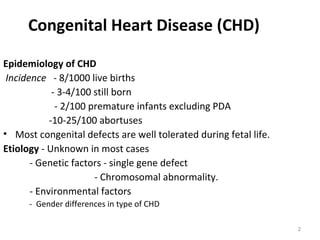
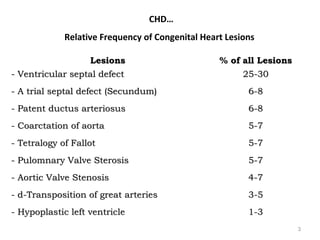
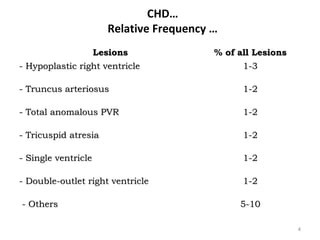
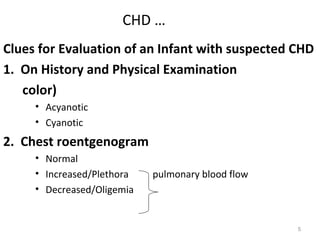
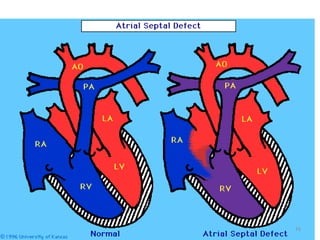
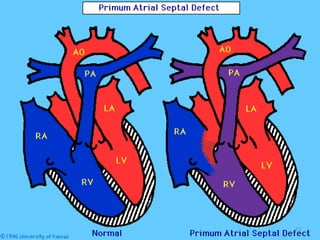
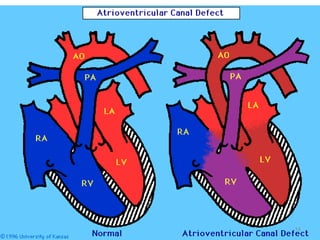
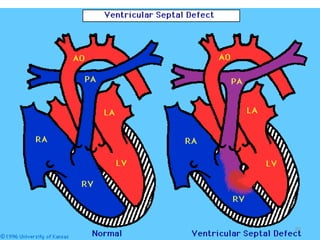
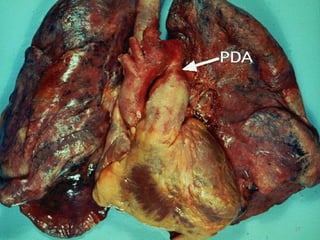
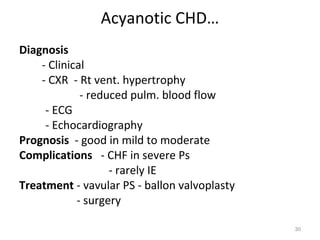
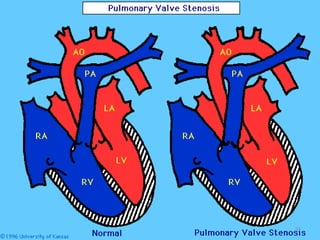
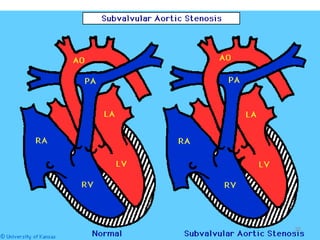
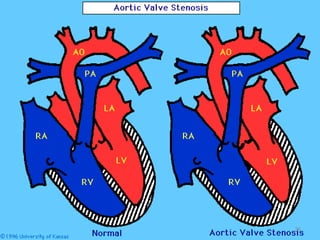
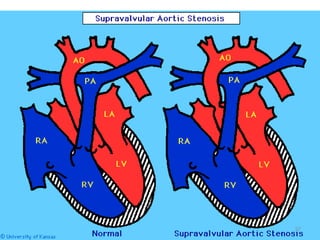
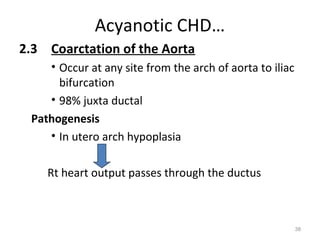
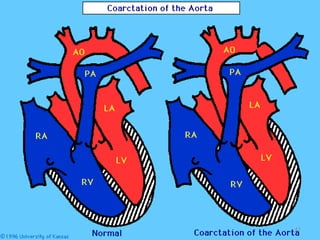
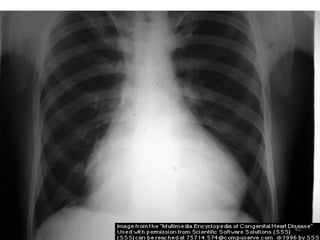
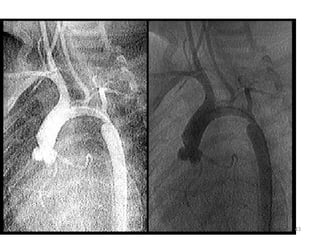
