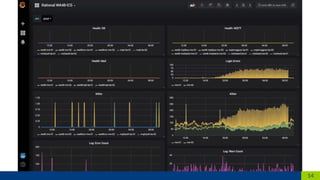
The document discusses the requirements and challenges related to developing an IoT platform for Rational AG, focusing on remote configuration, monitoring, and control of Rational Combi Ovens. It outlines technical considerations such as protocol support (MQTT, AMQP), issues with current integration and firmware management, as well as future improvements like enhanced monitoring and client requirements analysis. Additionally, it highlights the separation between the IoT platform and firmware development teams, leading to various operational complexities.