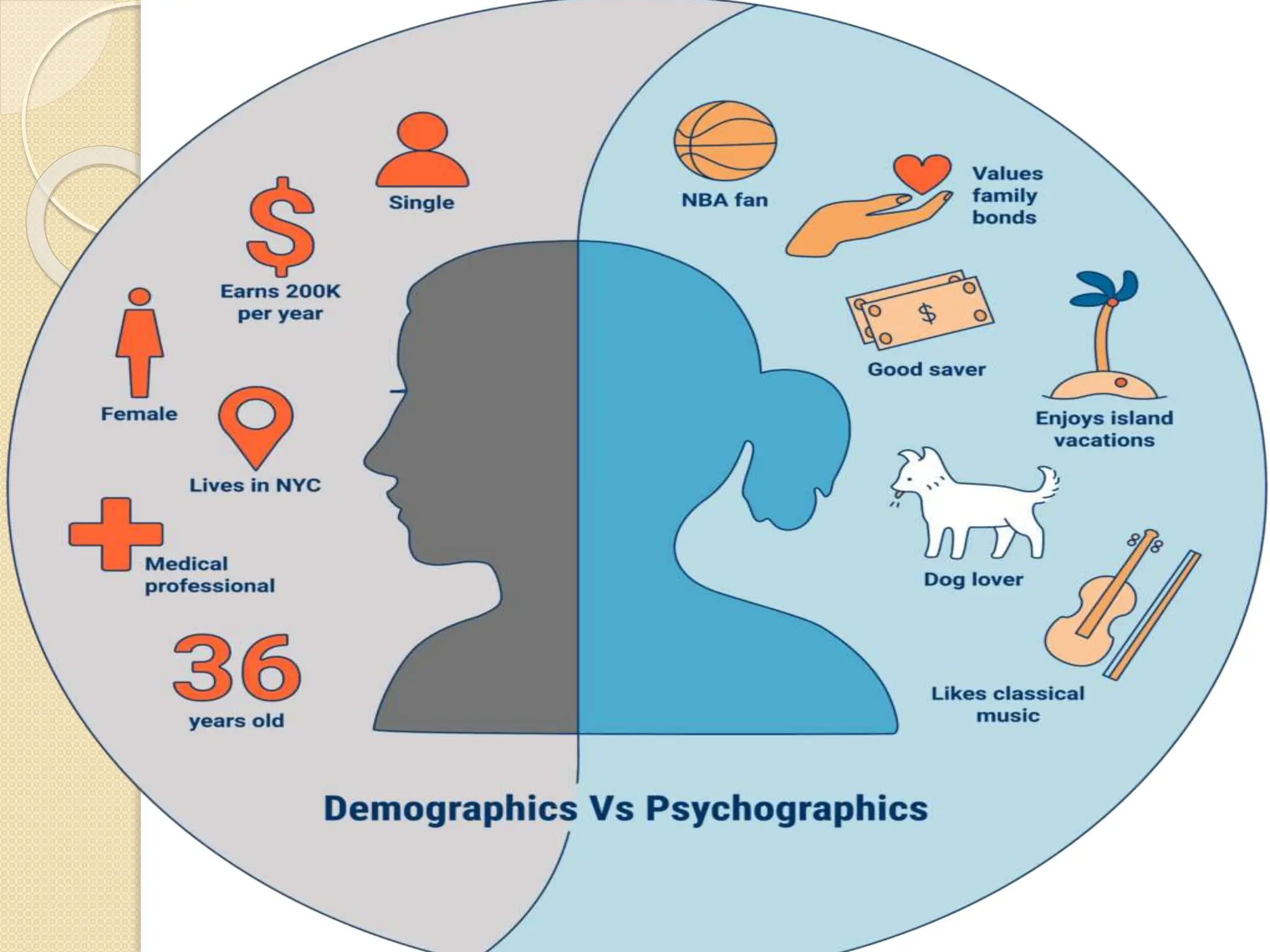
Psychographics uses psychological, sociological, and anthropological factors to segment the market based on groups' propensities. It helps marketers understand consumer segments beyond basic demographics. For example, there are three types of mobile phone users - the casual user who uses basic features, the business user who wants a simple integrated device, and the power user who uses all functions and additional software. Marketers can use psychographic data to better define and position products to target lifestyles through appropriate advertising and product strategies. However, psychographic-based marketing also risks consumer exploitation and addictive or compulsive consumption.