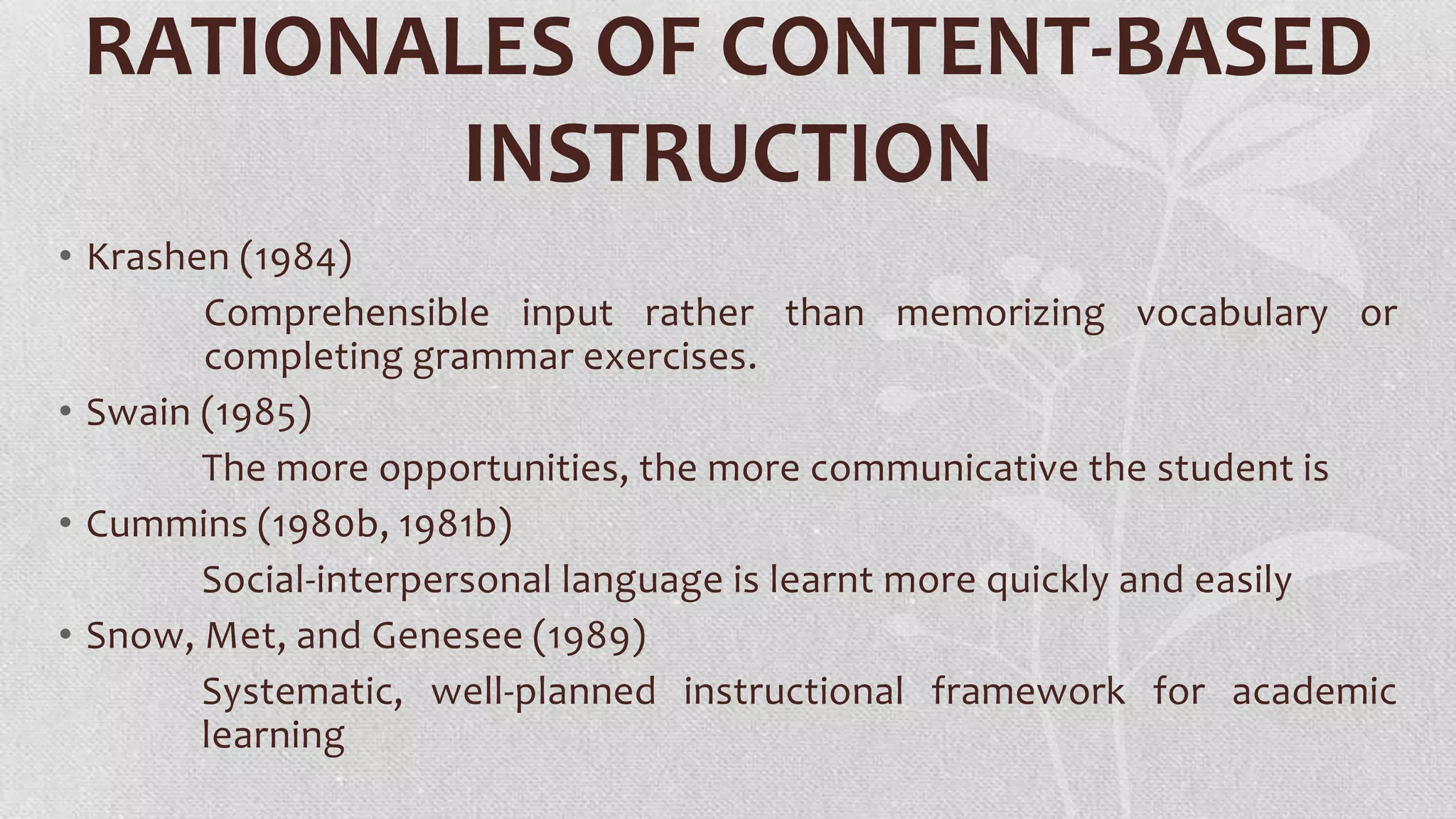
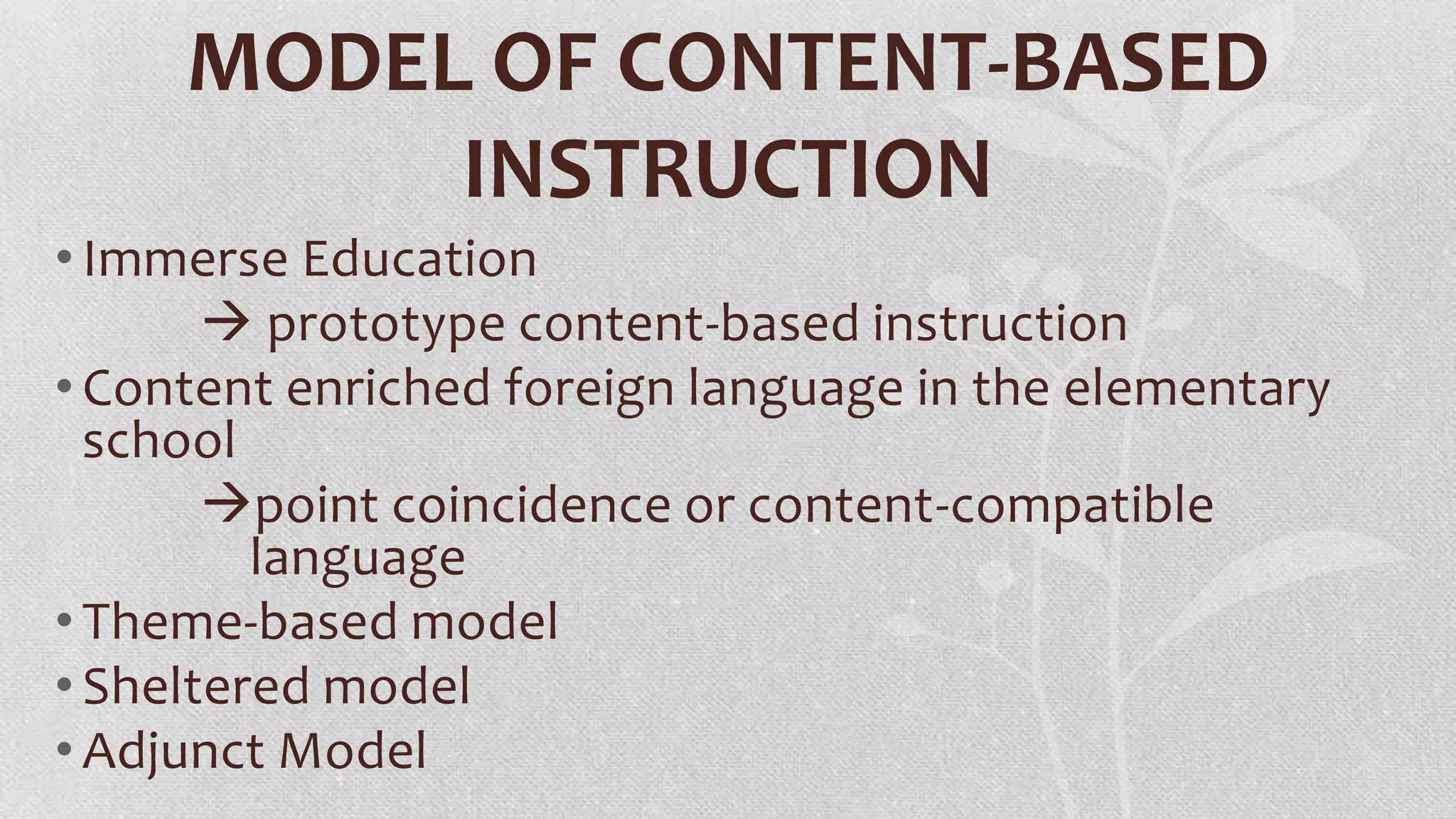
This document discusses content-based language instruction and integrating literature into language teaching. It provides rationales for content-based instruction including comprehensible input and developing communicative ability. Models of content-based instruction are described like immersion education. The document also discusses integrating the four language skills through content and strategies for content instruction. Sample lesson plans are provided and key issues addressed like the teacher's role in exploiting content and developing student-centered approaches. Finally, integrating literature is discussed in terms of vocabulary, grammar, reading, writing and oral skills.