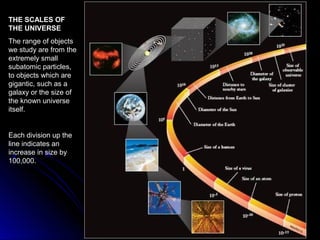
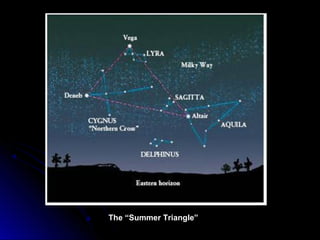
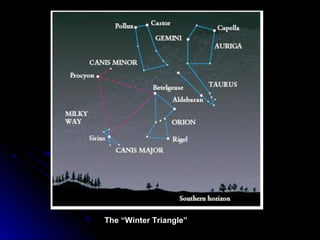
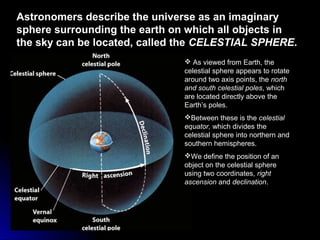
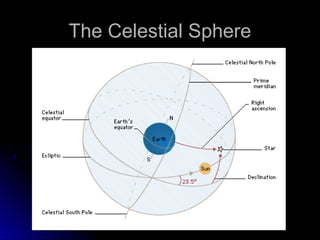
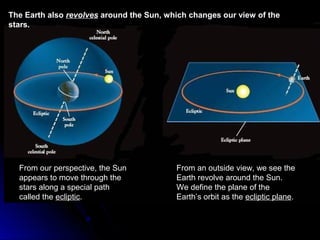
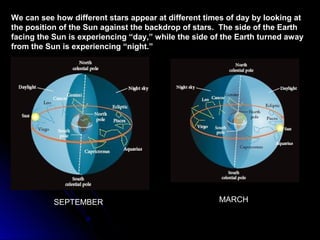
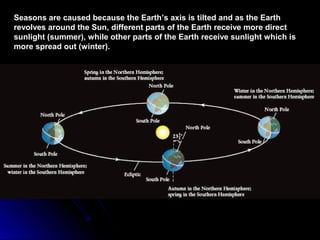
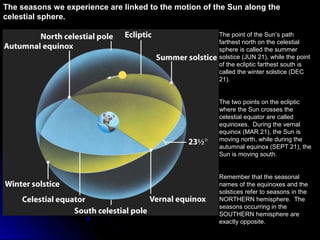
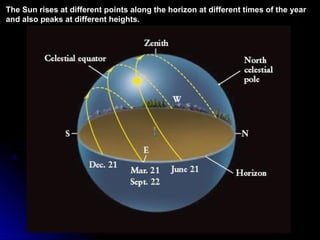
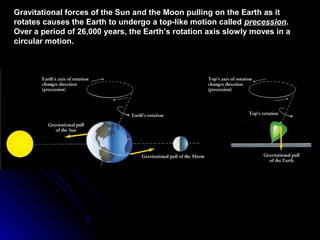
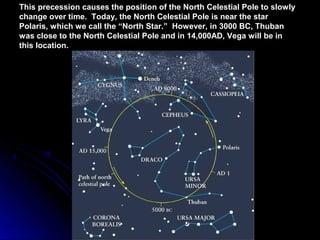
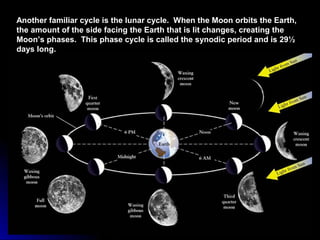
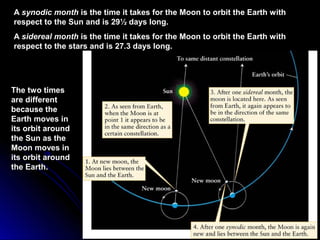
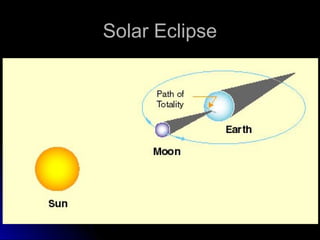
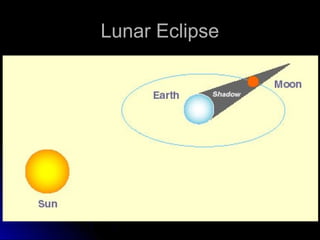
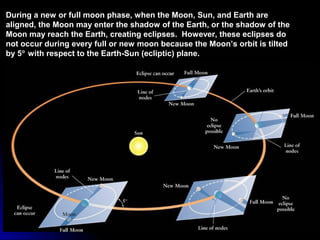
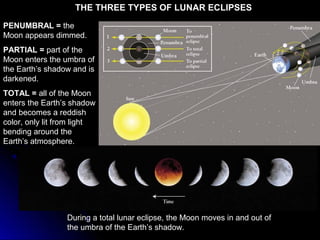
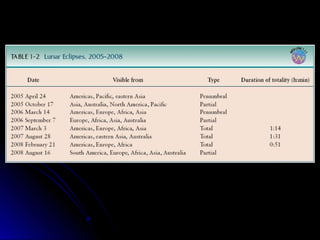
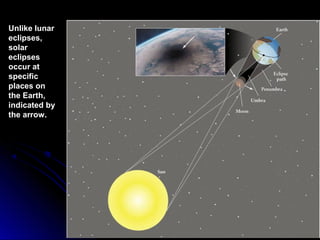
The document provides an overview of key concepts in astronomy including constellations, the celestial sphere, the motions of the Earth, moon phases, and eclipses. It explains that constellations help locate objects in the sky, and describes the celestial sphere model. It discusses how the Earth's rotation causes day and night while its revolution around the sun causes seasons. The phases of the moon are caused by its orbit around Earth. Solar eclipses occur when the moon blocks the sun, and lunar eclipses occur when Earth blocks the sun's light from reaching the moon.