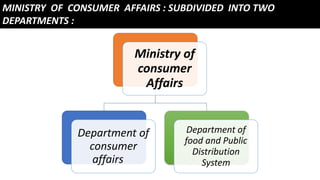
The document summarizes consumer rights and responsibilities in India. It discusses that a consumer is defined as a person or organization that uses economic services or commodities. The Consumer Protection Act of 1986 was introduced to better protect consumer interests. The main objective of the Act is to provide simple and speedy redressal for consumer disputes. The Ministry of Consumer Affairs is subdivided into two departments, including the Department of Consumer Affairs, which handles consumer awareness campaigns and implementation of standards. The key consumer rights are the right to safety, information, choice, being heard, seeking redressal, and consumer education. Consumer responsibilities include keeping documentation of purchases, making reasonable claims, self-help where possible, and not being misled by advertisements.