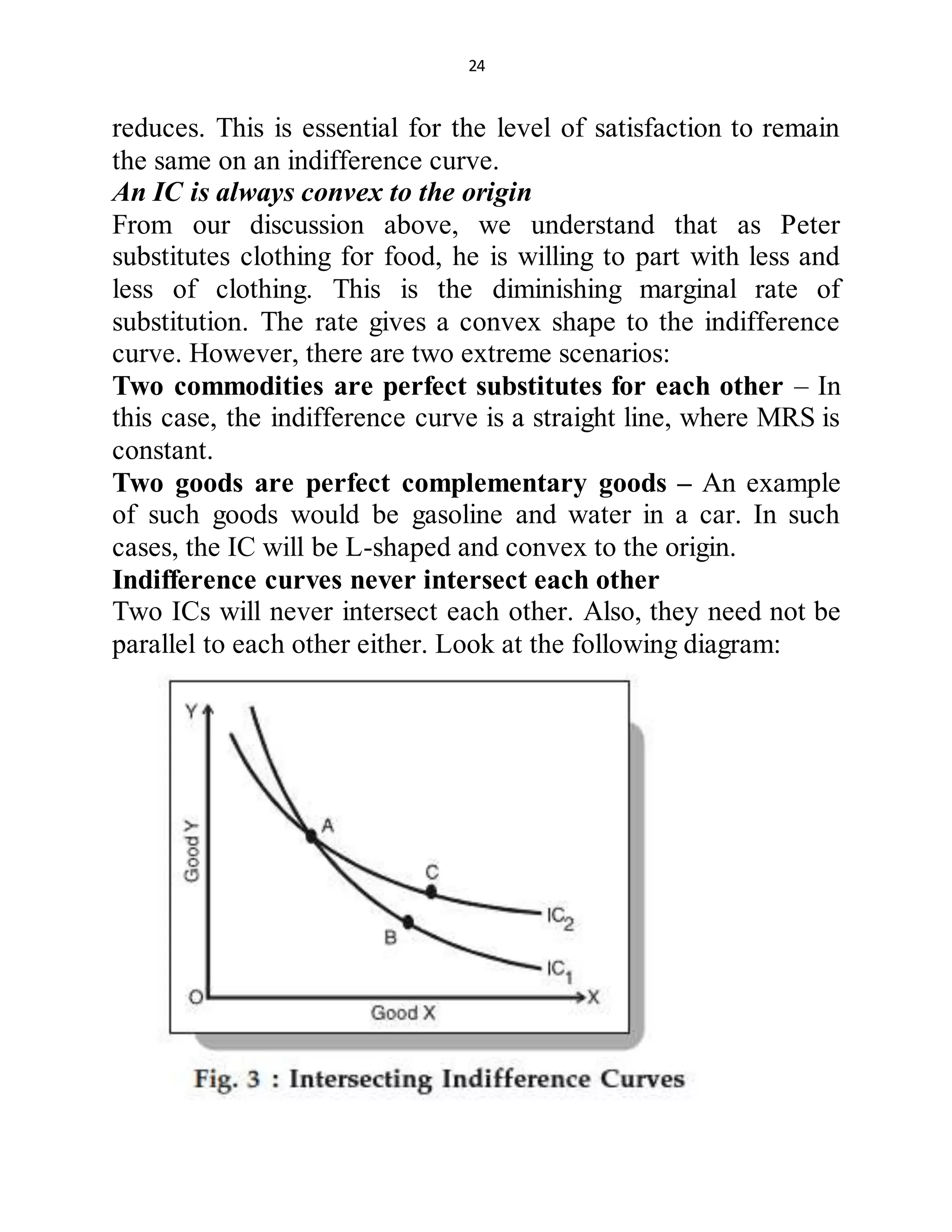
The document discusses consumer equilibrium, which occurs when a consumer reaches the maximum level of satisfaction given their resources and prices. It provides an example using a single good to show that a consumer will purchase more of a good as long as the marginal utility of the good is greater than the price. Equilibrium is reached when the marginal utility of the good equals the price. This is shown graphically as the intersection of the marginal utility curve and the price line. The document then extends the analysis to multiple goods, stating that equilibrium occurs when the marginal utility per unit of expenditure is equal for each good.