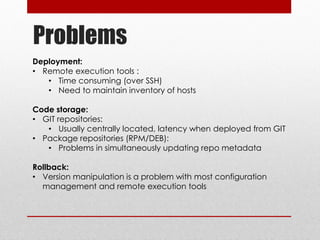
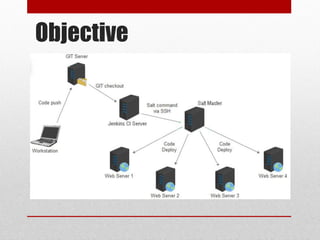
The document discusses continuous deployment using Jenkins and Salt in a cloud environment, highlighting methods, tools, and challenges encountered in the deployment process. It covers configuration management, remote execution tools, and the advantages of using Salt for fast execution and orchestration. Finally, it outlines steps for deploying applications and managing version control effectively within a cloud infrastructure.















![Steps explained
• Salt cloud is used to spawn instances
• Following parameter is provided in the profile to push custom EC2 grains,
• sync_after_install: grains
• The node is registered and deregistered from the load balancer with the
following module definition,
register:
module.run:
- name: boto_elb.register_instances
- m_name: mywebapp
- instances:
- {{ grains['ec2']['instance_id'] }}
• Here ['ec2']['instance_id'] is one of the custom grains pushed to the node](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/continuousdeploymentwithjenkinsandsalt-150820112524-lva1-app6891/85/Continuous-Deployment-with-Jenkins-and-Salt-18-320.jpg)


![Steps explained
Deployment based on App version:
At every deploy, it is checked if the version to
be deployed is already on the node using the
app_version grain,
{% if grains['app_version'] != app_version %}
deregister:
fetch_app_archive:
deploy_app:
register:
{% endif %}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/continuousdeploymentwithjenkinsandsalt-150820112524-lva1-app6891/85/Continuous-Deployment-with-Jenkins-and-Salt-21-320.jpg)




