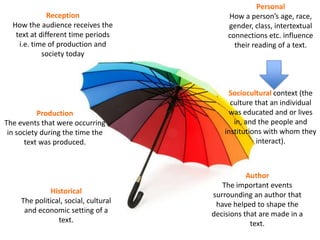
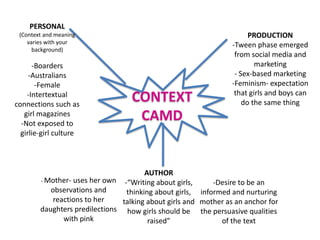
The document provides an overview of different contexts that can influence the production and reception of a text. It defines context as the environment in which a text was produced, set, or read, including social, political, historical, and physical factors. It then discusses several specific types of context - personal reception, sociocultural, production, author, and historical context. The document emphasizes that considering these various contexts is important for determining the meanings and interpretations that can be made from a text. It encourages engaging with different sources and perspectives to better understand context.