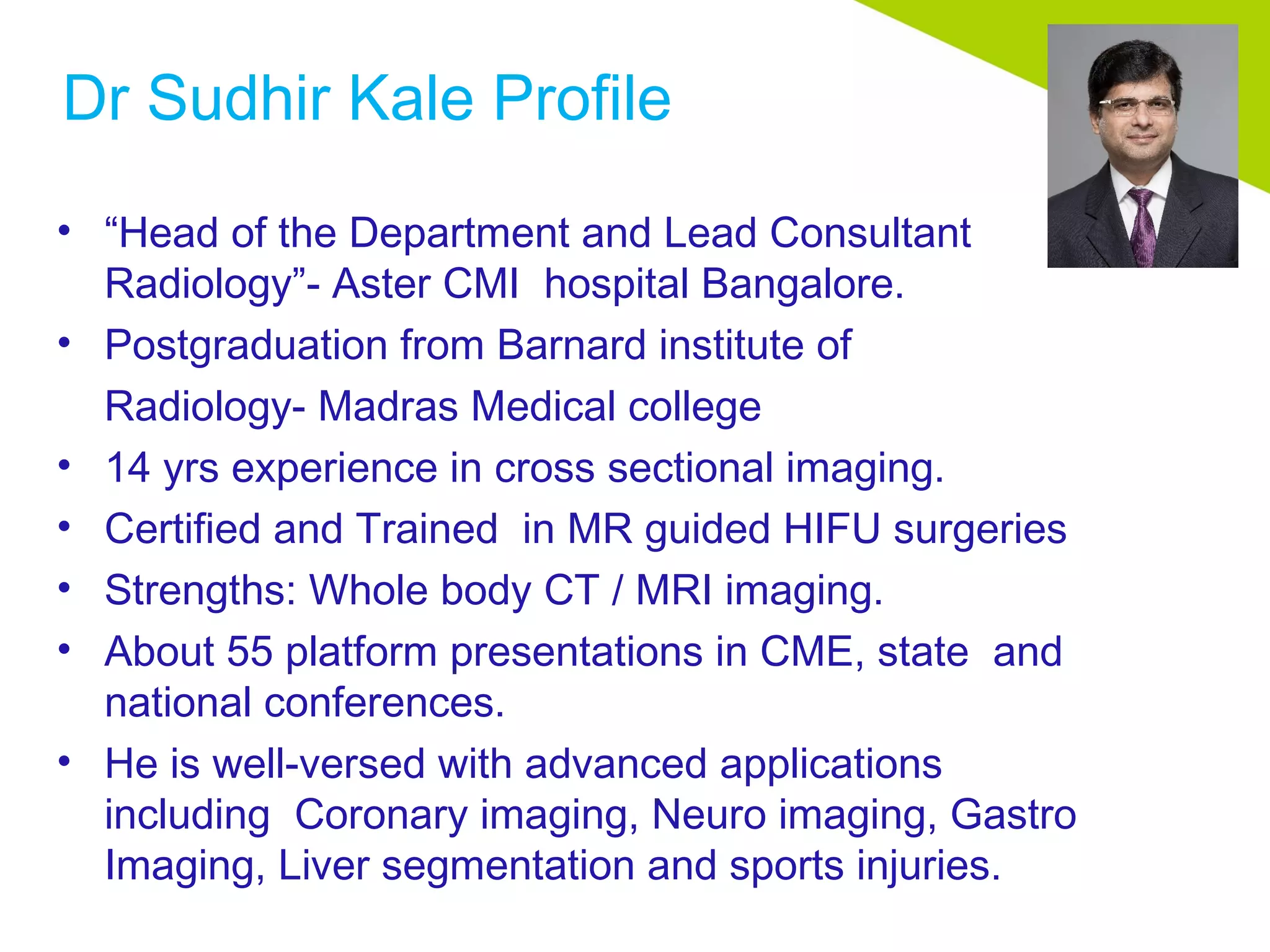
Dr. Sudhir Kale is the head of radiology and lead consultant at Aster CMI hospital in Bangalore, India. He has over 14 years of experience in cross-sectional imaging and specializes in whole body CT/MRI. He is certified and trained in MR-guided HIFU surgeries and has authored chapters in textbooks. Dr. Kale has participated in various research projects involving neuroimaging and has reported on imaging for professional cricket and soccer players in India. He regularly presents at CME conferences on advanced applications like coronary, neuro, and sports injury imaging.