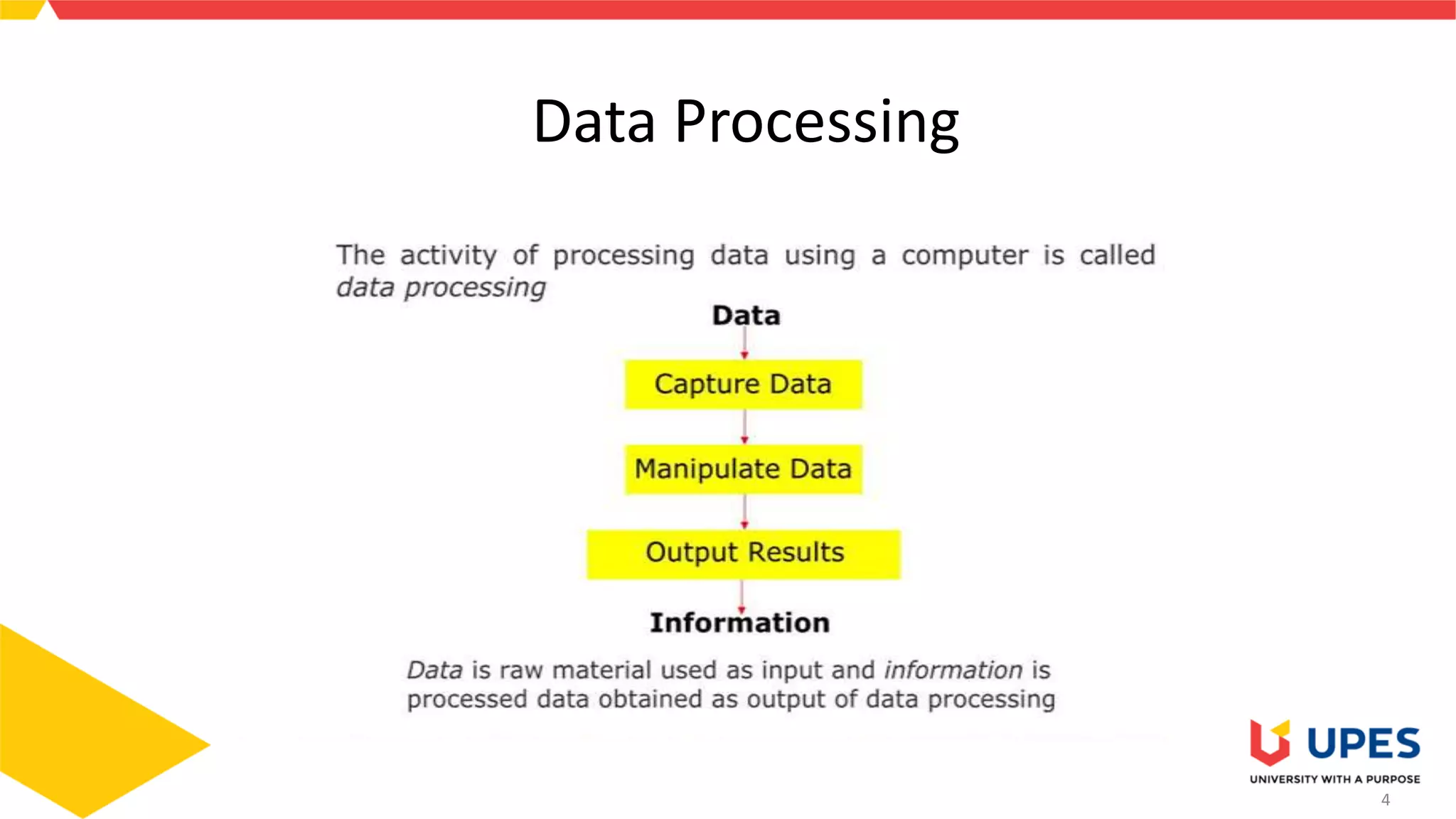
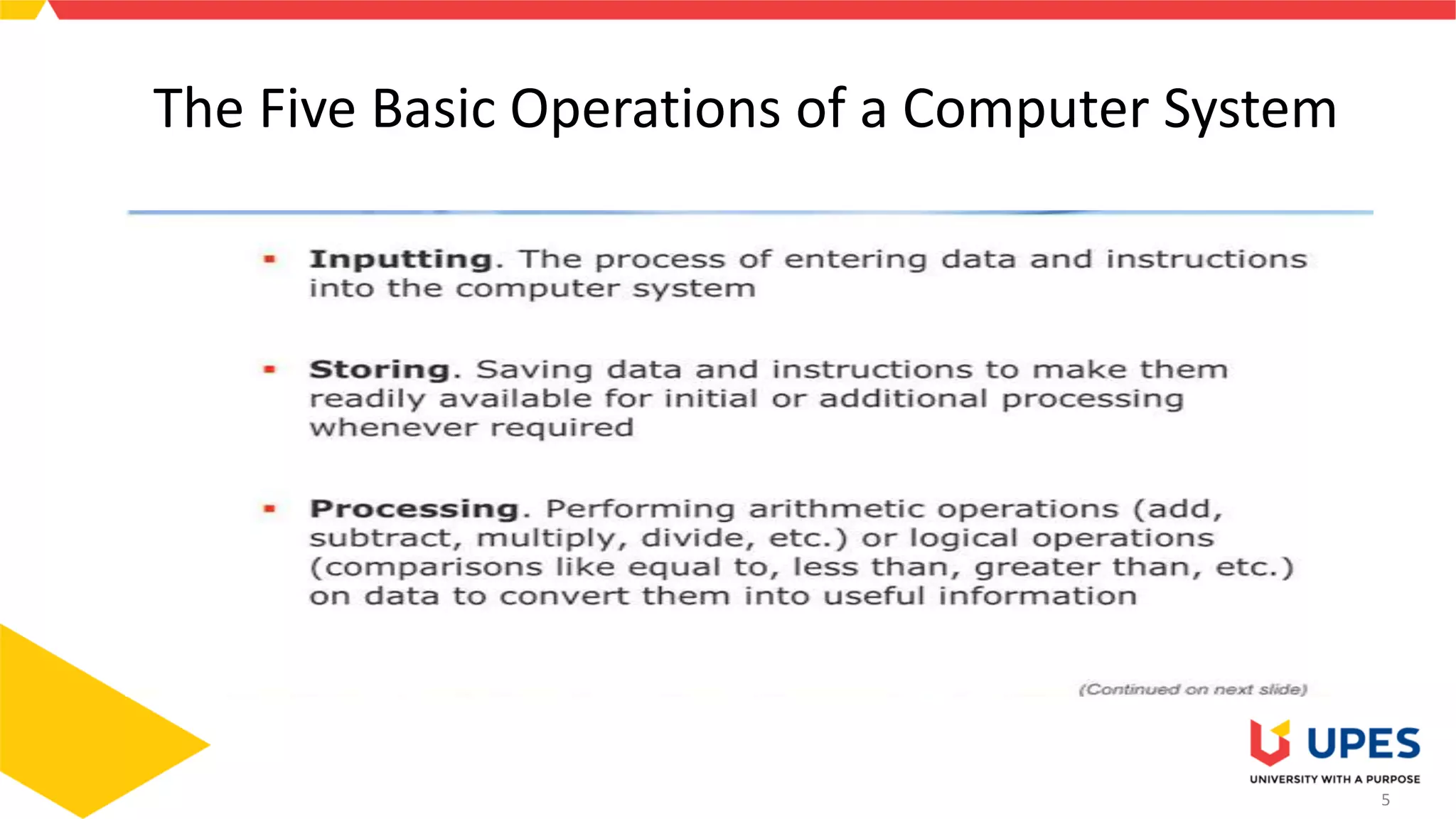
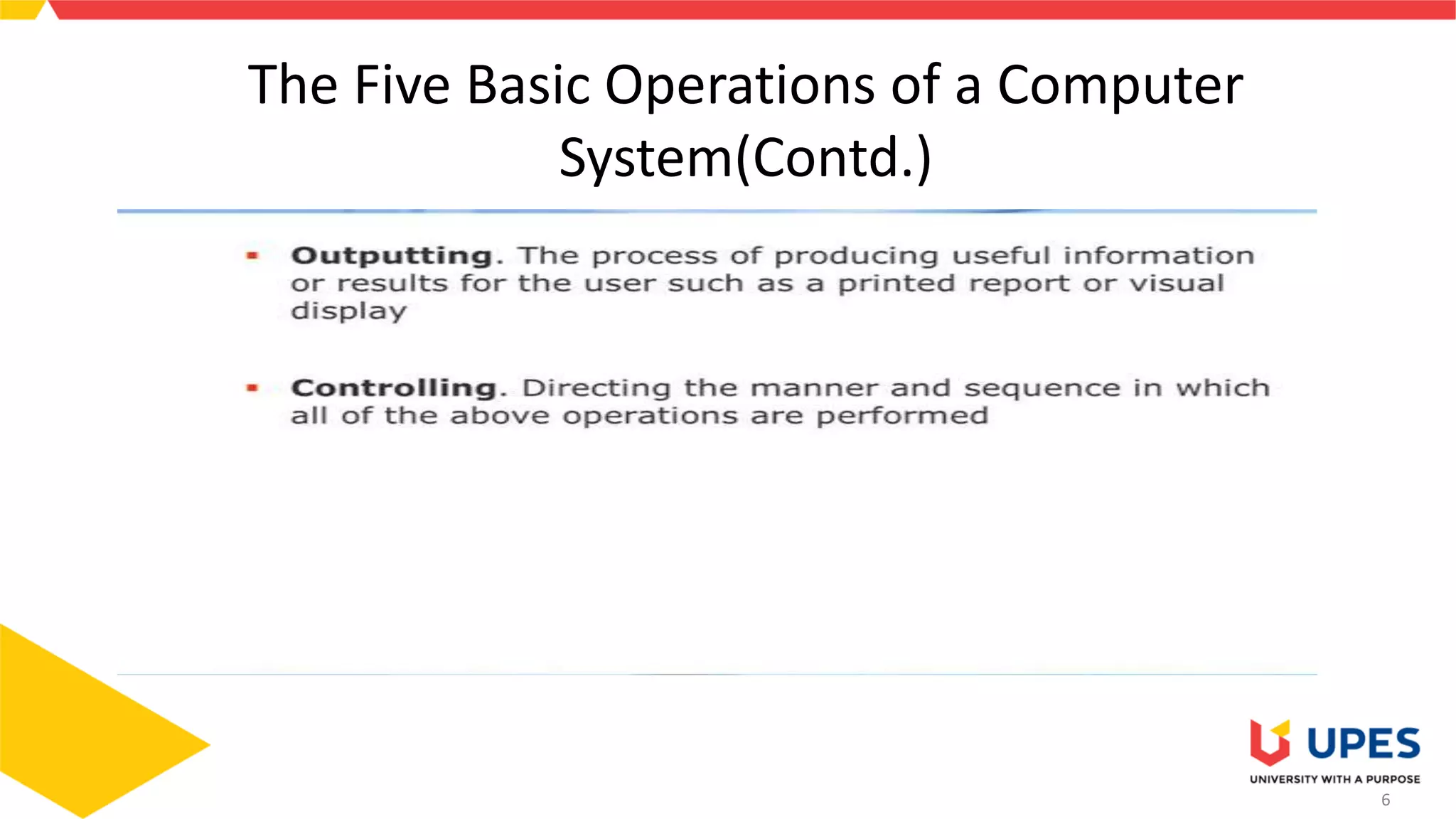