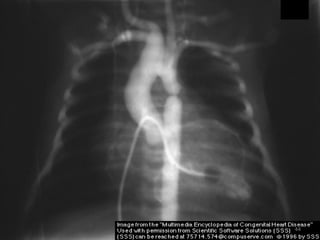
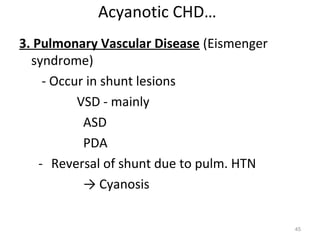
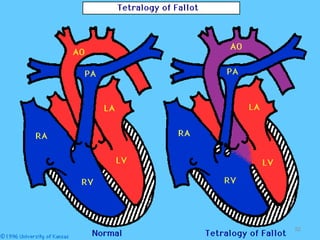
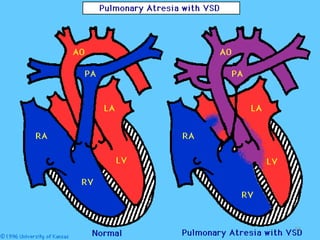
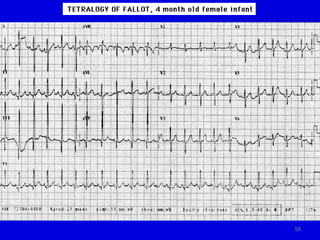
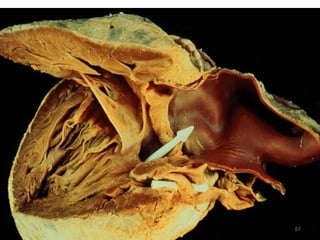
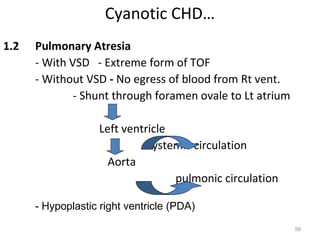
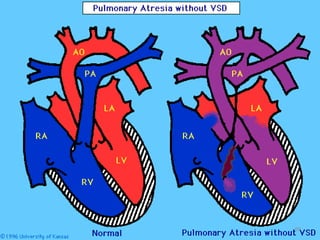
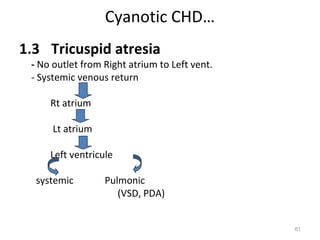
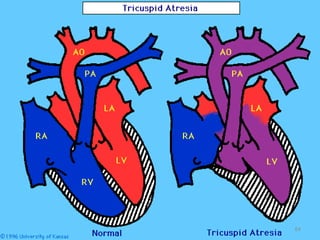
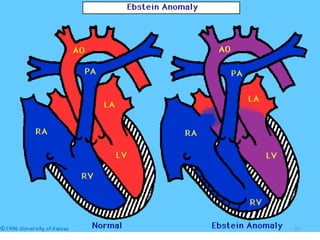
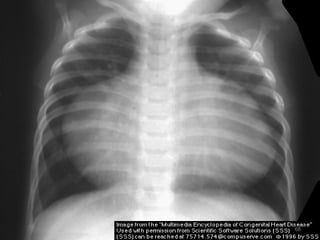
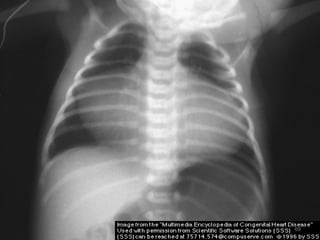
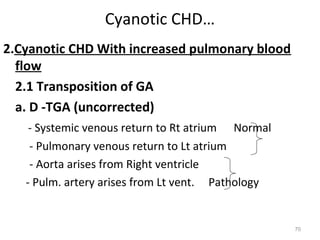
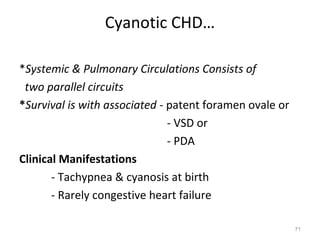
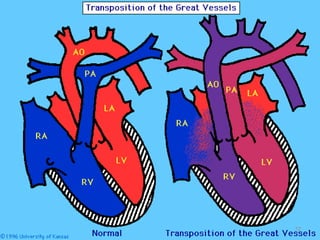
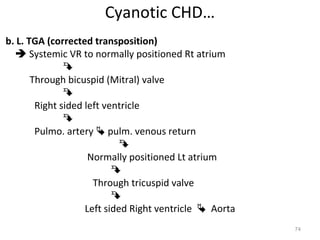
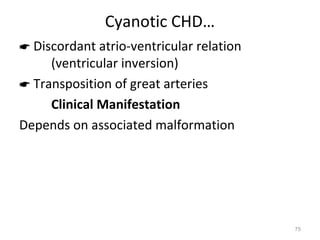
