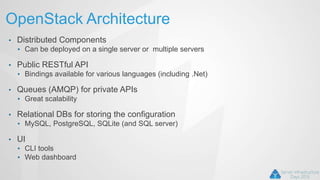
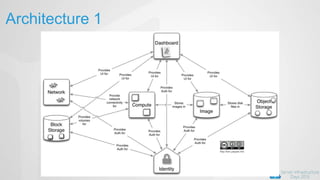
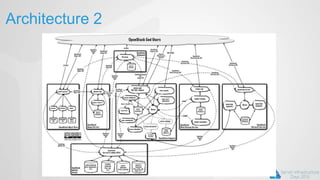
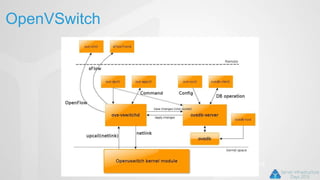
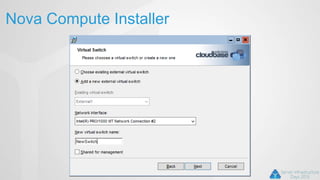
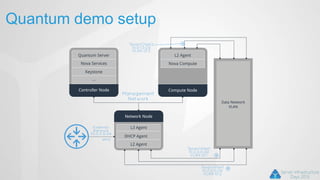
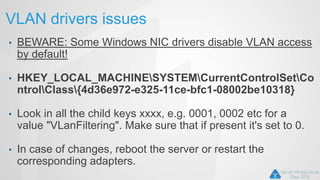
OpenStack is an open source cloud computing platform that can manage large networks of virtual machines and physical servers. It uses a distributed architecture with components like Nova (compute), Swift (object storage), Cinder (block storage), and Quantum (networking). OpenStack has been successful due to its scalability, support for multiple hypervisors including Hyper-V, and compatibility with popular programming languages like Python. While OpenStack is best suited for large public and private clouds, its complex installation and lack of unified deployment tools can present challenges, especially for small to mid-sized clouds.