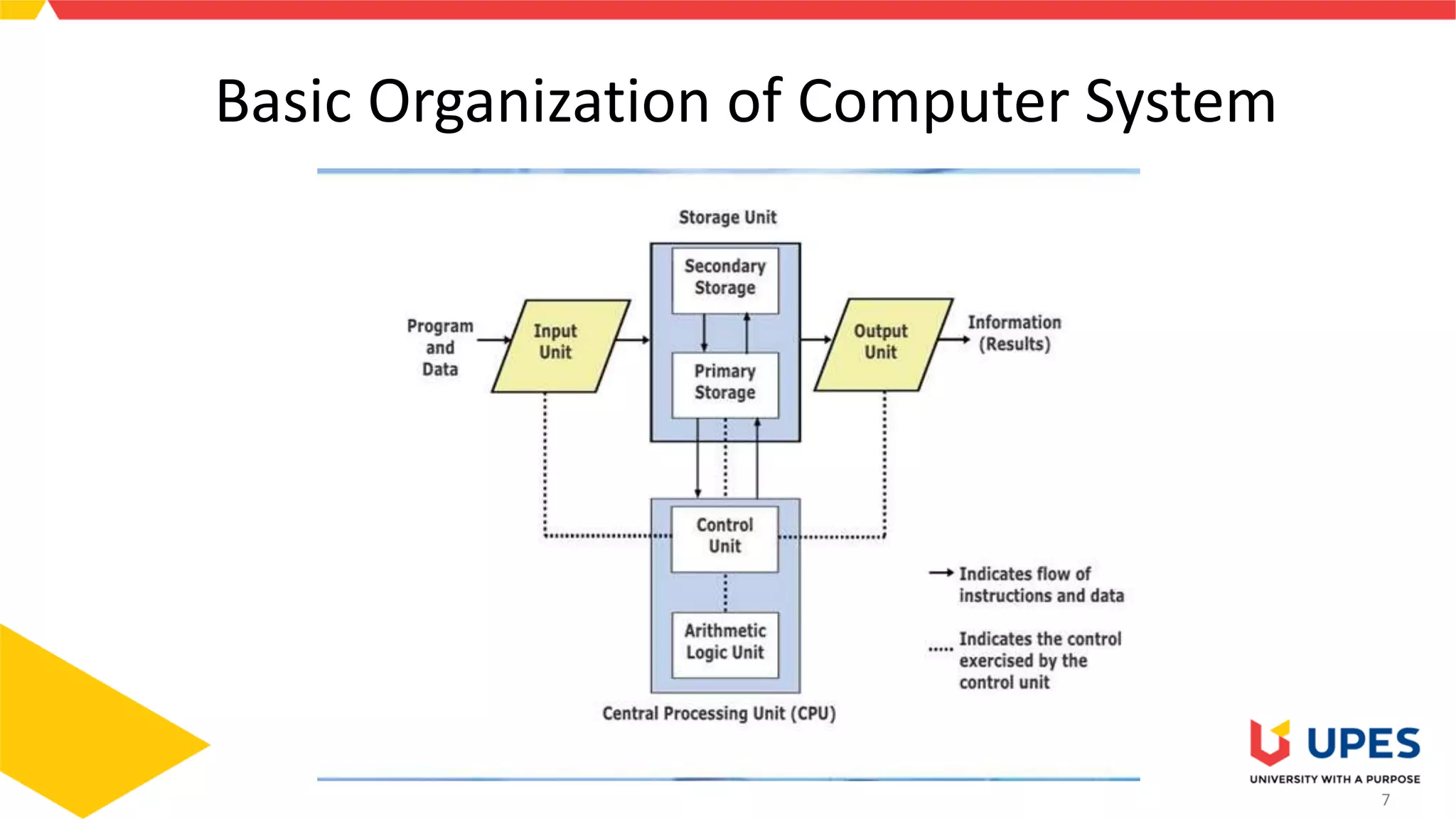
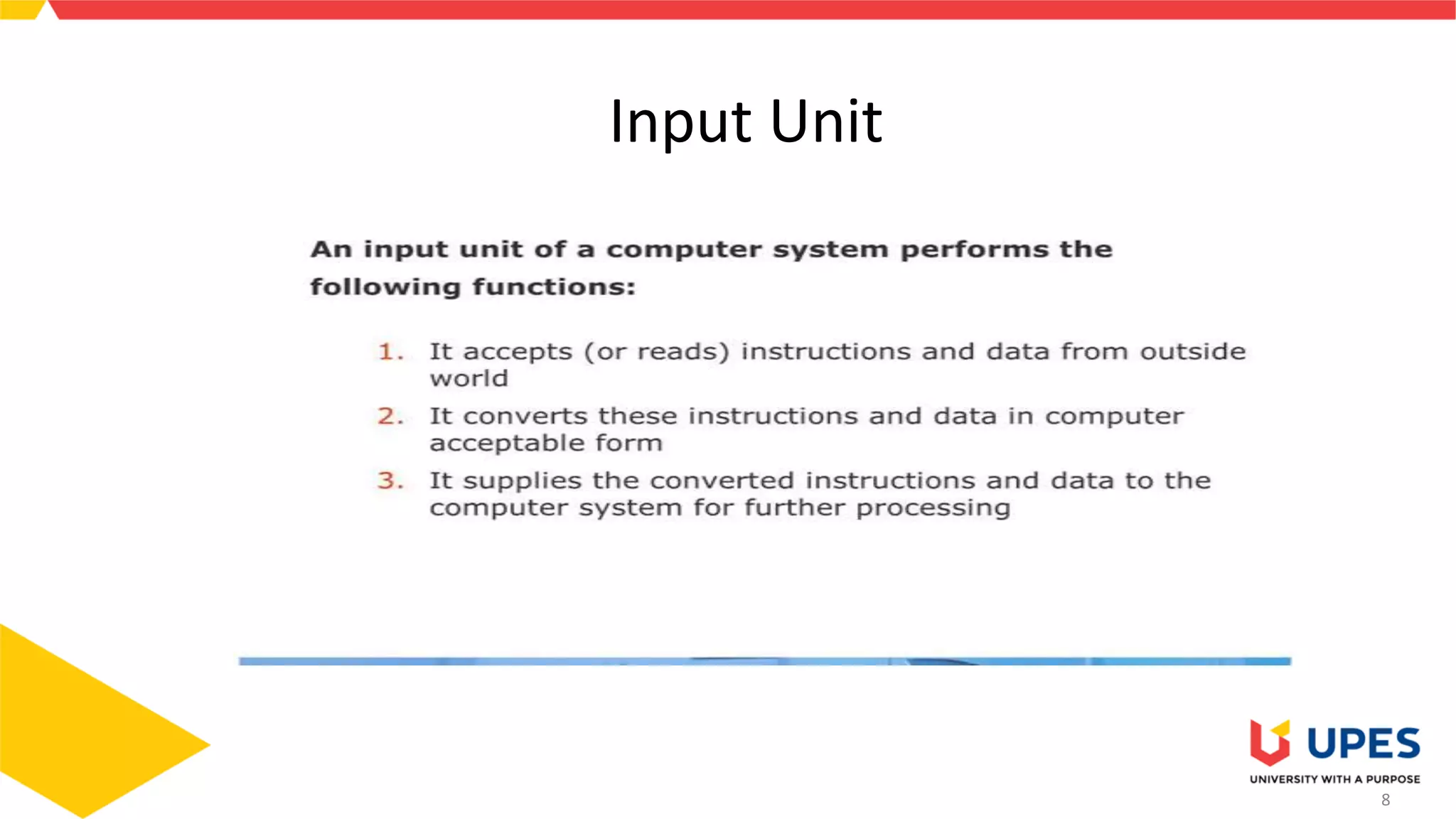
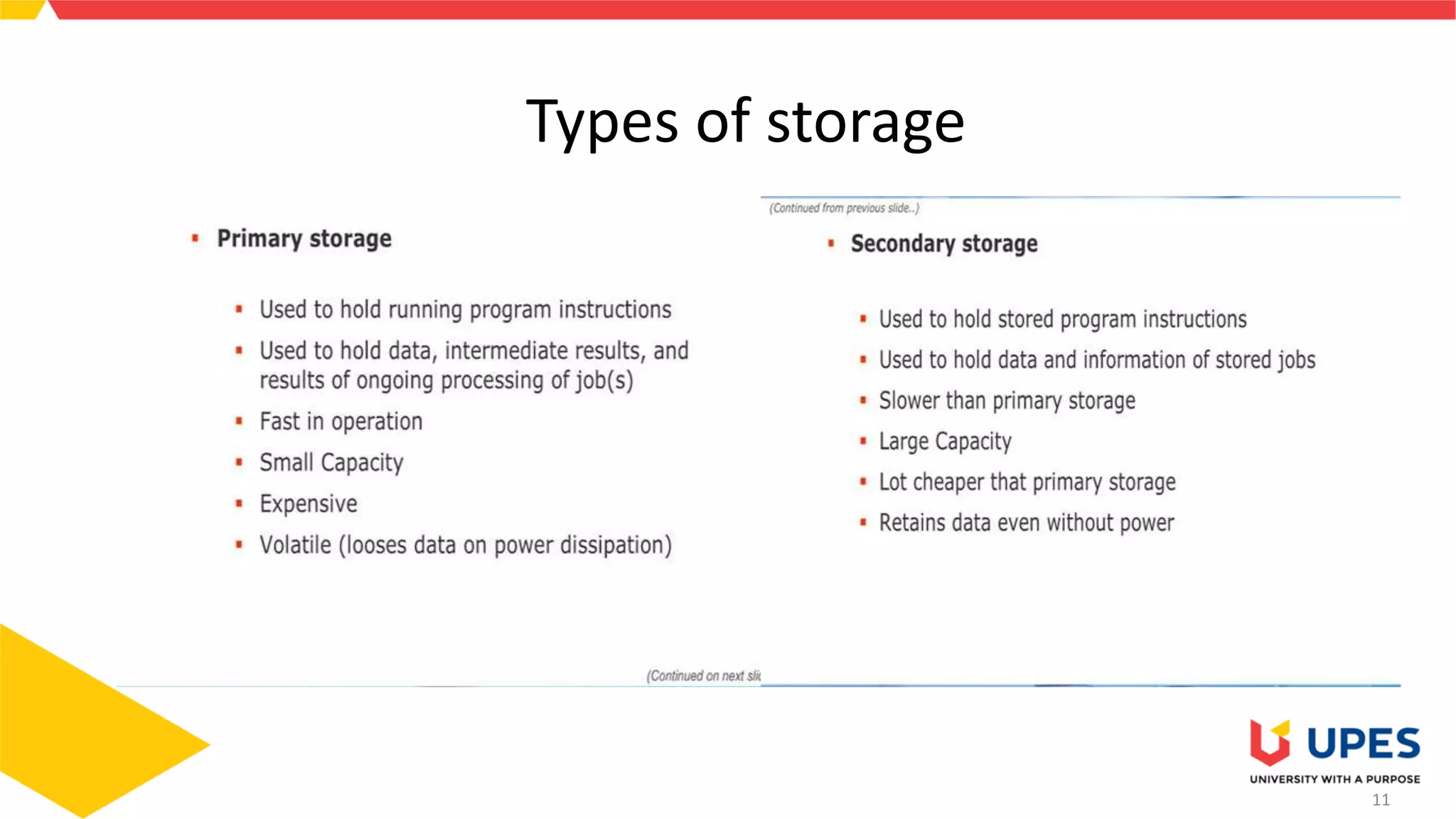
