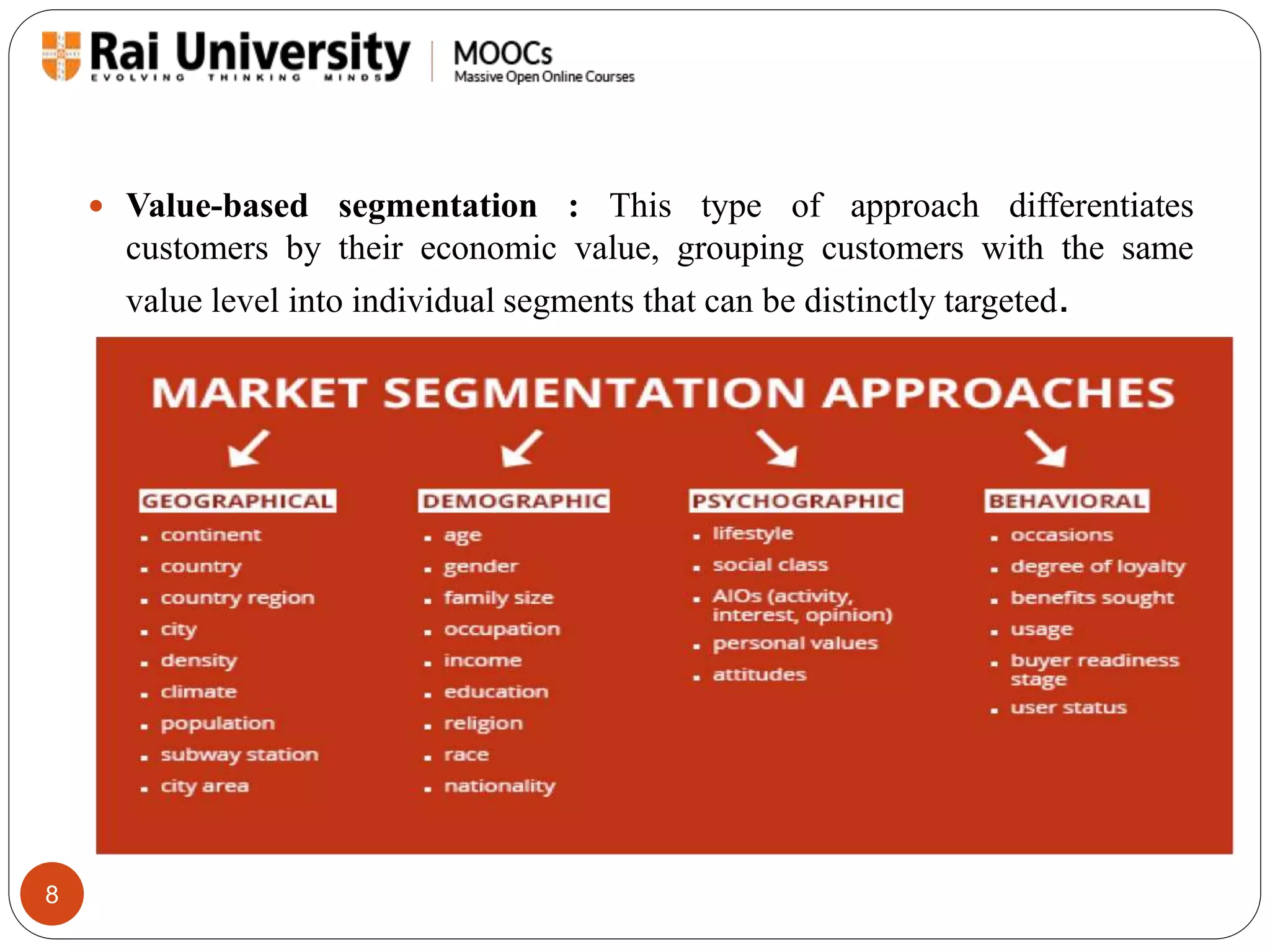
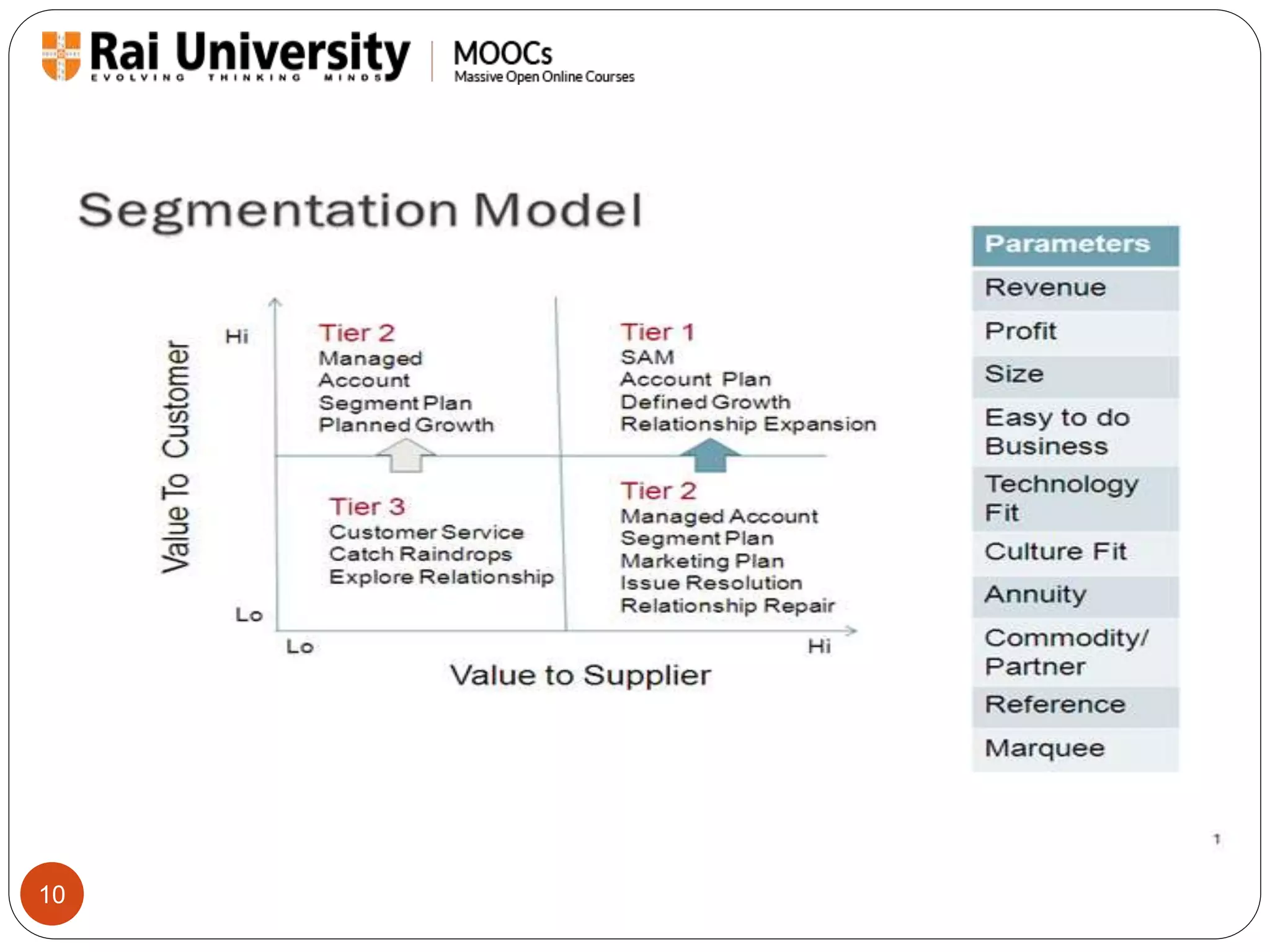
Customer segmentation is the practice of dividing a customer base into groups based on shared characteristics, helping businesses identify unmet needs and optimize marketing strategies. It involves measuring profit potential, targeting profitable segments, and continuously adjusting approaches based on market conditions. Methods of segmentation include a priori, needs-based, and value-based segmentation, each with its own advantages and limitations.