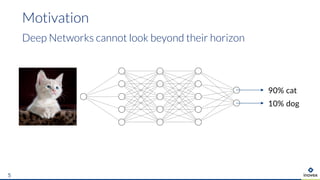
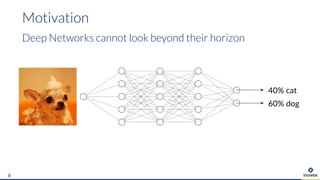
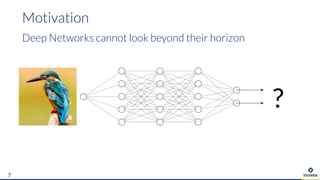
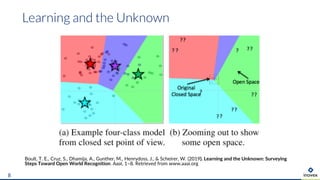
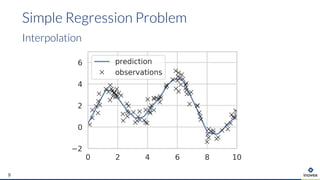
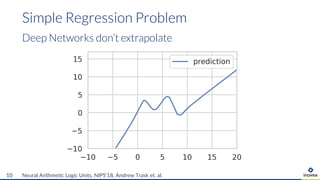
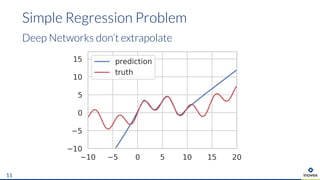
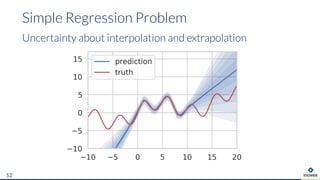
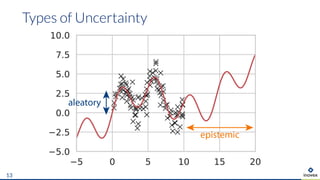
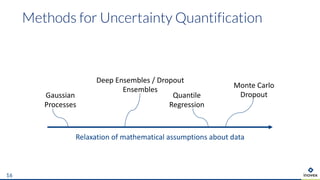
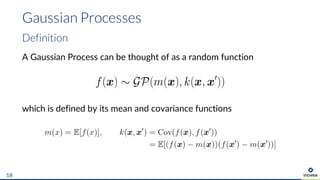
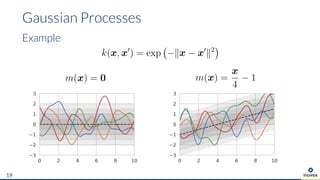
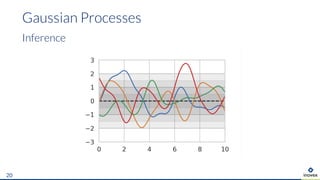
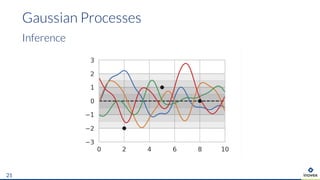
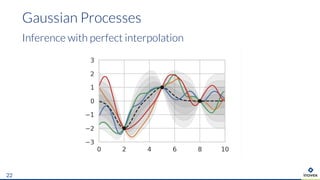
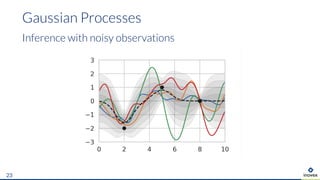
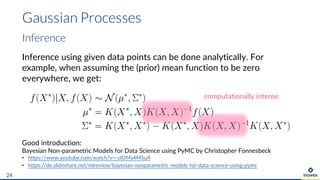
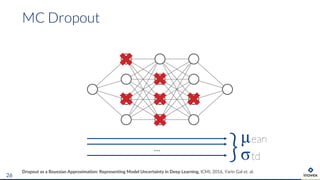
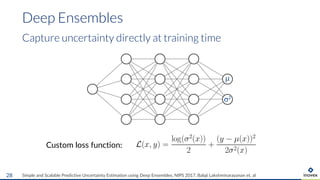
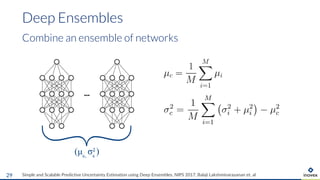
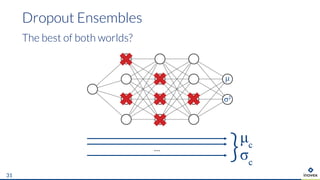
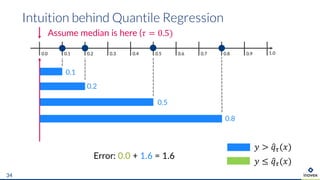
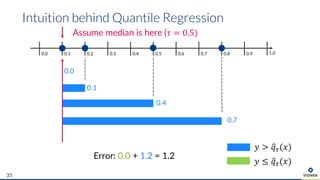
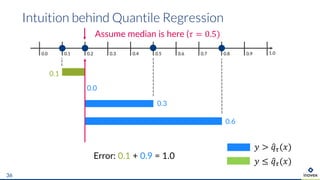
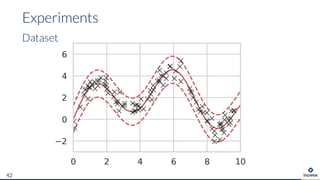
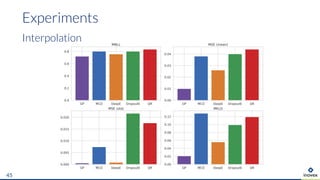
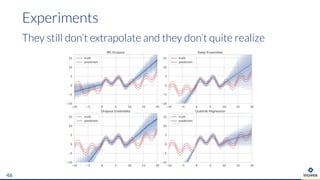
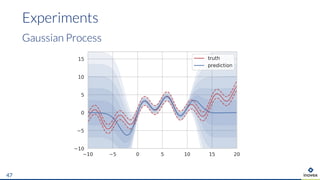
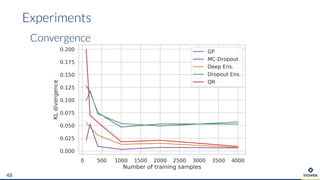
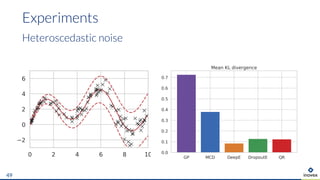
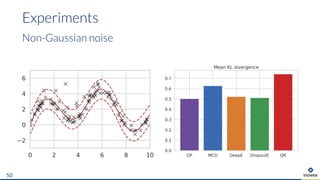
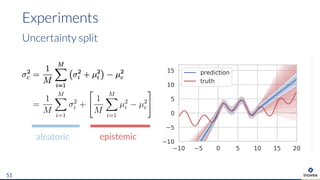
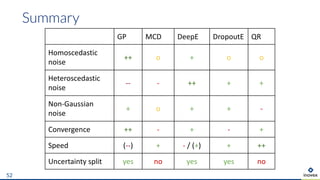
The document presents an overview of uncertainty quantification methods in artificial intelligence, focusing on deep learning techniques such as Gaussian processes, Monte Carlo dropout, and deep ensembles. It discusses the limitations of deep networks in extrapolation and the significance of estimating both aleatory and epistemic uncertainties. The conclusion emphasizes the need for developing combined solutions that effectively address uncertainty estimation in critical applications.