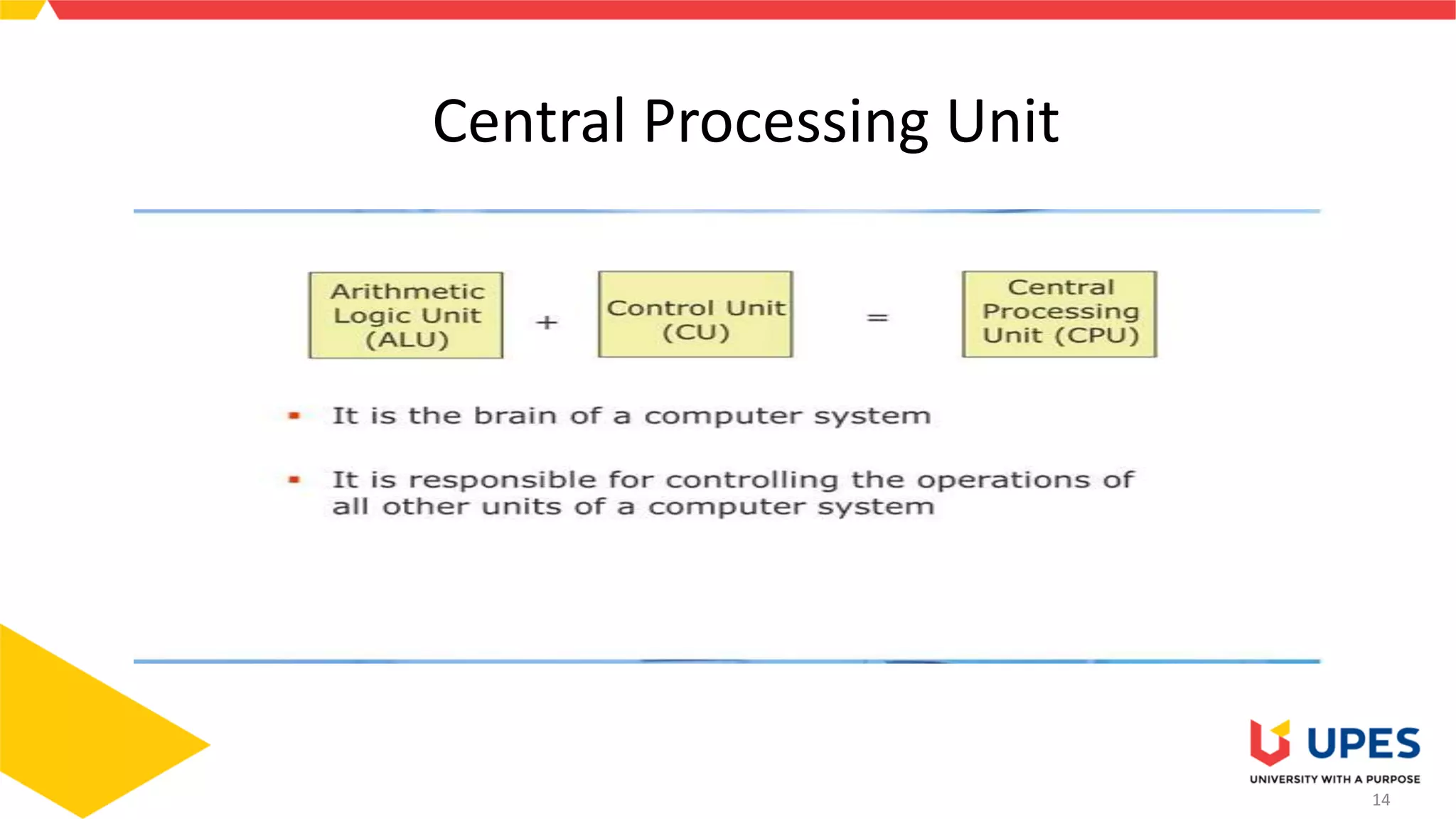
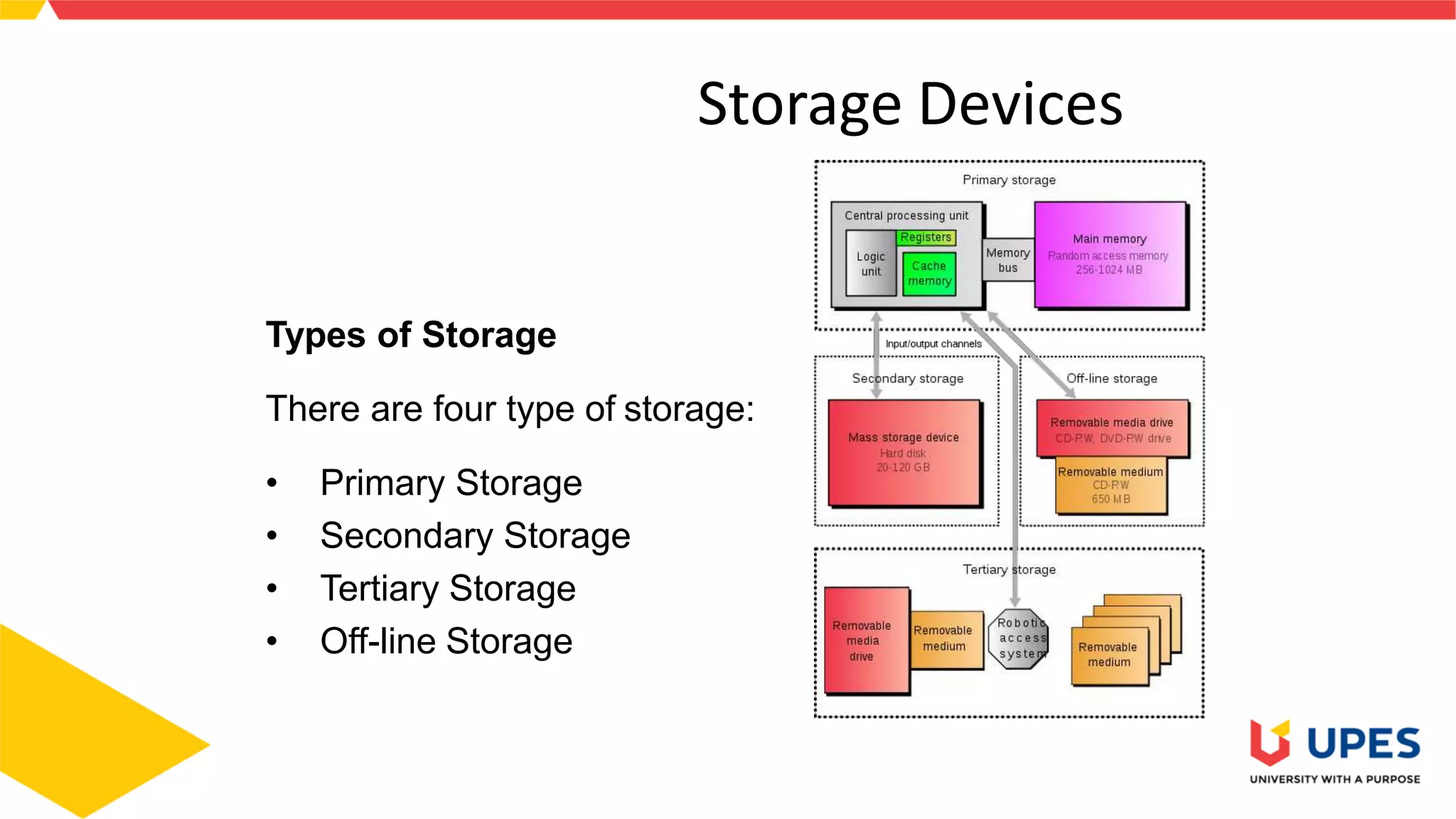
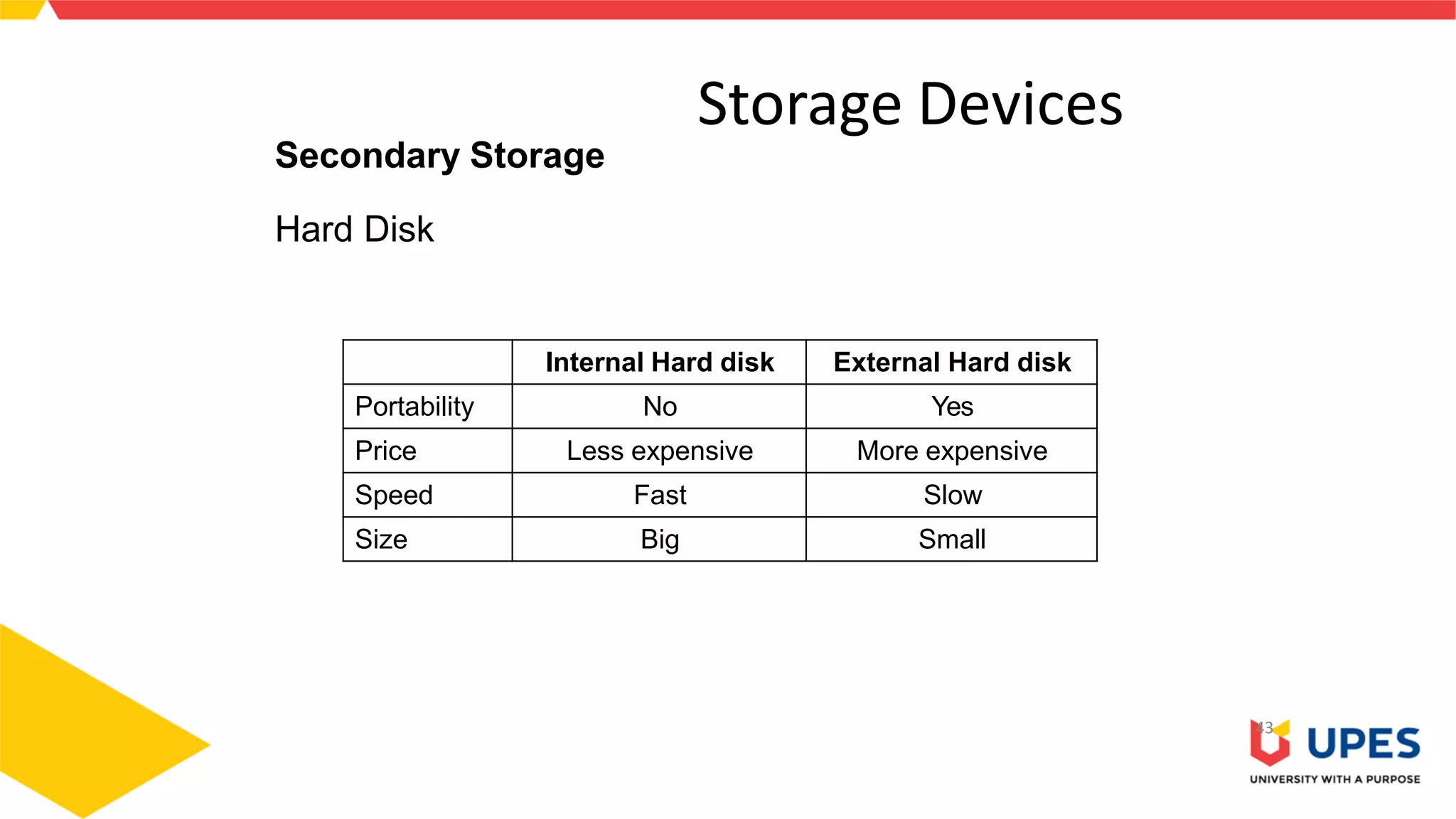
