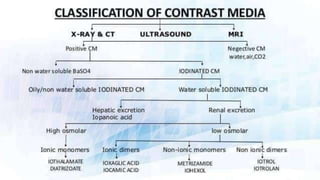
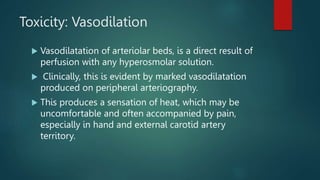
This document discusses contrast media used for medical imaging. It begins by explaining that most contrast media contain iodine, which provides high contrast due to its high atomic number and low toxicity. It then describes conventional, high osmolar contrast media that are salts consisting of iodinated benzoate anions bound to sodium or meglumine cations. The document discusses various contrast agents and notes their advantages and disadvantages, ideal properties of contrast media, risks of toxicity from hyperosmolarity, and treatments for adverse reactions.