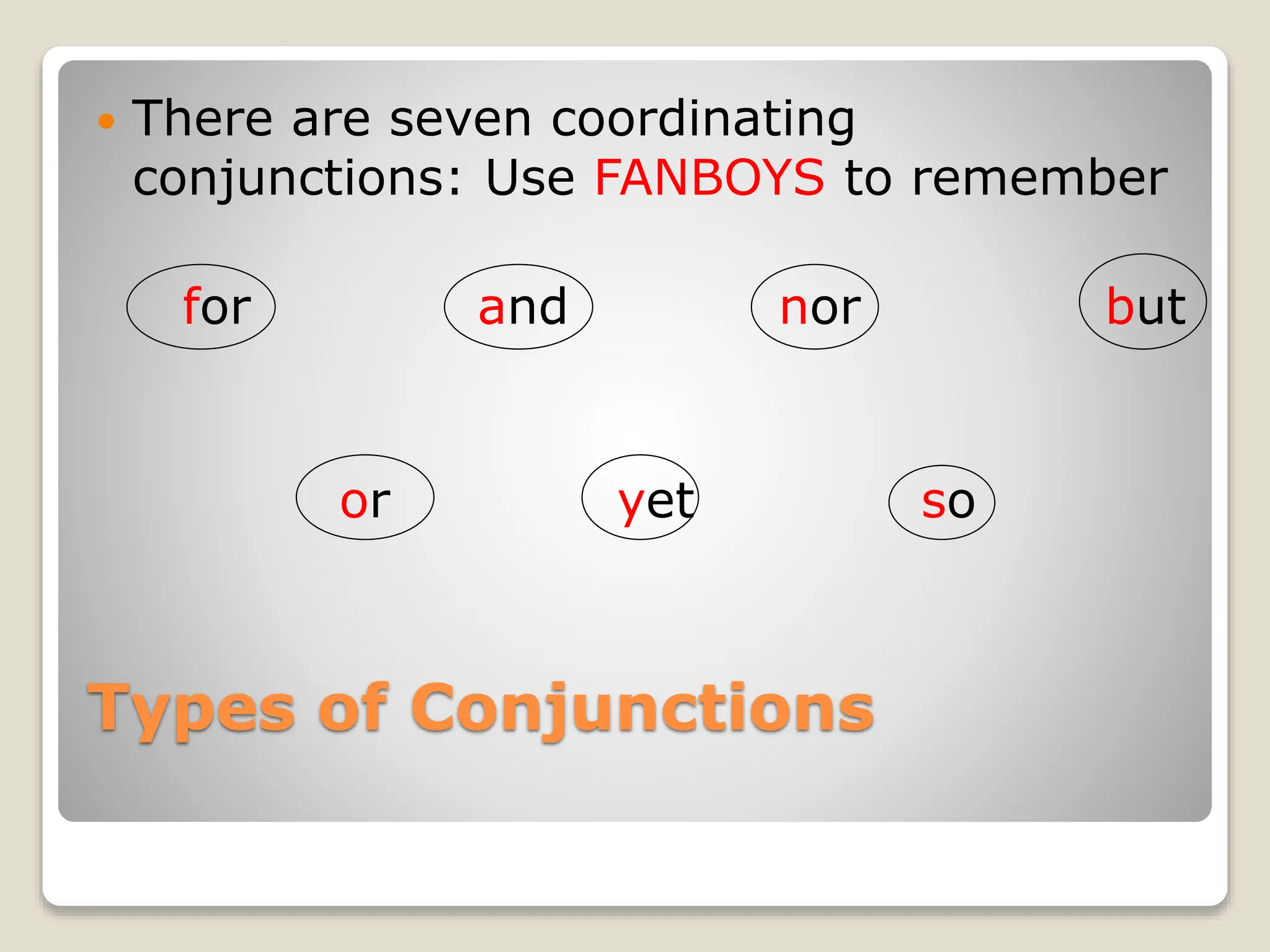
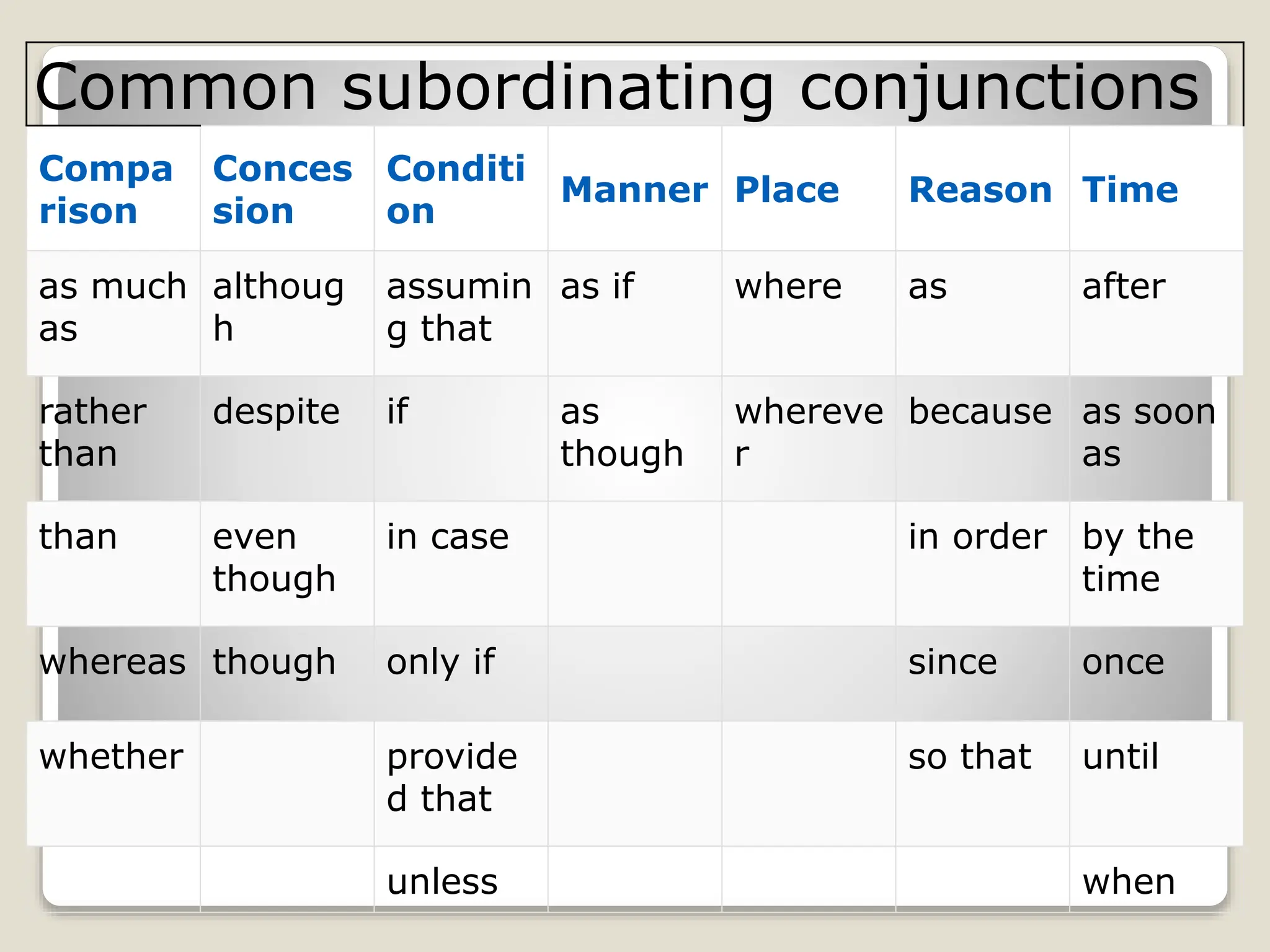
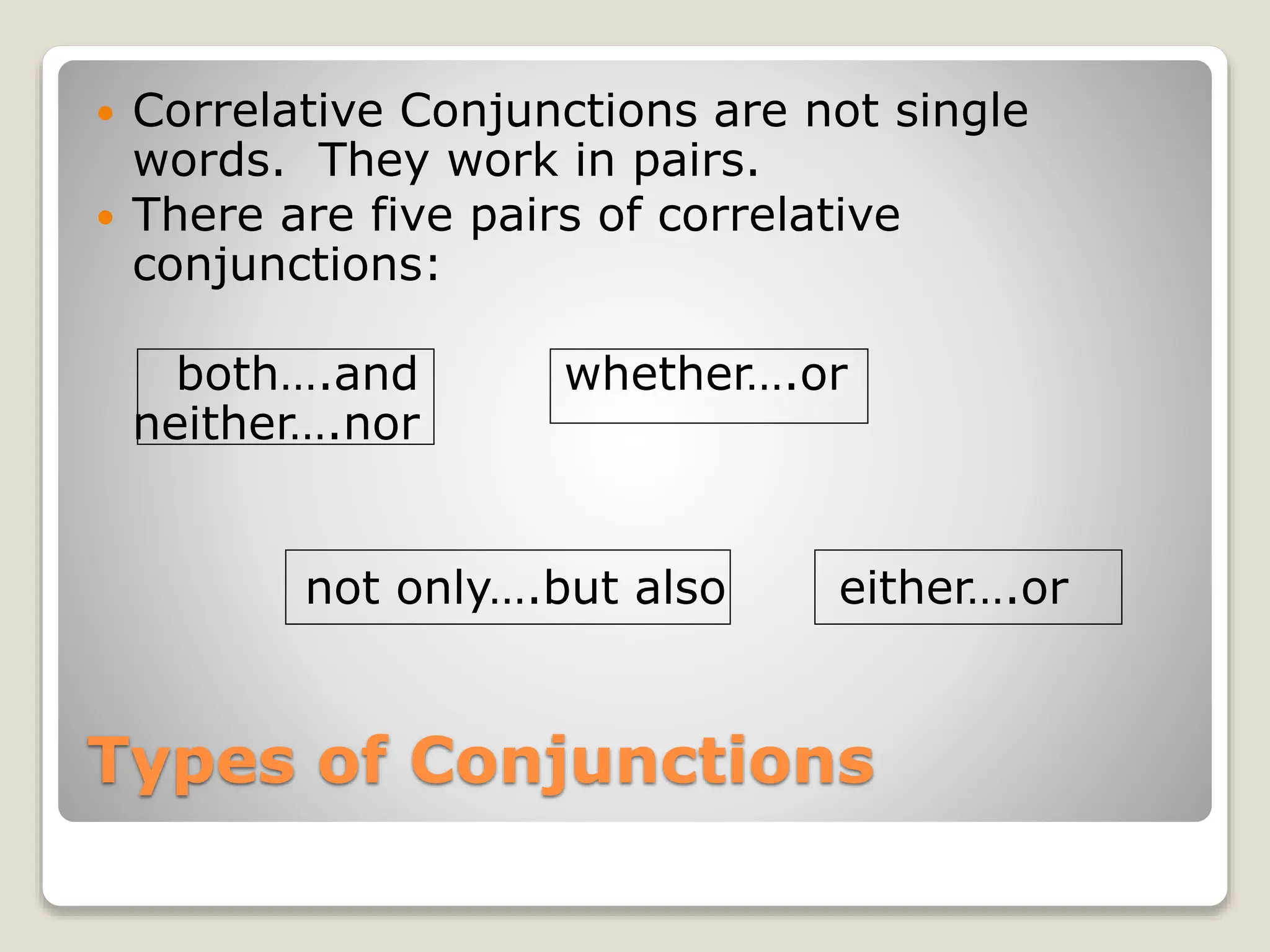
This document provides information about different types of conjunctions including coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, correlative conjunctions, and interjections. It defines what conjunctions are and explains that they are used to join words, phrases, and sentences. It lists the seven coordinating conjunctions and gives examples of how each one is used. It also discusses subordinating conjunctions and lists the main categories including comparison, concession, condition, manner, place, reason, and time. Examples of correlative conjunctions and how to punctuate interjections are also covered.