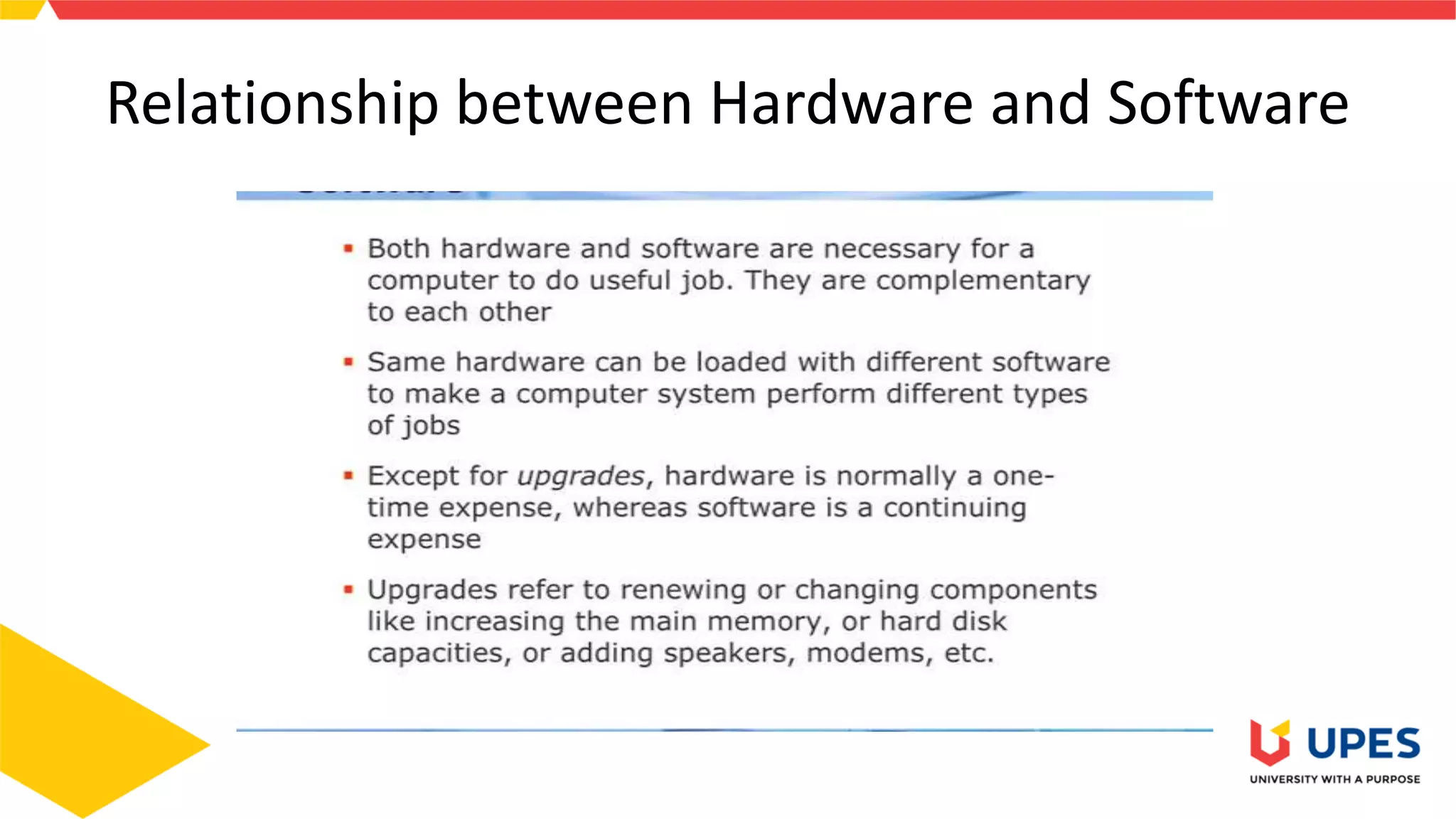
This document provides information on different types of storage devices used in computer systems. It discusses primary storage such as RAM, ROM, and cache that are directly connected to the CPU. Secondary storage devices include hard disks that are not directly accessible by the CPU. Tertiary storage examples are magnetic tapes and optical discs, which involve robotic mechanisms to access large volumes of archived data. Offline storage includes removable media like floppy disks, USB drives, and memory cards that require human insertion before the CPU can access the stored data.