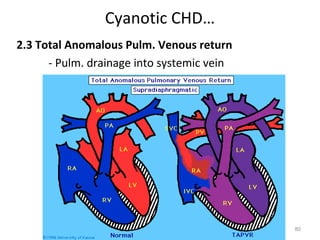
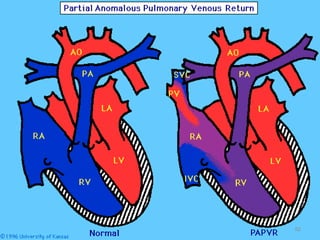
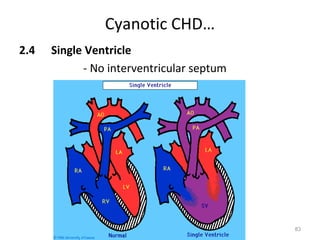
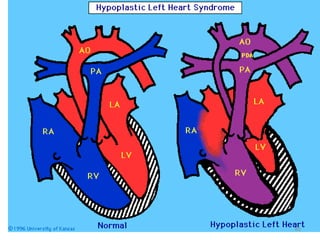
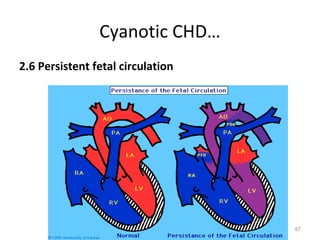
This document provides information on congenital heart disease (CHD). It discusses the epidemiology and etiology of CHD. It then describes the relative frequency of different congenital heart lesions. It provides clues for evaluating infants with suspected CHD and discusses various cyanotic and acyanotic CHD conditions like ventricular septal defects, tetralogy of Fallot, transposition of the great arteries and Ebstein's anomaly in detail including their pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment.