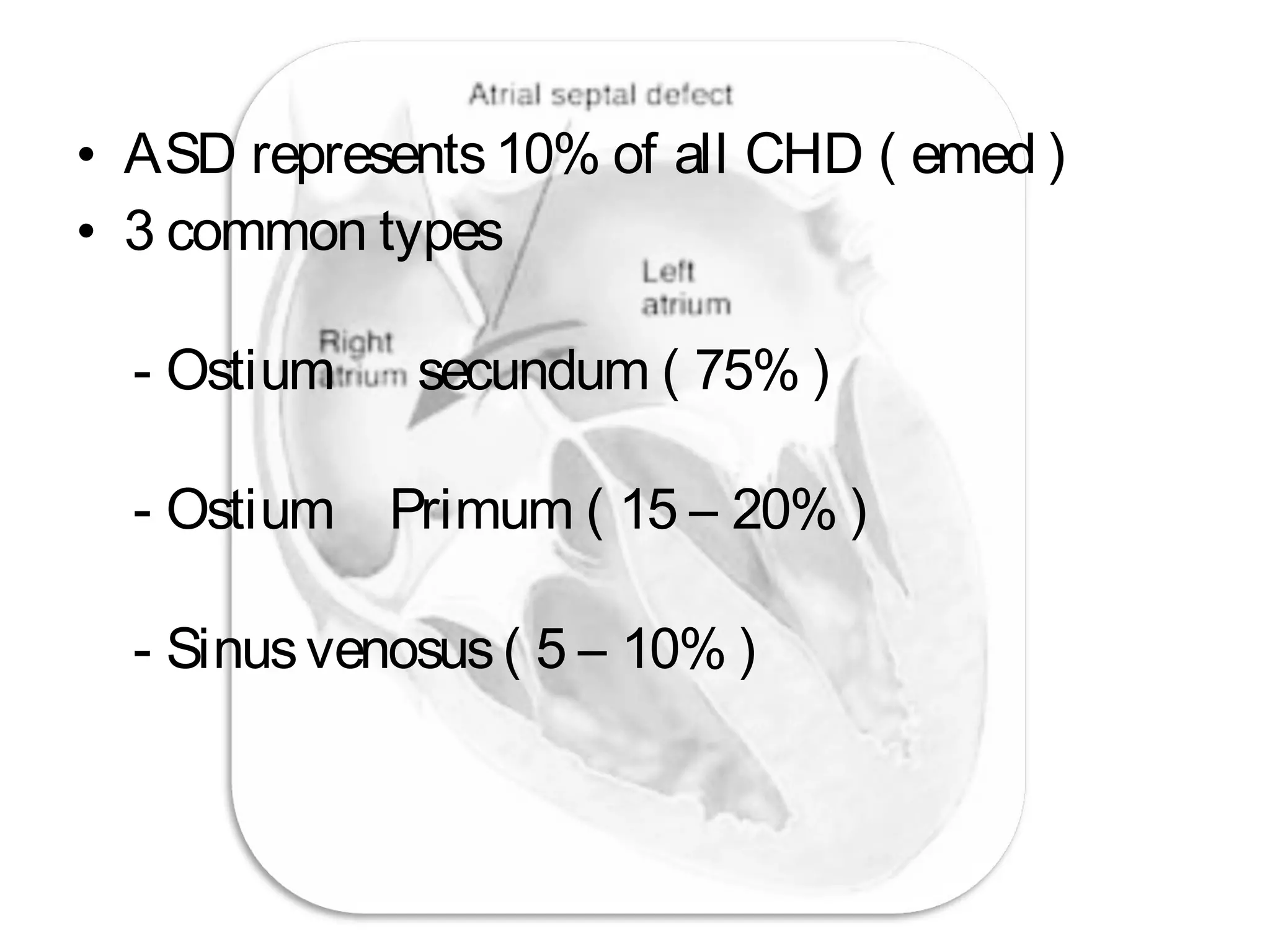
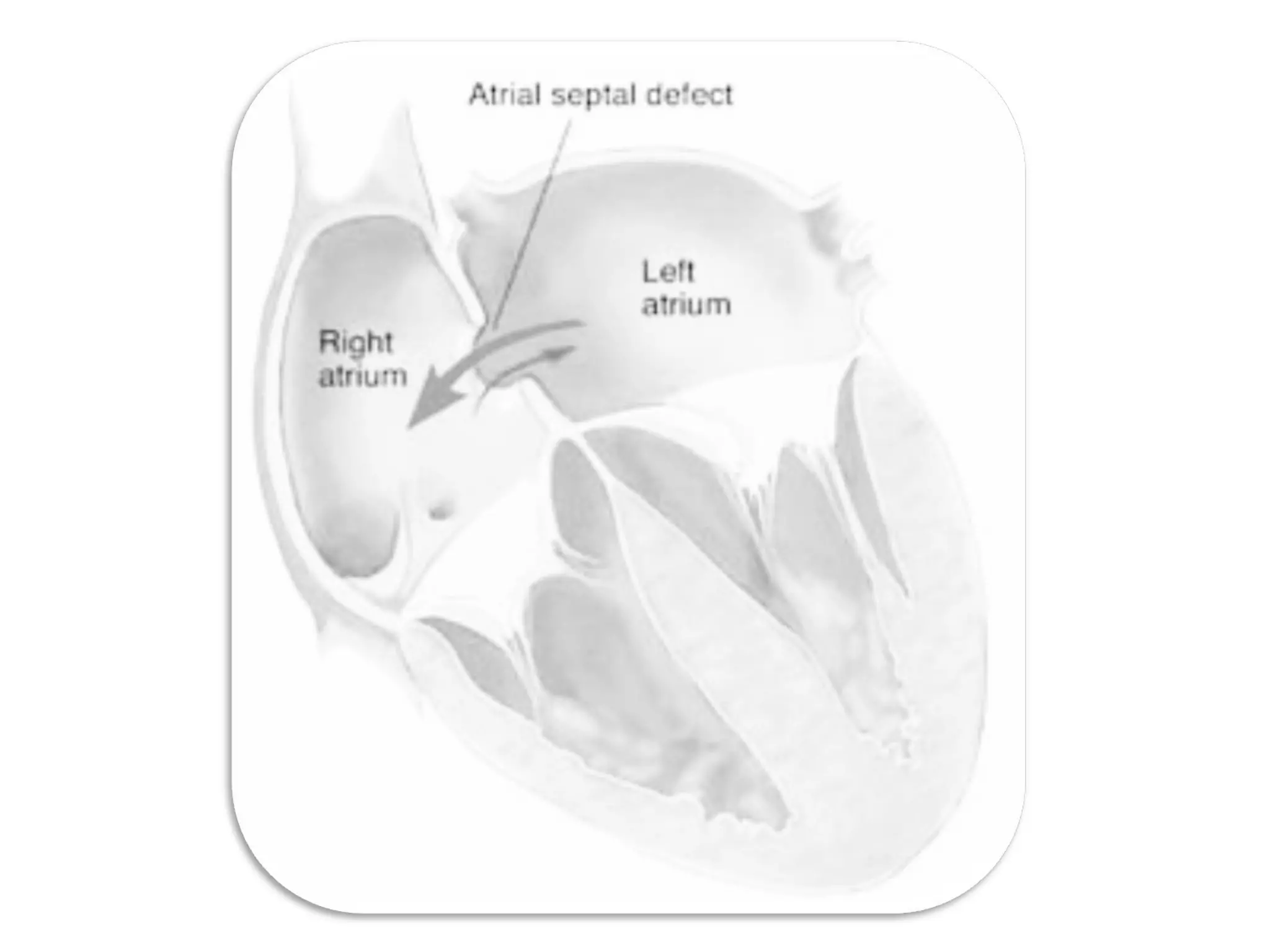
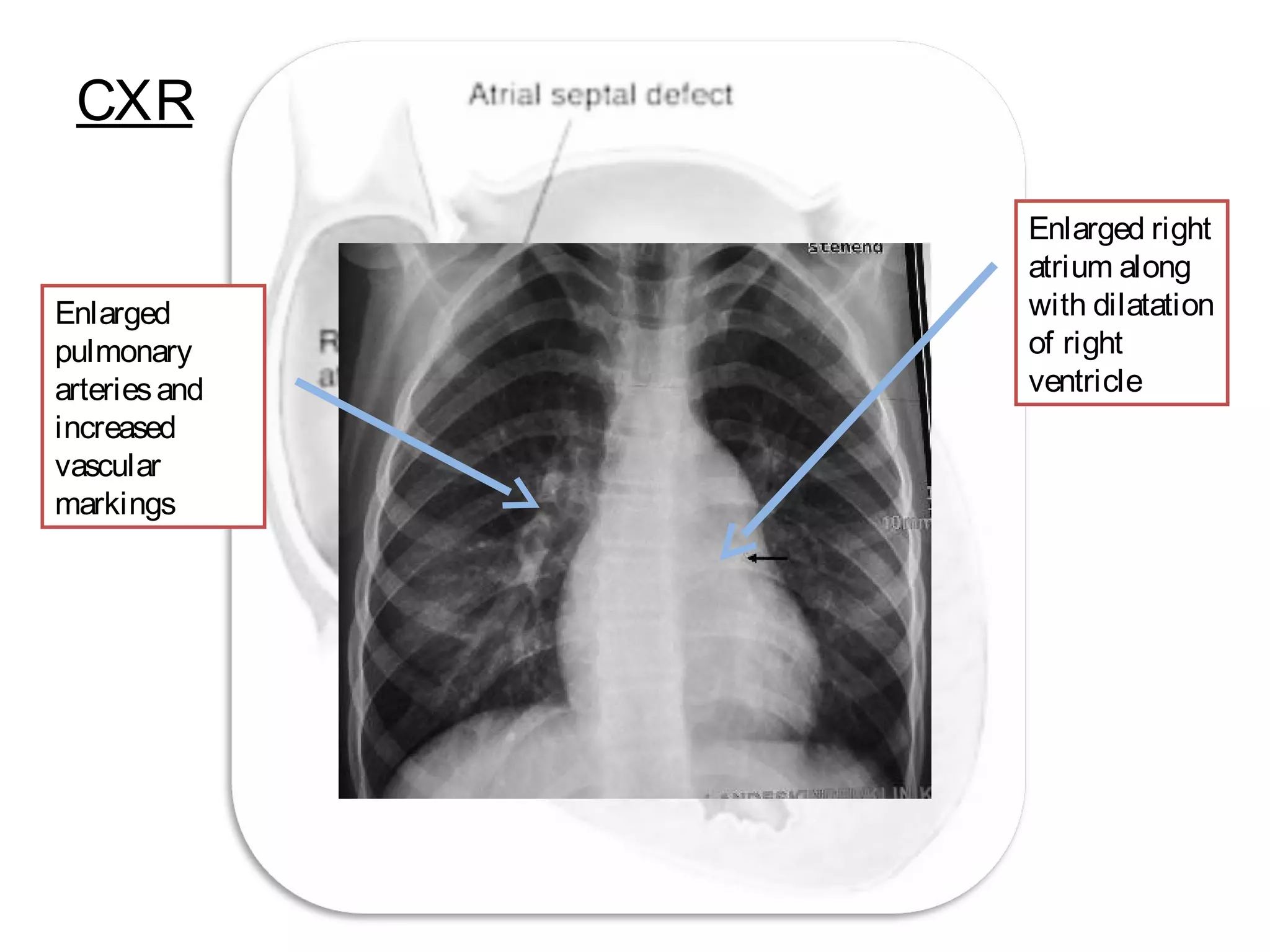
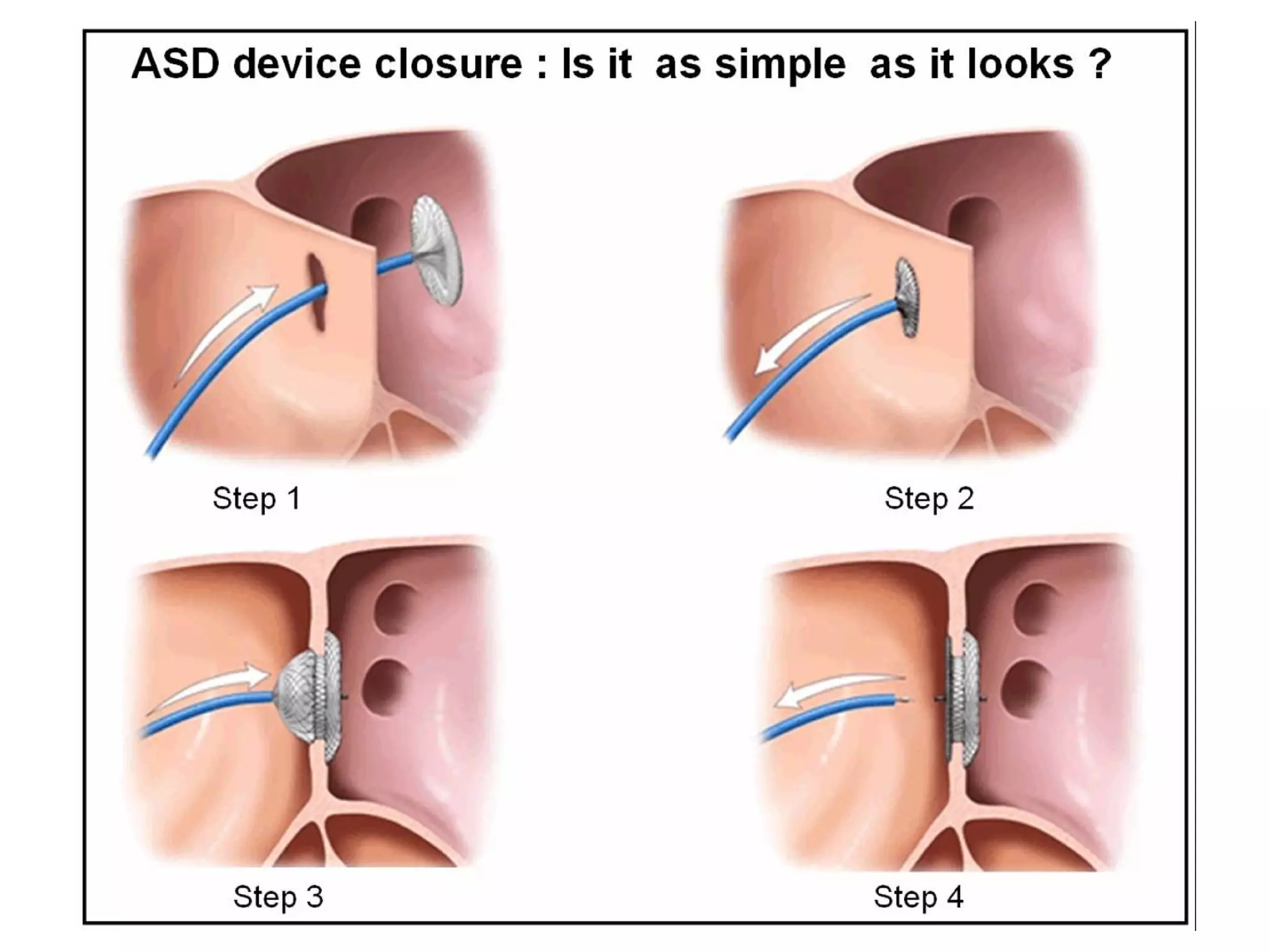
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect characterized by an opening in the interatrial septum, causing left-to-right shunting of blood. ASDs range in severity depending on the size of the defect and shunt. While often asymptomatic in children, symptoms of right heart overload can occur as patients age. Diagnosis is typically made through echocardiography or MRI imaging. Treatment options include surgical closure of small to moderate defects and percutaneous catheter closure of defects, both with high success rates.