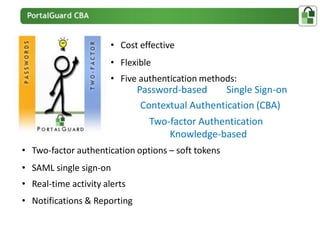
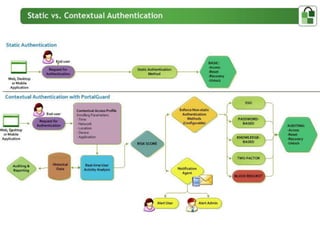
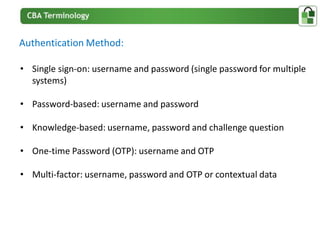
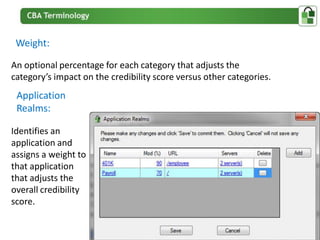
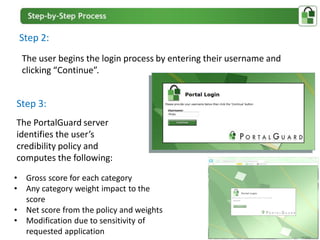
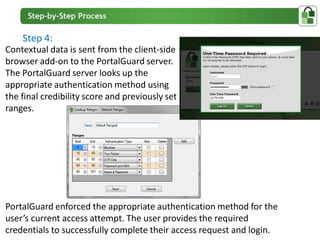
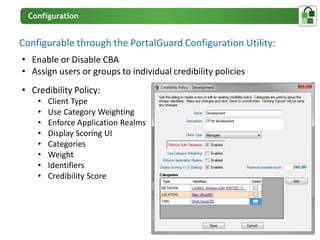
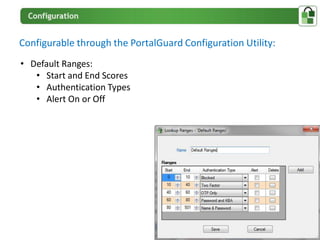
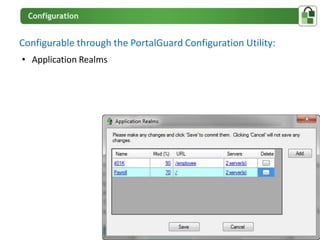
The document presents an overview of PortalGuard's contextual authentication platform, which balances usability and security through a multi-factor authentication approach. It highlights various authentication methods and their adaptability to different access scenarios, emphasizing a proactive approach to reducing threats while enhancing user experience. Technical requirements for installation and configuration details are also provided, ensuring compatibility with various systems.