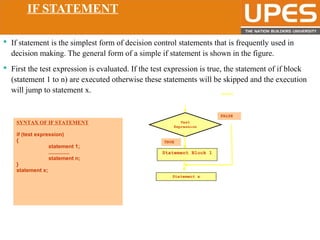
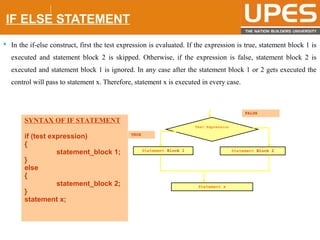
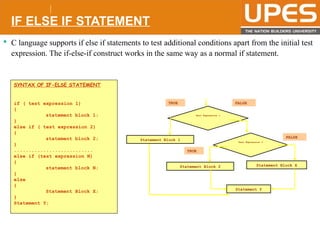
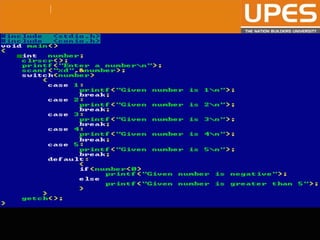
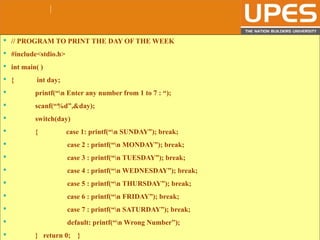
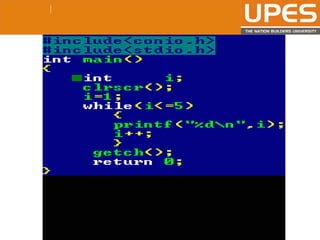
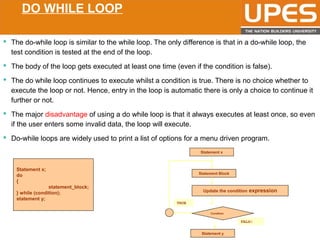
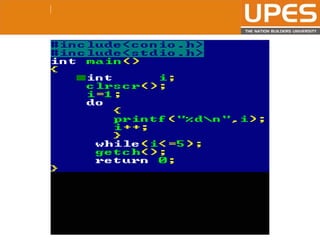
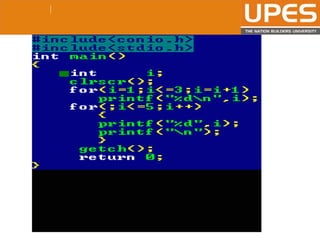
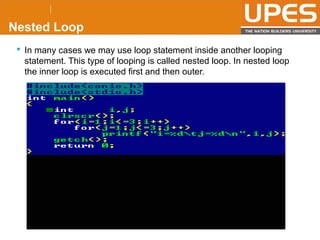
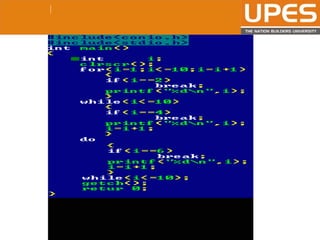
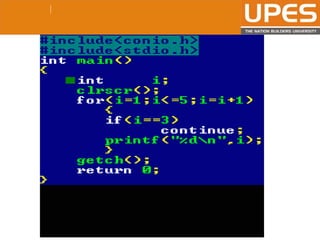
The document discusses various decision control and looping statements in C programming language including if, if-else, switch case, while, do-while and for loops. It provides syntax and examples to demonstrate how these statements work. Key decision control statements covered are if, if-else-if and switch case statements. The main looping statements discussed are while, do-while and for loops along with concepts like break, continue and goto statements to alter normal flow in loops.