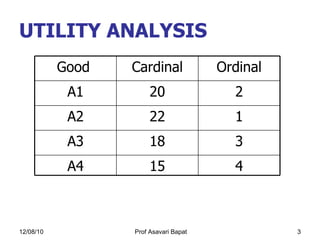
This document discusses key concepts in consumer behavior and consumer choice theory, including:
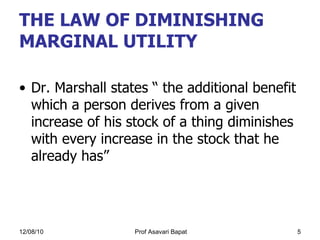
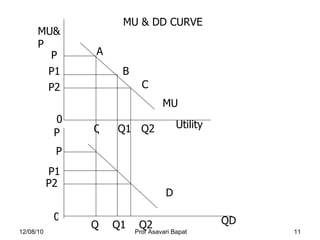
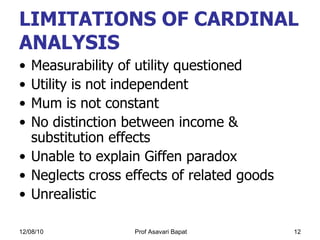
1) The law of diminishing marginal utility, which states that the marginal utility of additional units of a good decreases as consumption increases.
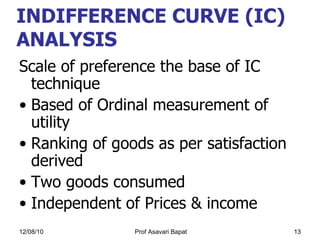
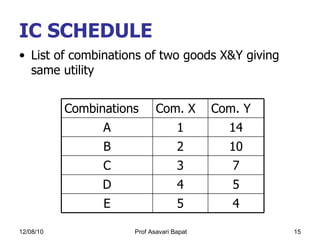
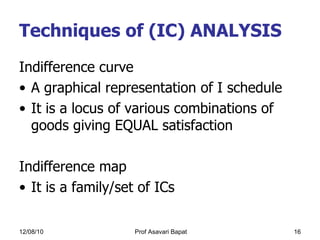
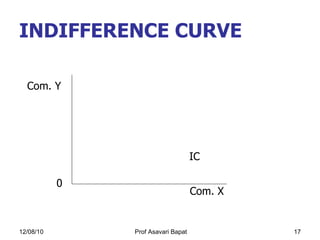
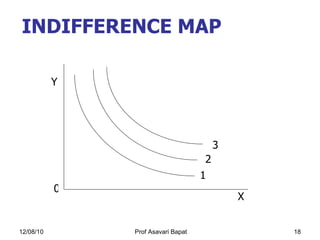
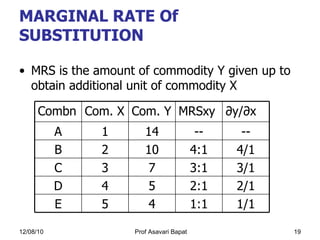
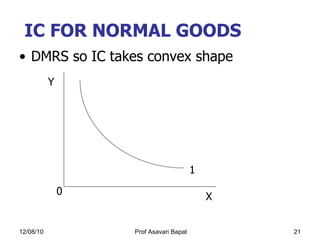
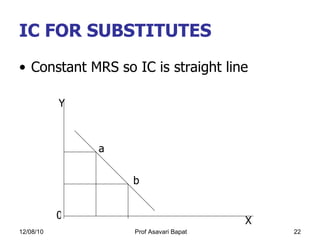
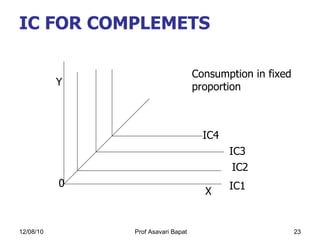
2) Indifference curve analysis, which uses indifference curves to represent combinations of goods that provide equal utility to a consumer.
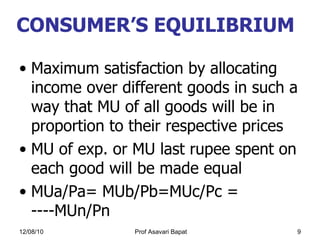
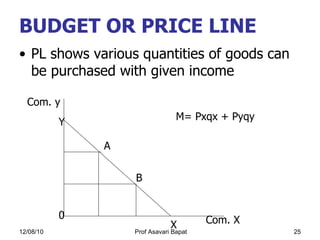
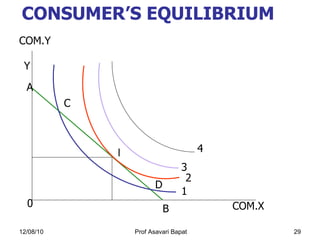
3) The concept of consumer equilibrium, which occurs when a consumer allocates their budget in a way that equalizes marginal utility per dollar across all goods purchased.
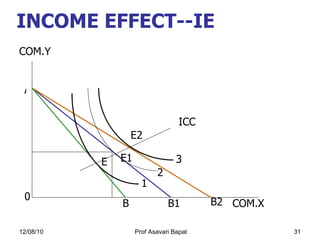
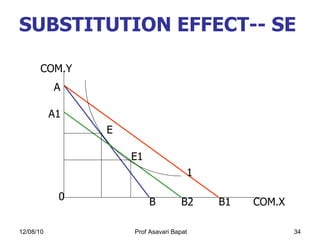
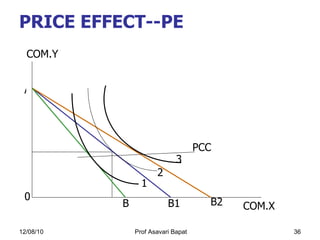
4) How changes in income or prices can impact consumer equilibrium through income and substitution effects.