previous inputs/computations through a memory-like mechanism. Word embeddings represent words as dense vectors that are learned from surrounding context in text.